How Room Temperature Affects Indoor Plants: Key Insights for Healthy Growth
Have you ever wondered why your indoor plants seem to struggle despite your best efforts? The secret to healthy plant growth may lie in something as simple as the room temperature. Understanding how room temperature affects indoor plants is crucial for their vitality. Whether it’s a tropical fern, a succulent, or a snake plant, each has its own temperature preference. Too hot or too cold, and your plants may show signs of stress, affecting their growth. In this article, we’ll explore how room temperature plays a vital role in the health of your indoor plants and provide practical tips to help them thrive.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Room Temperature and Plant Growth 🌡️🌱
Room temperature plays a crucial role in the growth and health of your indoor plants. But what exactly is room temperature, and why does it matter so much?
What is Room Temperature?
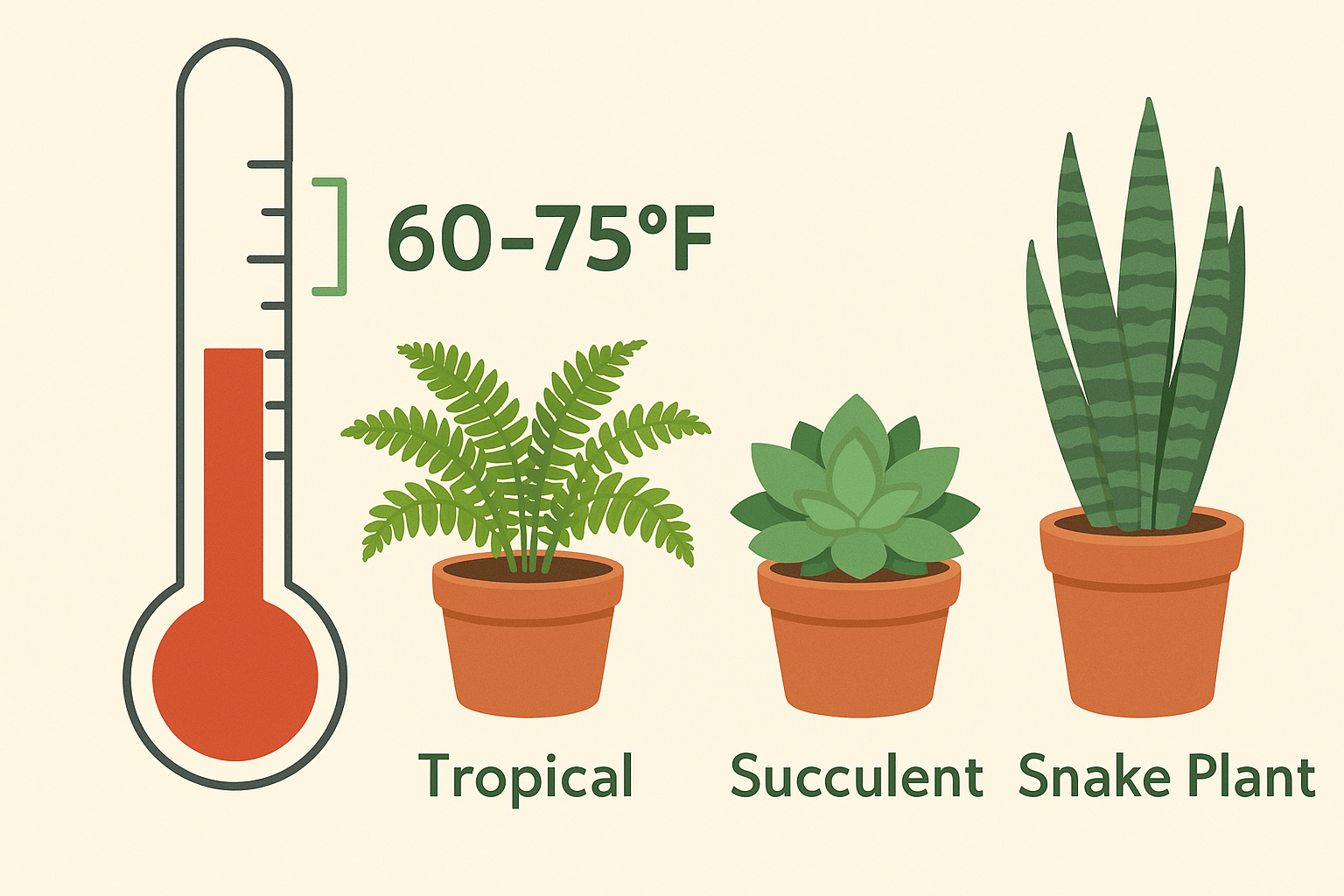
Room temperature is typically defined as the range between 60-75°F (16-24°C). It’s the temperature most of us feel comfortable with and where our indoor plants tend to thrive. But just like humans, plants also have preferences!
Why Does Room Temperature Matter?
Temperature affects plant processes like photosynthesis (how plants make food) and respiration (how they use that food). At the right temperature, these processes occur efficiently, leading to healthy growth. If the temperature is too high or too low, these processes slow down, and your plant might suffer. 🌡️
Different plants have different temperature needs:
- Tropical plants (like ferns and pothos) love warmth and humidity. 🌿
- Succulents and cacti prefer slightly cooler temperatures with drier air. 🌵
- Temperate plants (like spider plants) do well in moderate temperatures.
By understanding your plant’s specific needs, you can create the ideal environment for it to grow strong and healthy. 🌻
Effects of Room Temperature on Indoor Plants 🌞❄️
The temperature in your home directly influences your plant’s health and growth. Let’s dive into how the room temperature affects indoor plants and what happens when it’s too hot or too cold.
Optimal Temperature Range for Different Plants
Each plant species has an ideal temperature range where it thrives. For most indoor plants, the sweet spot is between 60-75°F (16-24°C). Here’s how temperature affects specific types of plants:
- Tropical plants like ferns, peace lilies, and monstera thrive in warm, humid conditions.
- Succulents and cacti enjoy slightly cooler temperatures (around 60-70°F or 15-21°C) with dry air.
- Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, lettuce) tend to do well in moderate temperatures, around 65-70°F (18-21°C).
Impact of Temperature Extremes
High Temperatures (above 75°F) 🌡️
When it’s too hot, plants experience stress. They may:
- Wilt due to dehydration 🌱💦
- Dry out and lose leaves
- Slow growth or stop growing altogether
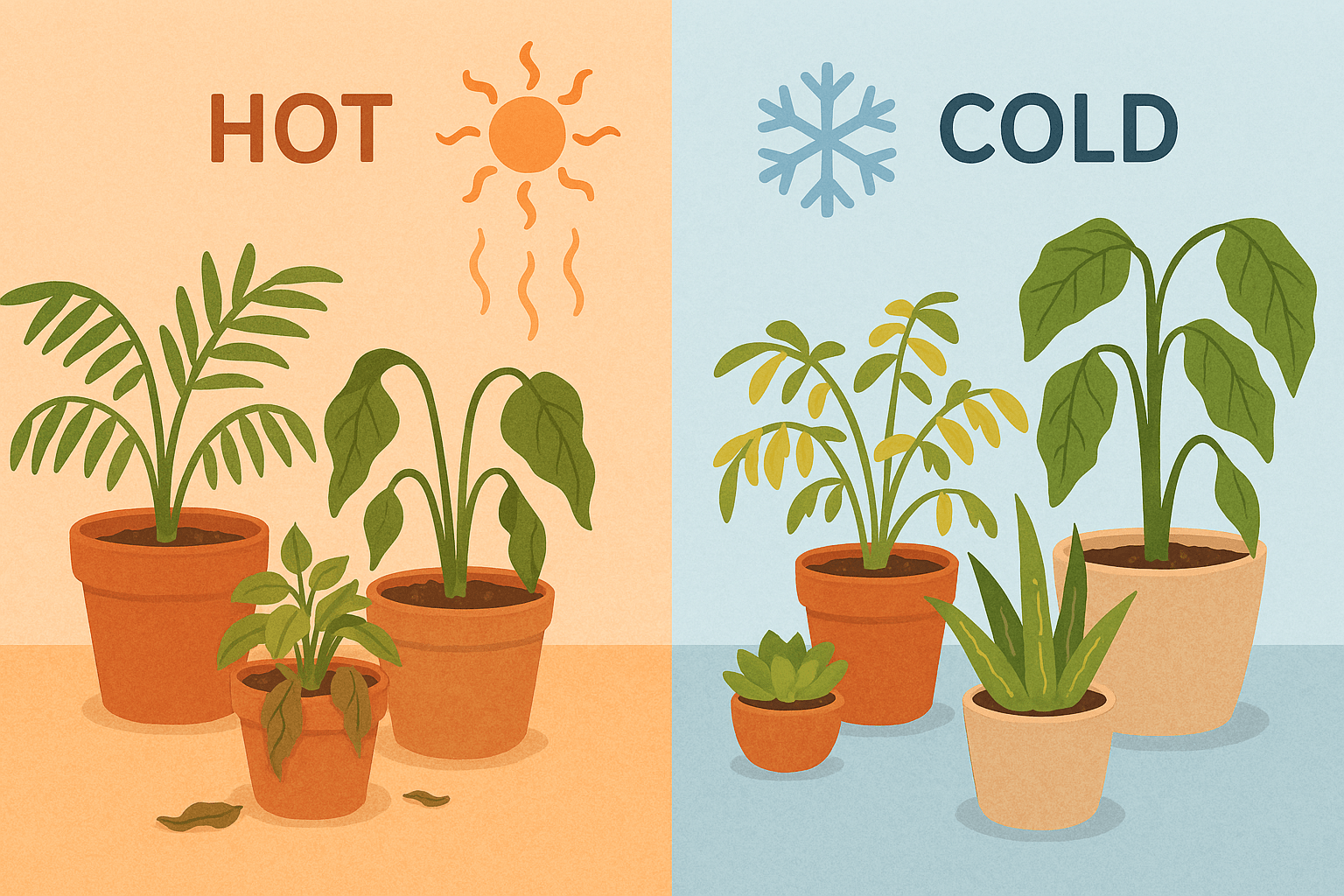
Low Temperatures (below 60°F) ❄️
When temperatures dip too low, plants struggle:
- Growth slows down or stops completely
- Leaves can turn yellow or even brown at the edges 🌿
- Plants can suffer from cold shock, especially if exposed to drafts or sudden temperature changes
To keep your plants happy and healthy, it’s crucial to maintain a stable temperature and avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold. 🌸
Signs Your Indoor Plant Is Affected by Temperature 🌡️🚨
It’s important to keep an eye out for any signs that your indoor plants are struggling with room temperature. Room temperature affects indoor plants seriously and here are the key indicators that your plants may be affected by temperature stress:
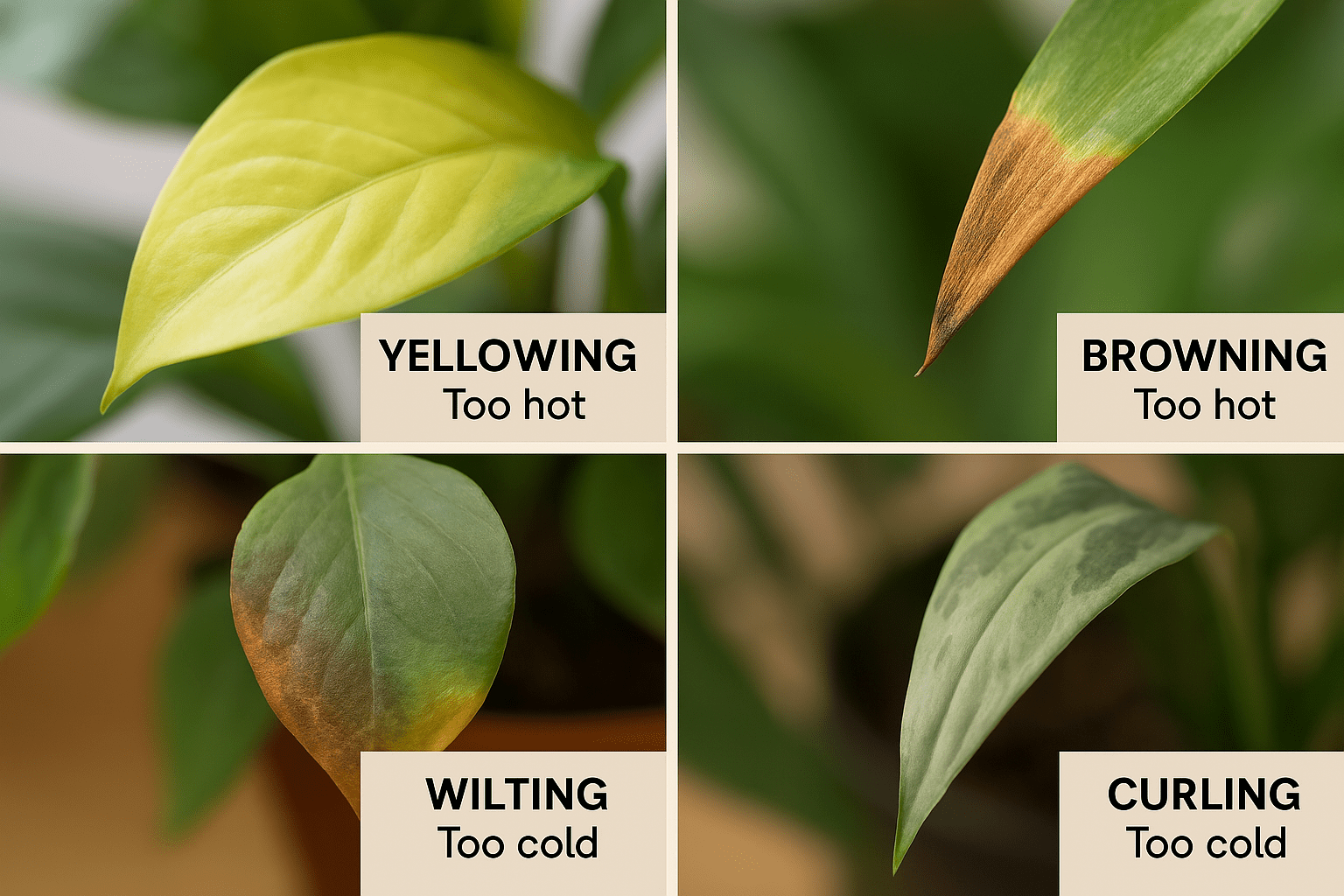
- Yellowing or Browning Leaves 🍂
If your plant’s leaves are turning yellow or brown, it could be a sign of either too much heat or too much cold. For example:
- Yellowing leaves often indicate stress from cold temperatures or drafts.
- Brown edges typically point to excessive heat or dry air.
- Wilting or Drooping Leaves 🌱
When temperatures get too high, plants may lose water quickly, leading to wilting or drooping leaves. Even with regular watering, they might not recover without cooler temperatures. - Slow or Stunted Growth ⏳
If your plant isn’t growing as fast as it used to or new leaves are smaller, temperature fluctuations could be the culprit. Both cold and hot temperatures can slow down a plant’s metabolism, affecting its growth rate. - Leaf Curling or Drooping 🌀
Curled or drooping leaves are a clear sign of environmental stress. Too much heat can cause leaves to curl inward, while too cold temperatures can cause them to droop or feel limp. - Increased or Decreased Watering Needs 💧
When temperatures are out of balance, your plant may need more or less water:
- Hot temperatures may cause your plant to dry out faster, leading to increased watering needs.
- Cold temperatures can slow down the plant’s water uptake, making it less thirsty.
By watching for these signs, you can adjust the room temperature to keep your plants in a healthy, happy state! 🌿
How to Maintain the Ideal Temperature for Your Plants 🌞🌱
Keeping your indoor plants at the right temperature is key to their health and growth. Here are some practical tips to help you create the perfect environment for your leafy friends:
- Monitor the Temperature with a Thermometer 🌡️
Using a simple thermometer will help you keep track of the temperature in your plant’s environment. Place it near your plants to ensure they’re in the optimal range of 60-75°F (16-24°C). This helps you avoid extremes that can stress your plants.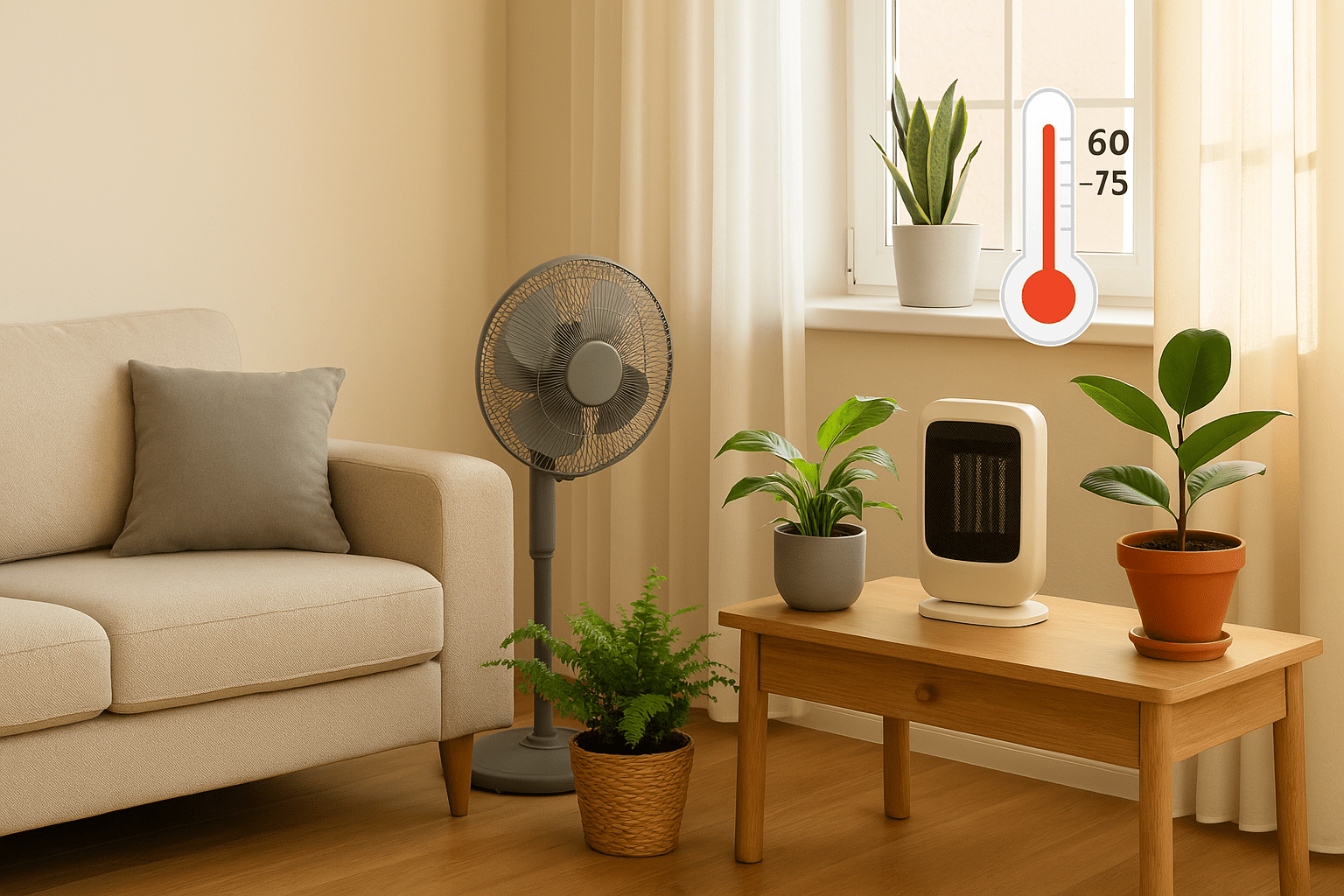
- Use Fans or Heaters for Temperature Control ❄️🔥
- Fans: During hot months, a fan can help maintain airflow and prevent overheating, especially in rooms that get too warm.
- Heaters: In colder months, use a space heater to keep the room warm, but make sure it’s not too close to your plants to avoid drying them out.
- Keep Plants Away from Temperature Extremes 🚪
- Windows and Drafts: Avoid placing plants near cold windows or air conditioning vents, especially in the winter. Drafts can shock your plants and cause leaf damage.
- Heat Sources: In the summer, keep plants away from radiators, fireplaces, or direct sunlight that can raise the temperature too much.
- Use Humidity Trays or Misters 🌬️💦
For tropical plants that love humidity, you can use humidity trays filled with water and pebbles to increase moisture in the air. Misting your plants occasionally can also help, but avoid over-wetting them, as this can lead to mold growth. - Rotate Plants Regularly 🔄
Move plants around to find the best spot for them. A location with consistent temperatures will help your plants grow strong, so rotate them occasionally to prevent them from getting too much direct heat or cold in one spot.
By following these simple tips, you can create a more stable and ideal temperature environment for your plants, leading to healthier growth and more vibrant foliage! 🌿
Seasonal Considerations for Room Temperature 🌦️🍂
As the seasons change, so do the temperatures in your home, and that can affect how your indoor plants respond. Here’s how to manage room temperature for your plants during different times of the year:
Winter Temperature Management ❄️
Winter can bring cooler indoor temperatures, especially near windows and doors. To help your plants thrive:
- Move plants away from cold windows: Windows can get chilly, causing your plants to suffer from drafts. Try to move them to a warmer spot.
- Use a space heater: If your room temperature drops below 60°F (15°C), a space heater can help, but make sure it’s not directly blowing on your plants.
- Increase humidity: The dry indoor air in winter can be tough on tropical plants. Use a humidifier or place humidity trays under plants to keep the air moist.
Summer Temperature Considerations 🌞
In the summer, temperatures can rise quickly, especially with air conditioning and direct sunlight. To protect your plants from overheating:
- Move plants out of direct sunlight: During peak sunlight hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), move plants away from windows where the sun’s rays can cause them to dry out.
- Use fans for airflow: To prevent your plants from getting too hot, use a fan to circulate air and cool down the space.
- Be mindful of temperature fluctuations: Avoid placing plants near air conditioners, as sudden temperature shifts can stress them.
Transitioning Between Seasons 🌸🍁
As the seasons change, your plants may need time to adjust:
- Spring & Fall: These transitional seasons can have more unpredictable temperatures, so check your plant’s environment regularly. Keep an eye on temperature fluctuations, and adjust their position in the room accordingly.
- Adjust watering: As the seasons change, so does the plant’s need for water. Warmer temperatures may require more frequent watering, while cooler months might need less.
By paying attention to these seasonal changes, you can ensure that your indoor plants are always in the best possible environment to thrive year-round! 🌿

Final Thought
Room temperature affects indoor plants and maintaining the right room temperature is essential for your indoor plants to grow strong and healthy. Whether it’s the warmth tropical plants crave or the cooler temperatures succulents prefer, each plant has its own needs that can be met with just a little attention. By monitoring temperature, avoiding extremes, and making seasonal adjustments, you can create a comfortable environment where your plants thrive.
Remember to keep an eye on signs of temperature stress, like yellowing leaves or wilting, and adjust your care accordingly. With the right temperature, your indoor plants will not only survive—they’ll flourish!
Happy planting, and may your greenery always be vibrant and full of life! 🌱✨
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the ideal room temperature for most indoor plants?
Most indoor plants thrive between 65°F and 75°F during the day and slightly cooler at night.
Can temperature fluctuations harm my plants?
Yes, sudden drops or spikes in temperature can stress plants, causing leaf drop, wilting, or stunted growth.
Do different plants prefer different temperature ranges?
Yes, tropical plants like warmer, more humid conditions, while some succulents tolerate cooler, drier air.
How do heaters and air conditioners affect indoor plants?
They can dry out the air and cause temperature extremes, especially if plants are placed too close to vents.
Is it okay to place plants near windows in winter?
Be cautious—cold drafts from windows can damage leaves. Use insulation or move plants slightly away from the glass.
Why are my plant’s leaves turning brown at the edges?
It may be from dry air or heat stress, often caused by warm, dry indoor environments or proximity to radiators.
How does night temperature affect plant growth?
Cooler night temps help mimic natural cycles, but extreme drops can slow growth or trigger dormancy in some plants.
Should I move my plants when the seasons change?
Yes, reposition plants to avoid drafts in winter or intense sunlight and heat in summer.