
Top Working Pecan Trees: How to Choose, Plant, and Maintain the Best Varieties for Maximum Yield
Table of Contents
Toggle🌰 Why Pecan Trees Are a Great Investment 🌳
Pecan trees are more than just a source of delicious nuts 🥜; they’re a long-term investment 💵 that can yield rewards for years to come. Whether you’re planting for personal enjoyment 🌱 or looking to start a commercial orchard 🌾, pecan trees offer a range of benefits that make them a smart choice for any grower. Let’s dive into why pecan trees are worth considering! 😊
💰 1. Long-Term Profit Potential 💸
Pecan trees are a long-term investment that keeps giving. 🌿 While they take a few years to mature and produce nuts (usually 6–10 years) ⏳, once they start bearing fruit 🍂, they can continue producing for decades—some trees live for over 100 years! 🏡 That’s a lot of harvests to look forward to. If you’re thinking of starting a business 🏢, pecans are a high-value crop that can generate significant returns over time. 🌱 High Profit Potential: Pecan nuts are highly sought after in the market 📈. Their rich, buttery flavor 🧈 and nutritional benefits make them popular for snacking, baking 🍪, and even in savory dishes 🍽️. Stable Income: After the initial investment and growth period 🏗️, pecan trees can provide a stable income 💵 for commercial growers. Even if you’re planting just a few trees 🌳 for personal use, the long-term production can be rewarding.🌱 2. Low Maintenance, High Reward 🌞
Once established, pecan trees are surprisingly low-maintenance. 🌿 They require minimal care compared to many other fruit 🍉 and nut trees 🌰. If you plant them in the right environment 🌍 and with the right care initially, they’ll thrive with little intervention from you. 💧 Drought-Tolerant: Pecan trees can handle dry conditions 💧 once their roots are well-established, making them an excellent choice for areas with water restrictions 🚱 or periods of drought 🌵. Minimal Pruning: While some pruning ✂️ is required to shape the tree and remove dead branches, pecans don’t demand constant attention 🕑. A few key maintenance tasks like watering 💦 and fertilizing 🌱, and you’re good to go!🏡 3. Environmental Benefits 🌳
Pecan trees aren’t just good for your wallet 💸—they’re also beneficial for the environment 🌍. As a tree species 🌳, pecans contribute to air quality 🌬️, provide habitat 🦉 for wildlife, and help prevent soil erosion 🌾. The shade 🌞 from a mature pecan tree can reduce heat around your home 🏡 and lower energy costs 💡, making them an eco-friendly choice. Carbon Sequestration: Like all trees 🌲, pecans help absorb carbon dioxide 🌫️ from the atmosphere, contributing to a cleaner environment 🌱. Wildlife Habitat: Pecan trees provide food 🍽️ and shelter 🏠 for a variety of wildlife 🦜, from birds 🦉 to small mammals 🐇.🥜 4. Nutritional Value & Market Demand 🍽️
Pecans are a nutritional powerhouse 💪 packed with healthy fats 🥑, fiber 🍞, and vitamins 💊. This makes them a highly desired food source 🍏 both for personal consumption 🥗 and in the market 🛍️. The demand for pecans continues to rise 📈 due to their health benefits, making them a great crop 🌾 to grow. Health Benefits: Pecans are rich in antioxidants 🧬, heart-healthy fats 🧡, and essential minerals 🧂 like magnesium and zinc. They’re perfect for snacking 🍿 or adding to recipes 🥘. Growing Market: With more people turning to healthy, plant-based snacks 🥒, the demand for pecans is expected to grow 🚀. It’s a good time to get in on the action! 🛍️🥳 5. A Low-Stress, Rewarding Hobby 🍃
For home gardeners 🏡, growing pecan trees can be a rewarding hobby 🎨. While they may take a bit of patience ⏳ to reach maturity, the satisfaction 😄 of harvesting your own fresh pecans is worth the wait. Whether you’re enjoying the nuts with family 👨👩👧👦 or selling them at local markets 🏪, growing pecans adds value to your life in many ways. Personal Enjoyment: There’s something special ✨ about harvesting fresh pecans from a tree you’ve cared for. It’s a tangible reward 🏆 for your patience and effort. Connection to Nature: Gardening 🌱, in general, promotes well-being 🌸, and growing pecans gives you a deeper connection to nature 🌳 and the food you eat 🍽️. Pecan trees are a smart investment 💡 whether you’re in it for the long-term profit 💸, the low maintenance 🧑🌾, or the enjoyment of harvesting your own healthy nuts 🥜. With their low-maintenance needs 🌱, high market value 📈, and environmental benefits 🌍, planting pecan trees is a win-win 🏆 for anyone interested in gardening 🏡 or starting a business 🌿. Whether you’re planting a few trees 🌳 in your backyard or planning a larger orchard 🌳, you’re making a choice that pays off for years to come.🌳 Types of Pecan Trees 🌳 – What to Choose for Maximum Yield 🌳
When it comes to growing pecans, choosing the right tree variety is crucial for getting the best possible yield. 🌱 There are many varieties out there, each with unique characteristics, and picking the right one for your specific climate and space can make all the difference. 🌍 In this section, we’ll explore the most popular pecan tree varieties and what makes each one special. Let’s dive in! 🍃🥜 Popular Pecan Tree Varieties for High Yield 🥜
Choosing the right pecan tree variety is the first step to ensuring a bountiful harvest. 🌾 Here are a few top varieties that consistently produce high yields:
🌟 ‘Pawnee’ 🌟
Known for its early production, ‘Pawnee’ starts producing nuts earlier than many other varieties. 🏃♂️💨 This variety also shows strong resistance to common diseases like scab 🦠, making it a favorite for growers. If you’re looking for a tree that’s relatively low-maintenance but still delivers big, ‘Pawnee’ is a great choice! 🌟🍂 ‘Desirable’ 🍂
As the name suggests, ‘Desirable’ is one of the most sought-after varieties. 💯 It produces high-quality, delicious pecans 🥧 with a strong yield. Though it takes a bit longer to mature compared to other varieties 🕰️, the large nuts and excellent flavor make the wait worth it! 😋🌰 ‘Stuart’ 🌰
If you’re looking for a robust tree 🌳 that can thrive in a range of conditions, ‘Stuart’ is an excellent option. 🌞 It’s highly tolerant of drought 💧 and cold weather ❄️, making it ideal for regions with harsher climates. The large, meaty nuts produced by ‘Stuart’ are perfect for baking 🍪 and snacking 🍿.🏜️ ‘Chickasaw’ 🏜️
This variety is known for being drought-resistant 🌵, making it an ideal choice for warmer climates 🌞. ‘Chickasaw’ trees tend to have a higher yield in such conditions 🌾 and are particularly hardy in areas that don’t see a lot of rain 🌧️. Plus, they’re fairly easy to grow 🌱, making them a popular choice for beginners 👩🌾.❄️ ‘Mahan’ ❄️
For colder climates 🌬️, ‘Mahan’ is a great pick. It’s well-suited to regions that experience cooler winters ❄️, and it produces large, tasty nuts 🥜. These trees can tolerate freezing temperatures 🥶 better than other varieties, so if you live in a frost-prone area 🏔️, this is a solid option.🏞️ Factors to Consider When Choosing Pecan Trees 🏞️
When selecting a pecan tree variety, it’s important to consider your local climate 🌤️, space 🌍, and maintenance capabilities 🧑🌾. Here’s what to think about:🌡️ Climate Compatibility 🌡️
Pecan trees thrive in warm, humid climates 🌞🌧️, but they also need a cold winter period ❄️ to produce nuts. Make sure you pick a variety that suits your region’s temperature range 🌡️. For example, ‘Chickasaw’ is perfect for hot, dry areas 🌵, while ‘Mahan’ is better suited for cooler climates 🌬️.🌳 Space Requirements 🌳
Pecan trees can grow quite large 🌳, so you need to ensure you have enough space for them to spread their roots and branches 🌿. Standard varieties typically need 30-40 feet of space between trees 📏, while dwarf varieties like ‘Pawnee’ and ‘Desirable’ need less room. If you have a smaller garden 🌱, go for a compact or semi-dwarf variety.🦠 Disease Resistance 🦠
Some pecan varieties are more resistant to diseases like scab and mildew 🦠 than others. If you’re concerned about pests 🐛 and diseases, look for varieties that offer better resistance 🛡️. ‘Pawnee’ is a great option for this, as it’s resistant to several common issues.🌼 Pollination Needs 🌼
Pecan trees typically need another tree nearby 🌳🌳 for cross-pollination. Some varieties, like ‘Desirable’ 🍂, need a pollinator variety, while others, such as ‘Pawnee’ 🌟, are self-pollinating. If you have limited space 🏡, be sure to select varieties that can pollinate each other. 🌸 By choosing the right variety of pecan tree 🌳, you’ll be setting yourself up for a great harvest 🌾. Whether you’re planting for the first time or looking to upgrade your existing orchard 🌳, consider your climate 🌞, space 🌍, and care requirements 🧑🌾 before selecting the best variety for maximum yield. Happy planting! 🌱🌱 How to Plant Pecan Trees for Optimal Growth 🌳
Planting pecan trees properly is the foundation for a healthy, high-yielding orchard 🌰. Whether you’re growing pecans for personal use 🍽️ or commercial purposes 🏢, getting the planting process right will set your trees 🌳 up for long-term success. Let’s dive into the steps to ensure your pecan trees thrive from day one! 😊
🗓️ 1. Best Time to Plant 🕰️
The timing of planting is crucial for the health of your pecan trees 🌳. The best time to plant pecans is in late winter to early spring 🌷. This allows the tree to establish its root system before the heat of summer sets in 🌞. Optimal Planting Window: Planting in the spring gives your tree a head start ⏳, allowing it to absorb nutrients and water during its active growing period 💧.🌍 2. Choosing the Right Location 🌿
Pecan trees need space to grow 🌱, so choose a location that allows them to reach their full potential. Ensure the following: Full Sun: Pecan trees thrive in full sunlight 🌞—at least 6 hours per day. Too much shade 🌚 will limit their growth and nut production 🌰. Well-Drained Soil: Pecan trees are susceptible to root rot 🦠 in soggy soil. Make sure your planting site has well-drained soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0–7.0) ⚖️. Protection from Wind: Pecan trees have large canopies 🍃, and strong winds 🌬️ can damage the branches. If your location is windy 🌪️, consider planting near a natural windbreak or installing a fence for protection.🕳️ 3. Preparing the Planting Hole 🌿
A properly prepared hole is key to strong root development 🌱. Follow these steps for the best results: Dig a Wide Hole: The hole should be about 2 to 3 times wider than the tree’s root ball, but only as deep as the root ball itself. This ensures the roots have enough space to spread out and establish a solid foundation 🌳. Loosen the Soil: Gently loosen the soil around the hole 🌍 to encourage the roots to grow outward. This helps with water 💦 and nutrient absorption 🍃.🌳 4. Planting the Tree 🌱
Now it’s time to plant your pecan tree! 🌰 Follow these steps for optimal planting: Positioning the Tree: Place the root ball in the hole, ensuring that the root collar (where the tree’s stem meets the roots) is level with the soil surface 🌱. Planting too deep can suffocate the roots 🌿, while planting too high can expose them to drying out 🌞. Backfill the Hole: Gently backfill the hole with the soil you removed. Avoid packing the soil too tightly ✋, as this can restrict root growth. Water 💦 the soil lightly to settle it in place.💧 5. Watering and Mulching 💦
Watering and mulching are critical for helping the tree settle into its new environment 🌍: Watering: Water the tree deeply 💦 after planting, soaking the root zone thoroughly. Ensure the water reaches the roots 🌱, not just the surface 🌊. Water regularly during the first few months 📅, but avoid overwatering, which can cause root rot 🦠. Mulching: Apply a 3–4 inch layer of mulch 🌾 around the base of the tree. This helps to retain moisture 💧, suppress weeds 🌿, and protect the roots from extreme temperatures 🌞. Use organic mulch like wood chips 🪓, straw 🍂, or leaves 🍁.🧑🌾 6. Tree Support and Protection 🌳
While pecan trees are sturdy 🌳, they benefit from a little support during the early stages: Staking: If you’re planting a younger or smaller tree 🌱, use a stake to keep it upright and stable. Make sure not to tie the tree too tightly 🪢—give it some room to move naturally in the wind 🌬️, which helps it build strength 💪. Tree Guards: Consider using tree guards or wire mesh 🧳 around the trunk to protect it from animals like rabbits 🐇 or deer 🦌, which may gnaw on the young tree.🚶♀️ 7. Spacing the Trees for Growth 🌳
When planting multiple pecan trees 🌳, space them properly to give them room to grow: Spacing Recommendations: For standard pecan trees 🌳, plant them 40 to 60 feet apart. This gives the trees enough space for their wide canopies 🍃 to spread out and for adequate air circulation 💨. Dwarf Varieties: If you’re planting dwarf varieties 🌱, they can be spaced closer—around 20 to 30 feet apart. Planting pecan trees 🌰 is a straightforward process, but it requires attention to detail 🧐 for optimal results. By choosing the right location 🌍, planting at the correct time 🕰️, and caring for your tree 🌳 with proper watering 💧, mulching 🍂, and protection 🛡️, you’ll set the stage for a healthy, high-yielding pecan orchard 🌰. Keep in mind that patience ⏳ is key—though pecans take a few years to mature, the reward of a bountiful harvest 🍂 is well worth the wait! 🌳🌳 Essential Care for Healthy Pecan Trees 🌰
Taking care of your pecan trees 🌳 is essential to ensure they grow strong, healthy, and productive 🌱. Whether you’re a beginner 👩🌾 or an experienced gardener 🌿, maintaining your pecan trees will reward you with a bountiful harvest year after year 🍂. In this section, we’ll cover everything you need to know about caring for your trees 🌳, from watering 💦 to pest control 🐞. 😊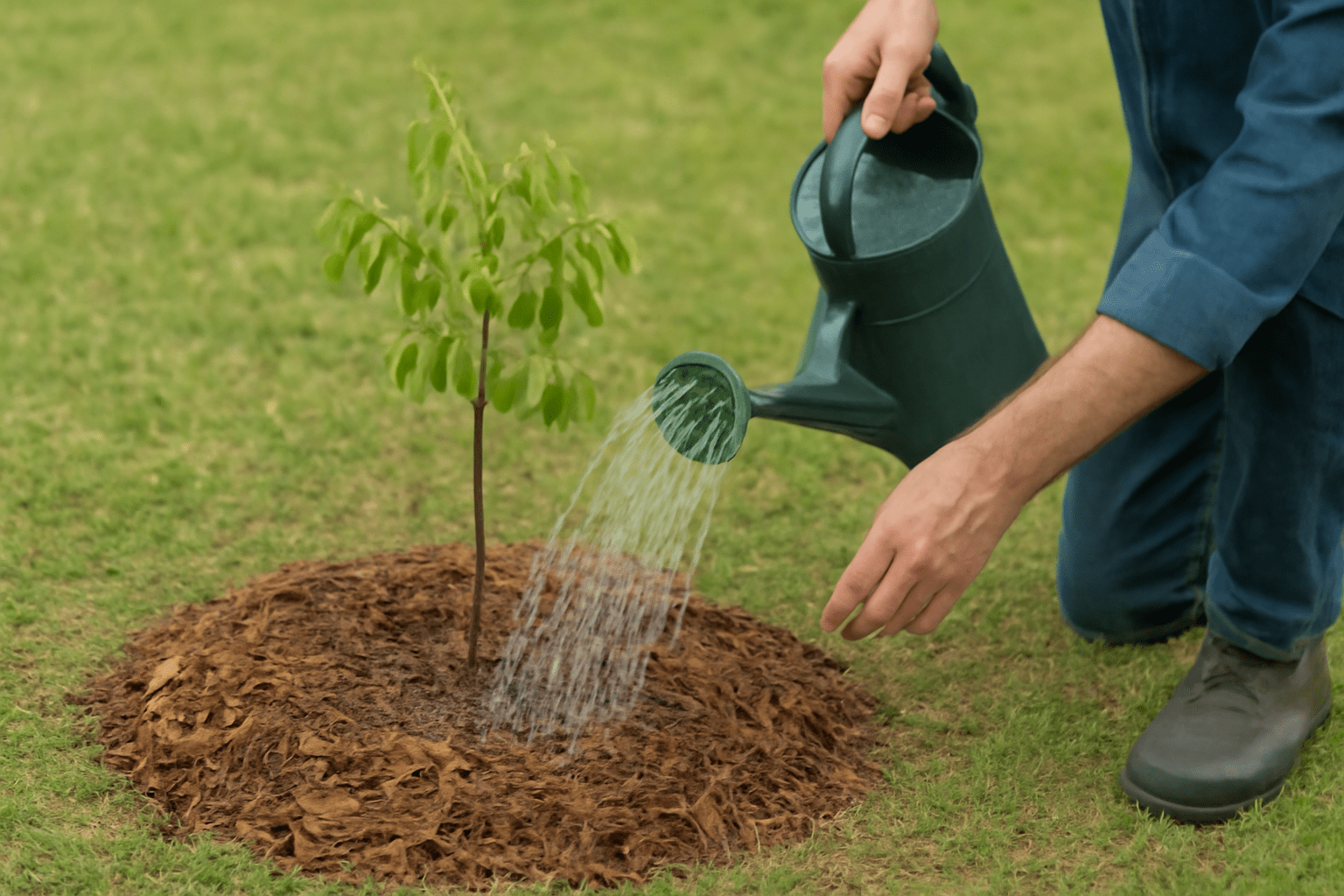
💧 1. Proper Watering 💦
Pecan trees need consistent moisture 💧 to thrive, especially during their growing season 🌱. However, it’s important to avoid overwatering, as this can cause root rot 🦠. Watering Frequency: Water the tree deeply 🌊, at least once a week during the growing season (spring to fall 🍂). During dry spells ☀️, increase the watering to ensure the roots stay hydrated 💦. Watering Tips: Water at the base of the tree 🌳, ensuring that the water reaches the roots 🌱. Use a soaker hose or a drip irrigation system 💧 to deliver water slowly and deeply. Signs of Overwatering: Yellowing leaves 🍂 or waterlogged soil 🌍 can indicate that your pecan tree is getting too much water 💧. Adjust watering accordingly.🌞 2. Fertilization for Strong Growth 🌱
Fertilizing your pecan trees 🌳 is key to providing the nutrients they need for healthy growth and good nut production 🌰. Fertilizer helps replenish essential nutrients that the soil may lack. When to Fertilize: Fertilize your pecan tree 🌳 in early spring 🌸 before the growing season begins. This gives the tree a nutrient boost as it starts its growth cycle 🌱. What to Use: Use a nitrogen-rich fertilizer 🌿 for healthy leaf and shoot growth 🌱. Over time, you can also add phosphorus and potassium to support fruit development 🍏. Fertilizing Tips: Spread the fertilizer evenly around the root zone 🌍 (but not directly on the trunk 🌳) and water it in well 💦. Don’t over-fertilize, as this can stress the tree and lead to poor nut production.✂️ 3. Pruning for Shape and Health 🌳
Regular pruning ✂️ ensures that your pecan tree remains healthy 🌿, maintains a strong structure 💪, and encourages better nut production 🌰. Pruning also helps prevent disease by improving air circulation 🌬️ through the canopy. When to Prune: Prune your pecan tree 🌳 during the dormant season (late winter or early spring ❄️🌸) before new growth begins. Avoid pruning during the growing season 🌞 as it can cause the tree to bleed sap 💧. What to Prune: Remove dead or damaged branches 🪓, suckers (shoots growing from the base), and crossing branches that rub against each other 🌳. This helps direct the tree’s energy to healthier branches 🌱. Pruning Tips: Always make clean cuts with sharp tools 🛠️ to avoid damaging the tree. Don’t over-prune; aim for a strong central leader and a balanced structure.🐜 4. Pest and Disease Control 🐞
Pecan trees are susceptible to a few common pests 🐛 and diseases 🦠. Regular monitoring and quick action are key to keeping your trees healthy 🌳. Common Pests:- Pecan Weevils: These pests can damage the nuts 🌰. Use insecticides or traps 🪤 to control them.
- Aphids: Aphids can be controlled using insecticidal soap 🧴 or by encouraging beneficial insects like ladybugs 🐞.
- Pecan Scab: A fungal disease 🦠 that causes black spots on leaves 🍂 and nuts 🌰. To prevent this, use fungicides and avoid overhead watering 🌧️.
- Powdery Mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white, powdery coating on leaves 🍂. Prune affected branches ✂️ and use fungicides as necessary.
🌱 5. Mulching for Moisture and Protection 🍂
Mulch is a great way to help your pecan tree 🌳 conserve moisture 💧, suppress weeds 🌾, and regulate soil temperature 🌡️. It also adds organic matter to the soil as it breaks down 🍂. How to Mulch: Apply a 3–4 inch layer of mulch 🍃 around the base of the tree 🌳, making sure to keep the mulch a few inches away from the trunk 🌳. This helps prevent rot 🦠 and pest infestation 🐛. Best Mulch Materials: Use organic materials like wood chips 🪓, straw 🌾, or leaves 🍁 for mulch. Avoid using grass clippings 🌿 or materials that could mat down and block airflow.🌿 6. Monitoring Soil Health 🧪
Healthy soil 🌍 is essential for the overall growth 🌱 and productivity 🌰 of your pecan tree 🌳. Regularly monitor the soil’s pH and nutrient levels to make adjustments when necessary. Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test 🧪 every 1-2 years to check for nutrient deficiencies or pH imbalances ⚖️. Pecan trees prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0–7.0) 🌿. Amending the Soil: If the soil is lacking in specific nutrients, amend it with the appropriate fertilizers or organic matter 🧑🌾. Compost 🍂 can also improve soil structure and increase nutrient availability 💪. Caring for your pecan tree 🌳 doesn’t have to be complicated. With regular watering 💧, proper fertilization 🌱, periodic pruning ✂️, and pest control 🐞, your tree will be well on its way to producing healthy nuts 🌰. By staying on top of soil health 🧪, mulching 🍂, and monitoring for diseases 🦠 and pests 🐛, you’ll ensure a thriving pecan tree 🌳 that can produce a bountiful harvest 🍂 year after year 🌱. So roll up your sleeves 👕, put these care tips into action ⚒️, and watch your pecan tree flourish! 😊🛠️ Troubleshooting Common Pecan Tree Problems 🍂
Even with the best care 🌳, pecan trees can face a variety of challenges. Whether you’re a beginner 👩🌾 or an experienced grower 🌿, it’s important to recognize and address common issues quickly to keep your tree healthy 🌱 and productive 🌰. In this section, we’ll walk you through some of the most common pecan tree problems and how to troubleshoot them effectively. 😊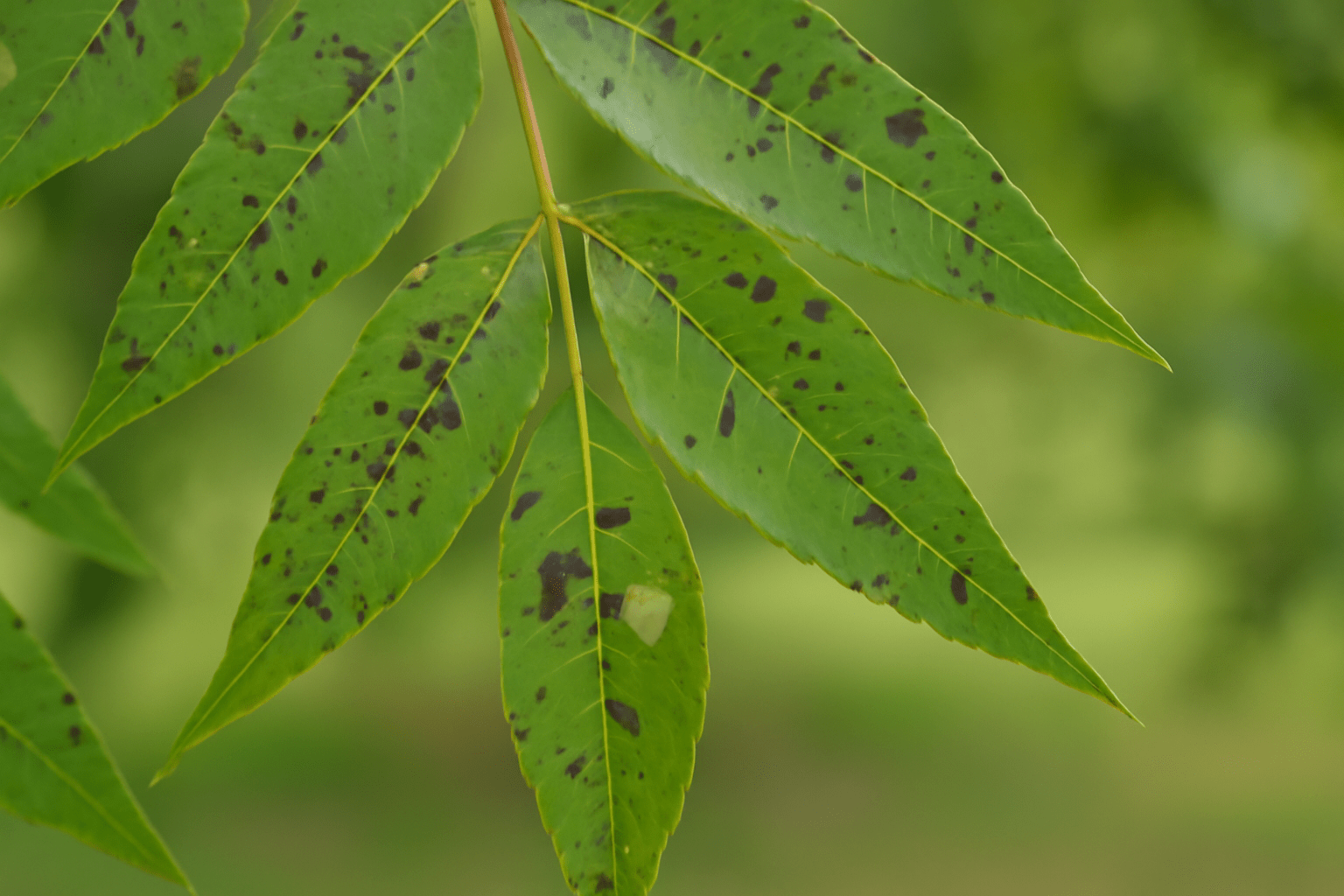
🍂 1. Yellowing Leaves: Lack of Nutrients or Water 💧
Problem: If your pecan tree’s leaves 🍂 are turning yellow, it could be a sign of several issues, including nutrient deficiencies or watering problems 💦. Possible Causes:- Nutrient Deficiency: A lack of nitrogen, iron, or magnesium can cause yellowing leaves 🌿.
- Overwatering or Underwatering: Inconsistent watering 💧 can stress the tree 🌳, leading to yellowing leaves 🍂.
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test 🧪 to check for nutrient deficiencies. Based on the results, you may need to adjust your fertilization schedule or add specific nutrients 🌱.
- Watering Adjustment: Ensure the tree is getting the right amount of water 💦. Deep watering once a week is usually enough for mature trees 🌳. Avoid soggy soil 🌍 by improving drainage or adjusting watering habits.
🦗 2. Pecan Weevils: Destroying Nuts and Leaves 🥜
Problem: Pecan weevils 🐞 are a common pest that can cause serious damage to your pecan tree 🌳. These insects burrow into the nuts 🌰, destroying them, and sometimes they also damage the tree’s leaves 🍂 and branches 🌿. Symptoms:- Holes in the nuts 🌰 or damaged, dried-up pecans 🍂.
- Small, round holes on the bark 🌳 where adult weevils have entered 🦗.
- Insecticide: Use an appropriate insecticide 🧴 to control weevil populations. Apply it during the spring 🌸, just before the nuts begin to develop.
- Traps: Use sticky traps 🪤 to monitor and reduce weevil numbers.
- Cultural Controls: Clean up fallen nuts 🌰 and debris around the base of the tree to remove hiding spots for pests 🐜.
🍂 3. Pecan Scab: Fungal Disease That Affects Leaves and Nuts 🌿
Problem: Pecan scab 🦠 is a common fungal disease that affects the leaves 🍂, nuts 🌰, and stems 🌿 of pecan trees. It can severely reduce the quality of the nuts 🌰 and damage the tree’s foliage 🌳, limiting photosynthesis ☀️. Symptoms:- Black, circular spots on leaves 🍂 and nuts 🌰.
- Deformed or shriveled nuts 🌰.
- Premature leaf drop 🍂.
- Fungicide Application: Apply a fungicide regularly 🧴, especially during the wet, humid months 🌧️ when the disease is most active. Be sure to follow the label instructions 📜.
- Proper Watering: Avoid overhead watering 💧 to keep the foliage dry 🍂 and reduce fungal spread.
- Pruning: Remove and dispose of affected leaves 🍂 or nuts 🌰 to reduce the spread of the disease.
🌱 4. Poor Nut Production: Lack of Pollination or Stress 🌳
Problem: If your pecan tree 🌳 is healthy but not producing many nuts 🌰, it could be due to poor pollination 🌸 or environmental stress 🌡️. Possible Causes:- Pollination Issues: Pecan trees require cross-pollination 🌼 from another variety to produce nuts 🌰. If you only have one variety 🌳 or incompatible varieties, nut production will be low.
- Environmental Stress: Drought 🌞, extreme temperatures ❄️, or poor soil conditions 🌍 can cause the tree to produce fewer or no nuts 🌰.
- Ensure Proper Pollination: Plant at least two compatible pecan varieties 🌳 that bloom around the same time to ensure effective cross-pollination 🌸.
- Reduce Stress: Provide consistent water 💦 during dry periods 🌞, ensure your tree is fertilized 🌿, and protect it from extreme weather conditions 🏜️ with shade or windbreaks 🌬️.
🍂 5. Leaf Drop: Pests, Disease, or Weather Stress 🌧️
Problem: Early or excessive leaf drop 🍂 can be caused by a number of issues, including pest infestations 🐛, diseases like powdery mildew 🦠, or environmental stress 🌡️ like drought 🌞 or heavy winds 🌪️. Possible Causes:- Pest Infestations: Aphids 🐜, caterpillars 🐛, or scale insects 🦠 can weaken the tree 🌳, leading to premature leaf drop 🍂.
- Diseases: Fungal infections like powdery mildew 🦠 or bacterial leaf scorch 🦠 can cause leaves 🍂 to fall early.
- Environmental Factors: Drought 🌞, high winds 🌪️, or extreme temperatures ❄️ can lead to leaf loss 🍂.
- Pest Control: If pests 🦠 are the issue, use an appropriate insecticide 🧴 or organic pest control methods 🌱 to remove the infestation.
- Disease Control: If a fungal or bacterial infection 🦠 is suspected, apply the recommended fungicide 🧴 and remove any infected leaves 🍂.
- Water and Mulch: Ensure the tree is watered consistently 💧, and mulch around the base 🍂 to retain moisture 💦 and protect roots 🌳 from heat stress 🌞.
🌿 6. Yellow or Brown Tips on Leaves: Over-Fertilization or Nutrient Imbalance 🌱
Problem: Yellow or brown tips 🍂 on leaves 🌿 often indicate a nutrient imbalance 🌿 or over-fertilization 🌱. Symptoms:- The tips 🍂 of the leaves turn yellow or brown 🍂.
- The tree may exhibit slow growth 🌱 or reduced nut production 🌰.
- Reduce Fertilizer: If you’ve been over-fertilizing with nitrogen, reduce the amount or switch to a balanced fertilizer 🌱 with lower nitrogen levels 🌾.
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test 🧪 to determine if there are any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances ⚖️ and adjust accordingly.
🌰 Harvesting Pecans: When and How 🥜
Harvesting pecans at the right time ⏰ and with the proper techniques 🛠️ is key to enjoying a high-quality, bountiful yield 🌳. Timing and method matter to ensure that the nuts 🌰 are mature, flavorful, and easy to process 🥘. In this section, we’ll walk you through the best time to harvest your pecans and how to do it effectively 😊.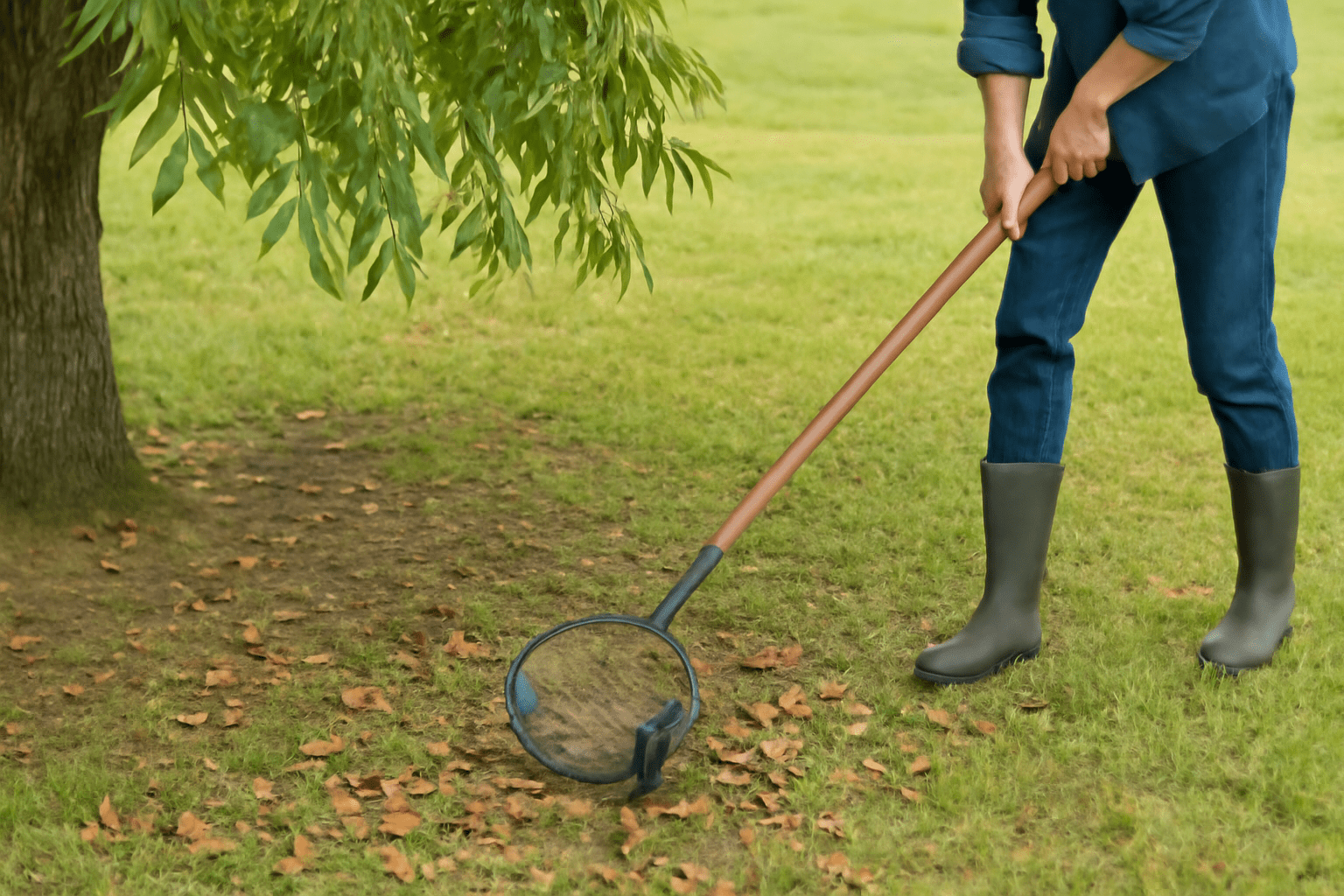
🗓️ 1. When to Harvest Pecans 🍂
Timing is everything ⏰ when it comes to harvesting pecans 🌰. Harvest too early, and your nuts 🌰 may be underdeveloped; too late, and they may fall and be damaged by pests 🦗 or weather 🌧️. Ideal Harvest Time: Pecans are usually ready to harvest in fall 🍁, typically from September to November 🍂, depending on your region 🌍 and variety 🌿. Signs of Maturity:- The outer shell of the pecan 🌰 will begin to crack open naturally, revealing the nut inside 🌰.
- Nuts 🌰 will fall from the tree 🌳 when they’re ripe. A tree shedding nuts 🌰 is a strong indication that they’re ready to harvest.
- Color Change: The green husk around the nut 🌰 will turn brown 🍂 as it begins to split open 🌰.
🌿 2. How to Harvest Pecans 🍃
Harvesting pecans doesn’t need to be complicated, but using the right techniques will save you time ⏳ and effort 💪 while keeping the nuts 🌰 in good condition. Hand Harvesting: If you have just a few trees 🌳, you can hand-pick the fallen nuts 🌰 from the ground. However, pecans 🌰 can be difficult to spot in grass 🍃 or under tree canopy 🌳, so be thorough! Tip: Use a nut gatherer (a wire basket on wheels 🛒) to collect fallen pecans 🌰 quickly and efficiently. Shaking the Tree: For larger orchards 🌳 or mature trees 🌳, you may need to shake the branches 🌿 to encourage the nuts 🌰 to fall. You can use a tree shaker 🌳 or a simple hand-held tool like a long pole 🪓 or rope to shake the tree gently 🌳. Important: Avoid shaking when the tree is too wet 🌧️, as this can cause damage to the nuts 🌰 and the tree 🌳.💡 3. Processing Your Pecans 🌰
After harvesting your pecans 🌰, it’s important to process them properly to preserve their quality and flavor 🌿. Here’s how: Remove the Husks: Once the nuts 🌰 fall from the tree 🌳, remove the outer husk from the nut 🌰. This husk can be tough to remove by hand 🖐️, so you may want to use a hulling machine 🔧 if you have a larger harvest. Drying: After removing the husk 🌰, dry the nuts 🌰 to prevent mold 🦠 or spoilage. Spread them out in a single layer 🧑🌾 in a dry, warm location 🌞 for about 2-3 weeks. You can also use a dehydrator for faster drying. Test for Dryness: The pecans 🌰 are fully dried when the shell sounds hollow when tapped 🥁. Cracking the Nuts: Once dried, you can crack the pecans 🌰 to extract the kernels 🥜. Use a nutcracker 🛠️ to break open the shells 🥜, being careful not to crush the delicate nut inside 🌰.🥜 4. Storing Your Pecans 🏠
Proper storage is essential 🏡 to maintain the freshness and flavor of your harvested pecans 🌰. Short-Term Storage: If you plan to use the pecans 🌰 soon, you can store them in a cool ❄️, dry place in an airtight container 🫙. They will keep for up to 3 months 🗓️. Long-Term Storage: For longer storage, you can freeze pecans 🌰 to preserve their freshness. Place them in airtight bags 🛍️ or vacuum-sealed containers 🏷️ and freeze them ❄️. They’ll keep for up to 1 year in the freezer 🧊.🌿 5. Tips for Harvesting Efficiency 🍃
Harvest Early in the Day: Harvest pecans 🌰 in the early morning 🌅 when the temperatures are cooler 🌤️. This will prevent them from being damaged by heat 🌞 and will make them easier to handle 👐. Don’t Delay the Harvest: Don’t wait too long ⏳ to harvest your pecans 🌰, as waiting for too long increases the risk of pests 🦗 and weather damage 🌧️. Once the nuts 🌰 start falling, try to harvest within a week or two to ensure the best quality 🌿. Harvesting pecans 🌰 at the right time ⏰ and using the proper techniques ensures that you get the best quality nuts 🌰 for consumption or sale 🛒. By paying attention to the signs of maturity 🌿, harvesting efficiently 🌳, and properly processing and storing the nuts 🌰, you’ll be able to enjoy the fruits of your labor 🌳. Whether you’re harvesting just a few trees 🌳 or an entire orchard 🍂, these tips will help you get the most out of your pecan trees 🌰. Happy harvesting! 🥳🌳 Maximizing Pecan Tree Yield for Commercial Growers 🌰
For commercial pecan growers, maximizing yield is a key goal to ensure profitability 💰 and long-term success 🌱. By focusing on tree care 🌳, soil health 🌿, pest management 🐜, and proper harvesting techniques 🛠️, you can significantly increase your harvest. In this section, we’ll cover the best practices for commercial pecan growers looking to boost their yield 🌿.
🌱 1. Choose the Right Varieties for Maximum Production 🌳
Selecting the right pecan tree varieties 🌰 is crucial for maximizing yield. Not all varieties are equal when it comes to productivity, and certain varieties perform better under specific climate conditions 🌍. High-Yield Varieties: Opt for varieties known for high productivity 💪 and disease resistance 🦠, such as Desirable, Pawnee, and Stuart. These varieties are ideal for commercial orchards 🌳 and produce large, high-quality nuts 🌰. Pollination Compatibility: Pecan trees 🌳 need cross-pollination to produce nuts 🌰. Plant at least two compatible varieties to ensure maximum pollination 🌸 and nut production. Varieties like Desirable and Stuart work well together 🌰.💧 2. Irrigation Systems for Consistent Watering 💦
Consistent watering 💧 is essential for healthy pecan trees 🌳 and a bountiful harvest 🌰. Water stress can reduce nut production 🌰, so it’s important to establish a proper irrigation system 💧. Drip Irrigation: Install a drip irrigation system 💧 to deliver water directly to the root zone 🌿. This is efficient and ensures deep watering 🌊, which is necessary for pecan trees 🌳. Soaker Hoses: If drip irrigation isn’t feasible, consider using soaker hoses 🌿. They allow for even water distribution 💦 across the root zone without wetting the foliage 🌳. Monitor Soil Moisture: Regularly monitor soil moisture levels 🌱, especially during dry periods 🌞, to avoid water stress. Use a soil moisture meter 🌡️ to help track water needs.🧪 3. Soil Health: Fertilization and pH Management 🌱
Healthy soil 🌍 is the foundation of high yields 🌰. Regular soil testing and proper fertilization are key to maintaining soil health 🌱 and optimizing tree growth 🌳. Soil Testing: Conduct soil tests 🧪 at least once a year 📅 to monitor nutrient levels and pH. Pecans prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0–7.0). Adjust the soil’s pH with amendments like lime 🌿 (to raise pH) or sulfur 🌱 (to lower pH) if needed. Fertilization: Apply nitrogen-rich fertilizers 🌿 in the early spring to support healthy leaf 🍃 and shoot growth 🌱. Follow up with potassium 🍃 and phosphorus 🌿 to encourage nut development 🌰 during the growing season. Organic Amendments: Adding compost 🍂 or organic matter improves soil structure 🌍 and water retention 💧, making it ideal for pecan trees 🌳.✂️ 4. Pruning for Better Airflow and Sunlight Exposure 🌞
Proper pruning ✂️ plays an important role in maximizing the yield of your pecan trees 🌳 by encouraging strong growth 🌱 and improving sunlight penetration 🌞. Prune for Structure: Focus on shaping the tree 🌳 to create a central leader 🌱 and strong scaffold branches 🌳. This encourages a sturdy structure 🌳 that can support large amounts of nuts 🌰. Remove Dead Wood: Regularly prune dead 🪓, diseased 🦠, or damaged branches 🌿 to maintain a healthy tree 🌳. This prevents the spread of diseases 🦠 and improves overall airflow 🌬️. Improve Sunlight Exposure: Thin out overcrowded branches 🌿 to allow more sunlight 🌞 to reach the inner parts of the tree 🌳, ensuring even growth 🌱 and nut development 🌰.🦠 5. Pest and Disease Management for a Healthy Orchard 🧑🌾
Pests 🐜 and diseases 🦠 can severely affect your yield 🌰 if not controlled. Managing these threats is essential 🧑🌾 to ensure the longevity 🌳 and productivity 💪 of your orchard. Monitor for Pecan Weevils: Pecan weevils 🐜 can cause significant damage to nuts 🌰. Use traps 🛑 or apply insecticides 🦠 as necessary to control their population. Fungal Diseases: Pecan trees 🌳 are prone to scab 🦠 and powdery mildew 🌿. Apply fungicides regularly during the growing season 🌱, especially during wet weather 🌧️, to protect the foliage 🍃 and nuts 🌰. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Adopt an IPM strategy 🌍, combining biological controls 🐝, traps 🧪, and judicious pesticide use 🦠 to manage pests without harming the environment 🌿 or beneficial insects 🦋.🌿 6. Proper Spacing and Planting Density 🌳
Planting your trees 🌳 with the right spacing ensures that they have room to grow 🌱 and that they get enough sunlight 🌞 and airflow 🌬️, both of which are essential for maximizing yield 🌰. Spacing Recommendations: For commercial orchards 🌳, space trees 40–60 feet apart 🌳 to allow for their large canopies 🌳 and to avoid overcrowding 🌿. This also promotes healthy airflow 🌬️ and reduces the risk of disease spread 🦠. Dwarf Varieties for Smaller Orchards: If land is limited 🌍, consider planting dwarf pecan varieties 🌱 that require less space and can be managed more easily 🧑🌾. These trees 🌳 will still produce good yields 🌰, especially in smaller orchards 🌿.🧑🌾 7. Harvesting at the Right Time for Peak Quality 🌰
Harvesting at the right time ⏰ ensures that your pecans 🌰 are mature and of high quality, both of which are essential for commercial sales 🛒. Timing: Wait for the outer husk 🌰 to crack open, signaling that the nuts 🌰 are ready for harvest 🌾. Typically, this occurs in late fall 🍂 (September to November), depending on the variety and climate 🌍. Efficient Harvesting: For large orchards 🌳, use mechanical tree shakers 🌿 to shake the pecans 🌰 off the trees 🌳. This is much faster than hand-picking 🖐️ and reduces labor costs 💸. Post-Harvest Handling: Dry the harvested nuts 🌰 thoroughly to prevent mold 🦠. Use commercial-grade drying systems 🌞 to speed up the process and maintain the quality of the nuts 🌰.🛠️ 8. Implementing a Tree Care Schedule 🌳
Creating and sticking to a regular tree care schedule 📅 is essential 🧑🌾 for optimizing yield 🌰 and tree health 🌳 in a commercial setting 🏢. Routine Checks: Schedule regular checks for soil health 🌱, pest control 🦠, watering 💧, and pruning ✂️. Having a systematic approach ensures that your orchard 🌳 remains in peak condition. Record-Keeping: Keep detailed records 📝 of your trees’ growth 🌱, pest management 🦠, and fertilization schedules 🌿. This will help you track which methods are most effective 💡 and allow for better decision-making over time. Maximizing pecan tree yield in a commercial orchard 🌳 requires a combination of the right variety selection 🌰, consistent care 🌱, and smart management practices 🧑🌾. By focusing on soil health 🌍, pest control 🦠, pruning 🌳, and timely harvesting 🌰, you can increase your yield and quality of nuts 🌰, ensuring that your orchard 🌳 is not only productive but profitable 💰. With the right strategies in place, your commercial pecan operation 🌳 will thrive for many years to come! 🌰🌿 Final Thoughts on Growing and Caring for Pecan Trees 🌰
Growing pecan trees 🌳 is a rewarding and long-term investment 💰 that requires patience 🕰️, dedication 💪, and knowledge 📚. Whether you’re a backyard gardener 🌱 or a commercial grower 🧑🌾, following best practices in choosing the right varieties 🌰, planting correctly 🌿, providing essential care 💧, and managing pests 🦠 and diseases 🦠 will set you up for success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best time to plant pecan trees?
The ideal time to plant pecan trees is in early spring or late winter, when the soil is warm enough for root growth but before the tree starts actively growing. Planting during these seasons gives your tree a strong foundation for the upcoming growing season.
How far apart should I plant pecan trees?
Pecan trees need plenty of space to grow. For standard trees, plant them 40 to 60 feet apart, allowing their large canopies to spread without overcrowding. Dwarf varieties can be spaced 20 to 30 feet apart for more compact planting.
How do I know when pecan trees are ready for harvest?
Pecans are ready to harvest when the outer husk cracks open, revealing the nut inside. You can also tell by observing the fallen nuts—when they drop naturally from the tree, it’s usually time to collect them.
What are the best varieties of pecan trees for high yield?
Varieties like Desirable, Pawnee, and Stuart are known for their high yield, disease resistance, and large nut size. These varieties perform well in commercial orchards and can adapt to different growing conditions, making them excellent choices for maximizing harvest.
How often should I water pecan trees?
Pecan trees need consistent moisture, especially during dry spells. Water the tree deeply at least once a week during the growing season. Adjust watering frequency depending on rainfall, but avoid overwatering, as soggy soil can damage the roots.
How can I protect my pecan trees from pests and diseases?
Monitor your trees regularly for pests like pecan weevils and diseases like pecan scab. Use insecticides, fungicides, and organic pest control methods, along with good orchard hygiene (removing fallen nuts and leaves), to keep pests and diseases under control.
How do I improve soil health for better pecan tree growth?
Test the soil for pH and nutrient levels regularly. Pecan trees thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0–7.0). Amend the soil with compost or organic matter and apply nitrogen-rich fertilizers in the spring to encourage healthy growth and nut production.
Can pecan trees grow in containers or small spaces?
Pecan trees need plenty of space to grow, so dwarf varieties are the best option for containers or small spaces. These trees will still produce nuts but have a more compact size, making them easier to manage in limited areas.
