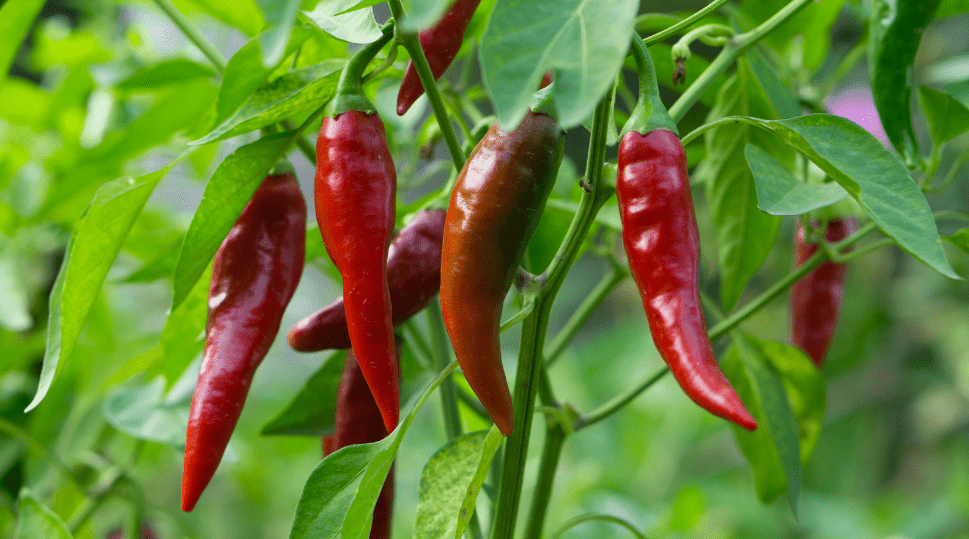

Skinny Red Chili Peppers: Perfecting Growth and Flavor in Your Garden
Growing skinny red chili peppers in your garden can be a rewarding and delicious experience. These fiery little peppers add a kick to any dish and are a staple in many cuisines around the world. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know to successfully grow skinny red chili peppers in your garden, from choosing the right location and soil to maximizing growth and flavor. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, these expert tips and advice will help you perfect the growth and flavor of your skinny red chili peppers.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Skinny Red Chili Peppers
A. Botanical name and classification
Skinny red chili peppers belong to the Capsicum annuum species and are classified as a type of hot pepper. They are known for their slender shape and intense heat, making them a popular choice for adding spice to dishes.
B. Description of the plant and its fruits
The skinny red chili pepper plant typically grows to a height of about 2-3 feet and produces long, slender, bright red fruits. The peppers start off green and gradually turn red as they ripen. They have a thin, wrinkled skin and a spicy flavor, with a heat level ranging from moderate to very hot, depending on the variety.
C. Native habitat and ideal growing conditions
Skinny red chili peppers are native to Central and South America but are now grown in many regions around the world. They thrive in warm and sunny climates and require well-drained soil with a pH of 6-7. The ideal temperature for growing skinny red chili peppers is between 70-90°F. They can be grown in containers or in the ground, and they benefit from regular watering and fertilization. It’s important to protect the plants from frost, as they are sensitive to cold temperatures.
Selecting the Right Variety
A. Popular skinny red chili pepper varieties
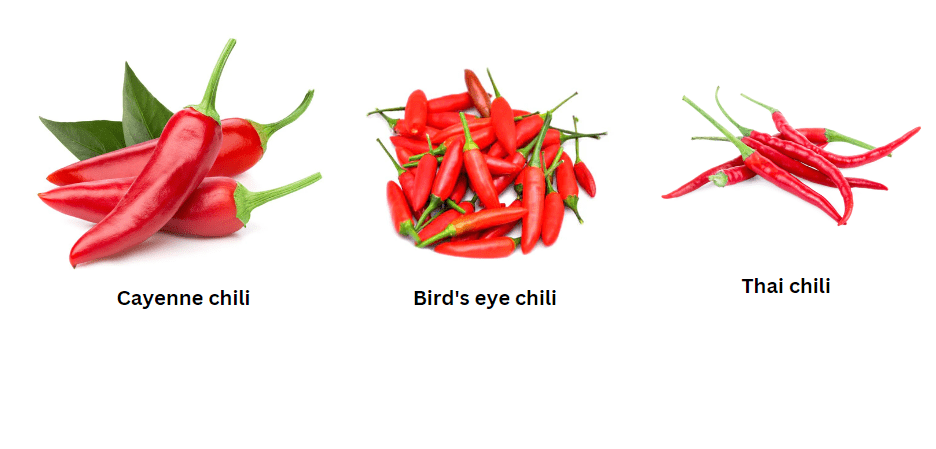
Some popular skinny red chili pepper varieties include cayenne, bird’s eye, and Thai chili peppers. Each variety may have slightly different growing requirements and heat levels, so it’s important to choose a variety that suits your climate and taste preferences. Cayenne peppers, for example, are known for their medium heat and are often used in cooking, while bird’s eye peppers are very hot and commonly found in Southeast Asian cuisine. Thai chili peppers are also hot and are often used to add heat to dishes. When selecting a variety, consider the heat level and flavor profile that you prefer.
B. Factors to consider when choosing a variety
When choosing a chili pepper variety, there are several factors to consider. First, think about the climate in which you will be growing the peppers and choose a variety that is well-suited to that environment. Additionally, consider the heat level and flavor profile of the peppers and choose a variety that aligns with your taste preferences. It’s also important to consider how you plan to use the peppers – whether it’s for cooking, pickling, or as a condiment. By taking these factors into account, you can select the right variety of chili pepper for your needs.
Preparing for Planting
A. Choosing the right location
When preparing to plant chili peppers, it’s important to choose the right location for optimal growth. Select a spot that receives plenty of sunlight and has well-draining soil. It’s also important to consider the spacing and airflow between plants to prevent overcrowding and disease. Additionally, think about protection from strong winds and potential pests. By choosing the right location, you can set your chili peppers up for success.
B. Preparing the soil
To prepare the soil for planting chili peppers, start by testing the pH level and adding any necessary amendments to achieve a pH level of around 6.0 to 6.8. This will ensure that the soil is at an optimal level for pepper growth. Next, ensure that the soil is well-draining by adding organic matter such as compost or peat moss to improve the soil structure. It’s also important to remove any weeds and debris from the planting area to create a clean and healthy environment for the peppers to grow. Taking the time to properly prepare the soil will set the stage for healthy and bountiful chili pepper plants.
Planting Skinny Red Chili Peppers
A. Starting from seeds vs. seedlings
Starting from seeds allows for more control over the growing process and can be a more cost-effective option. However, it requires more time and attention as the seeds need to be started indoors in a controlled environment before being transplanted outside. On the other hand, starting from seedlings provides a head start on the growing process as they are already established plants. This can result in an earlier harvest, but may be more expensive than starting from seeds. Both options can be successful, it just depends on your preference and the amount of time and resources you are willing to invest.
1. Seed selection and germination
When selecting seeds for skinny red chili peppers, it’s important to choose a variety that is well-suited for your climate and growing conditions. Look for reputable seed suppliers who offer quality seeds. To germinate the seeds, start by planting them in a seed starting mix in small containers. Keep the soil consistently moist and provide warmth and light for optimal germination. Once the seedlings have sprouted, they can be transplanted into larger pots or into the garden. It’s important to provide proper care and attention to ensure successful germination and healthy seedlings.
B. Planting tips
1. Proper spacing and depth
When planting seeds, it’s important to consider proper spacing and depth to ensure successful germination and healthy growth. Be sure to follow the specific instructions provided by the seed supplier for each type of seed, as different plants have different spacing and depth requirements.
In general, seeds should be planted at a depth that is about twice the diameter of the seed. This allows for adequate contact with the soil while still providing enough protection and moisture for germination. It’s also important to space seeds according to the recommended distance for each type of plant, as overcrowding can lead to competition for nutrients and sunlight.
Taking the time to plant seeds at the proper depth and spacing will help to promote strong root growth and healthy, vigorous plants. Always refer to the specific planting guidelines for each type of seed to ensure best results.

2. Companion planting considerations
When planning your garden, it’s important to consider companion planting, which is the practice of planting certain crops together to enhance growth, deter pests, and improve overall plant health. Some plants have natural affinities for one another, while others can help to repel pests or attract beneficial insects. For example, planting basil alongside tomatoes can help to improve the flavor and growth of the tomatoes, while planting marigolds near vegetables can help to deter harmful nematodes. It’s also important to consider the spacing and growth habits of plants when companion planting, to ensure that they won’t compete for space or resources. By carefully selecting companion plants and considering their spacing and growth habits, you can create a healthy and productive garden that thrives with the help of natural relationships between plants.
Care and Maintenance
A. Watering requirements
It’s important to consider the specific watering requirements for each type of plant in your garden. Some plants may require more frequent watering, while others may prefer drier conditions. It’s best to water in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize evaporation and ensure that the plants can absorb the water. Be mindful not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot and other issues. Additionally, consider using mulch to help retain moisture and reduce the need for frequent watering. Always refer to the specific planting guidelines for each type of plant to ensure that you are meeting their individual watering needs.

1. Mulching to retain moisture and control weeds
Mulching is a great way to help retain moisture in the soil and reduce the need for frequent watering. It also helps to control weeds by suppressing their growth and preventing them from taking over your garden. When applying mulch, be sure to spread it evenly around the base of your plants, leaving a small gap around the stem to prevent any moisture-related issues. Organic mulches, such as wood chips or straw, can also break down over time and add valuable nutrients to the soil. Just be sure to replenish the mulch as needed to maintain its effectiveness.
B. Fertilizing skinny red chili peppers
When it comes to fertilizing skinny red chili peppers, it’s important to follow the specific planting guidelines for this type of plant to ensure healthy growth. Typically, a balanced fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is recommended for chili peppers. It’s best to apply the fertilizer when the plants are actively growing, typically in the early spring and then again in mid-summer. Be sure to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production. Additionally, consider incorporating organic matter into the soil, such as compost, to provide a steady source of nutrients for the plants. Always monitor the plants for any signs of nutrient deficiencies and adjust your fertilization schedule as needed.
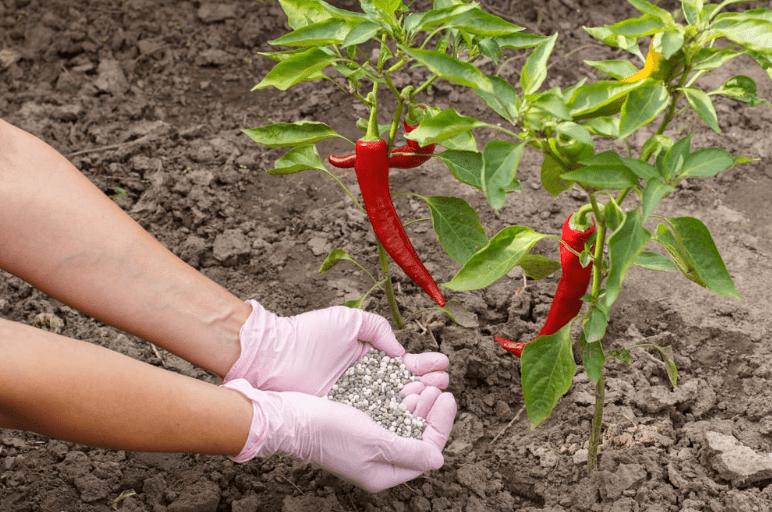

C. Pruning and staking
Pruning and staking can also help improve the overall health and yield of skinny red chili pepper plants. Regular pruning can help promote better airflow and sunlight exposure, while staking can help support the weight of the plants as they produce fruit. Overall, proper fertilization and care are essential for growing healthy and productive skinny red chili peppers.
Managing Pests and Diseases
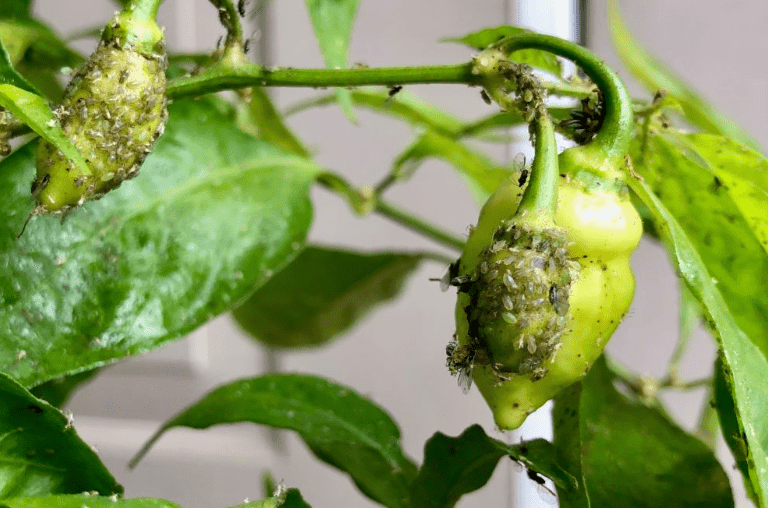
A. Common pests affecting skinny red chili peppers
Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. It’s important to regularly inspect your plants for any signs of infestation and take steps to manage and control these pests. One way to naturally deter pests is by planting companion plants like basil or marigolds, which can help repel insects that may harm your chili peppers. Additionally, using organic pest control methods such as neem oil or insecticidal soap can help manage pest infestations without harming the environment or beneficial insects. It’s essential to address pest issues promptly to prevent them from damaging your chili pepper plants.
In conclusion, growing skinny red chili peppers requires careful attention to soil, watering, fertilization, and pest management. By following these expert tips, you can successfully grow healthy and flavorful chili peppers in your garden. Remember to monitor your plants regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure their optimal growth and productivity.

B. Common diseases
Common diseases that may affect chili peppers include bacterial leaf spot, powdery mildew, and root rot. To prevent these diseases, it’s important to maintain good air circulation, avoid overwatering, and practice proper sanitation in the garden. Additionally, using disease-resistant varieties of chili peppers can help reduce the risk of disease. If you notice any signs of disease on your chili pepper plants, it’s important to take immediate action to prevent the spread and protect the overall health of your plants. By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage common diseases and promote the successful growth of your skinny red chili peppers.
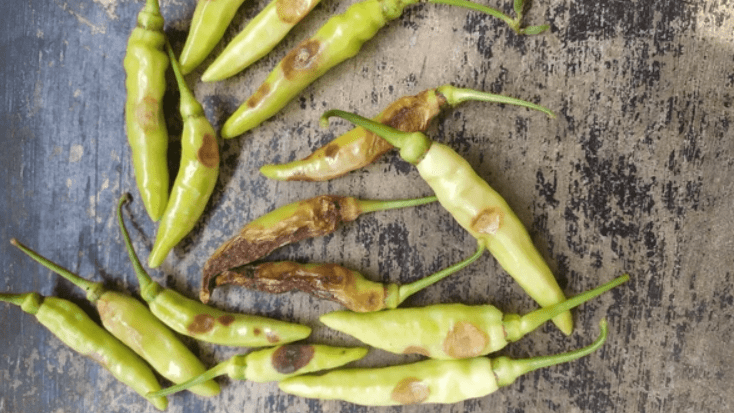
C. Organic and chemical control methods
Organic control methods for common diseases in chili peppers include using neem oil, copper sprays, and beneficial microorganisms. These options can help prevent and manage diseases without the use of synthetic chemicals. Additionally, cultural practices such as crop rotation and proper spacing can also aid in disease control.
Chemical control methods, such as fungicides and bactericides, can also be effective in managing diseases in chili peppers. However, it’s important to use these products carefully and according to label instructions to minimize negative impacts on the environment and beneficial organisms.
Ultimately, a combination of both organic and chemical control methods may be necessary to effectively manage common diseases and promote the overall health of chili pepper plants. It’s important to carefully consider the specific needs of your plants and the best approach for disease control in your garden.
Harvesting and Storing
A. Signs that skinny red chili peppers are ready to harvest
When the chili peppers are fully red and have reached their mature size, they are ready to be harvested. It’s best to use a pair of scissors or garden shears to carefully cut the peppers from the plant, leaving a small portion of the stem attached. After harvesting, store the peppers in a cool, dry place with good air circulation to prevent mold and rot. It’s important to check the peppers regularly for any signs of decay and discard any that are no longer in good condition. Proper harvesting and storing techniques can help ensure that you have a bountiful supply of chili peppers for your culinary needs.
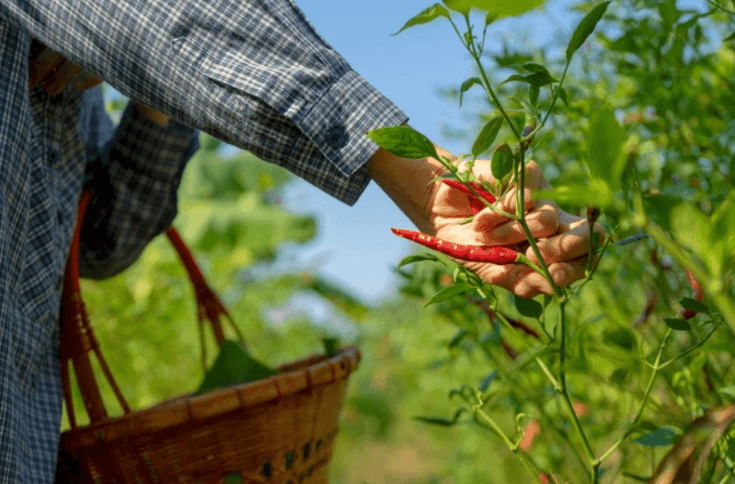

B. Storing and preserving the harvest
After harvesting your chili peppers, it’s important to properly store and preserve them to extend their shelf life. Once you have harvested the peppers, it’s best to lay them out in a single layer on a tray or drying rack and allow them to air dry for a few weeks. Once they are completely dry, you can store them in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. You can also preserve the chili peppers by making them into hot pepper flakes or powder. Simply grind the dried peppers into a fine powder using a spice grinder or mortar and pestle. Store the powder in an airtight container and use it to add a kick to your favorite dishes. Proper storing and preserving techniques can help you enjoy your chili peppers long after the harvesting season is over.
Enhancing Flavor and Heat
A. Factors influencing flavor and heat level
Factors influencing flavor and heat level in chili peppers include the variety of pepper, growing conditions, and ripeness at harvest. The longer peppers remain on the plant, the more developed their flavors and heat become. Additionally, peppers grown in hotter, drier conditions tend to have a higher heat level than those grown in cooler, wetter climates.
Culinary Uses
A. Popular dishes featuring skinny red chili peppers
Popular dishes featuring skinny red chili peppers include spicy stir-fries, salsas, and curries. The heat and flavor of skinny red chili peppers can add a bold and spicy kick to any dish. Whether you’re cooking up a Thai curry or a Mexican salsa, adding these peppers can take your dish to the next level. Just be sure to use them sparingly if you’re not used to the heat!
B. Preserving techniques
Popular preserving techniques for skinny red chili peppers include drying, pickling, and creating chili paste. Drying chili peppers can help preserve their heat and flavor for longer periods of time, while pickling them can create a tangy and spicy condiment. Chili paste can also be made by blending the peppers with oil and other spices, creating a versatile and long-lasting addition to your pantry. These preserving techniques are great for ensuring that you can enjoy the heat of skinny red chili peppers throughout the year.
In conclusion, growing skinny red chili peppers requires attention to detail and a bit of patience. It’s important to provide the right growing conditions, such as well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight. Additionally, regular watering and fertilizing can help maximize growth and flavor. When it comes to harvesting, make sure to pick the peppers at the right time to ensure the best flavor. With the right care and attention, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious skinny red chili peppers from your garden.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Skinny red chili peppers thrive in warm, sunny climates with well-drained soil. They require plenty of sunlight and consistent watering to grow successfully.
To enhance the flavor of your skinny red chili peppers, you can add organic compost to the soil and provide them with the right balance of nutrients. Additionally, allowing the peppers to fully ripen on the plant before harvesting can enhance their flavor.
It’s important to regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pests or diseases. You can use organic pesticides and fungicides to protect your skinny red chili peppers without harming the environment.
Skinny red chili peppers are ready to be harvested when they have reached their full size and have turned a vibrant red color. Be sure to use gloves when harvesting to protect your skin from the spicy oils in the peppers.
Yes, you can successfully grow skinny red chili peppers in a container as long as it provides enough space for the plant’s roots and has proper drainage. Be sure to choose a container with good depth and width to accommodate the plant’s growth.
Skinny red chili peppers are great for adding a spicy kick to a variety of dishes, including salsas, soups, and stir-fries. You can also dry the peppers and grind them into a spicy powder to use as a seasoning.
Skinny red chili peppers can be a good option for beginners as long as they have the right growing conditions and are given proper care. They are relatively low-maintenance and can be a rewarding addition to a home garden.
To save seeds from your skinny red chili peppers, simply allow the peppers to fully ripen on the plant, then remove the seeds and allow them to dry completely before storing them in a cool, dry place for future planting.
