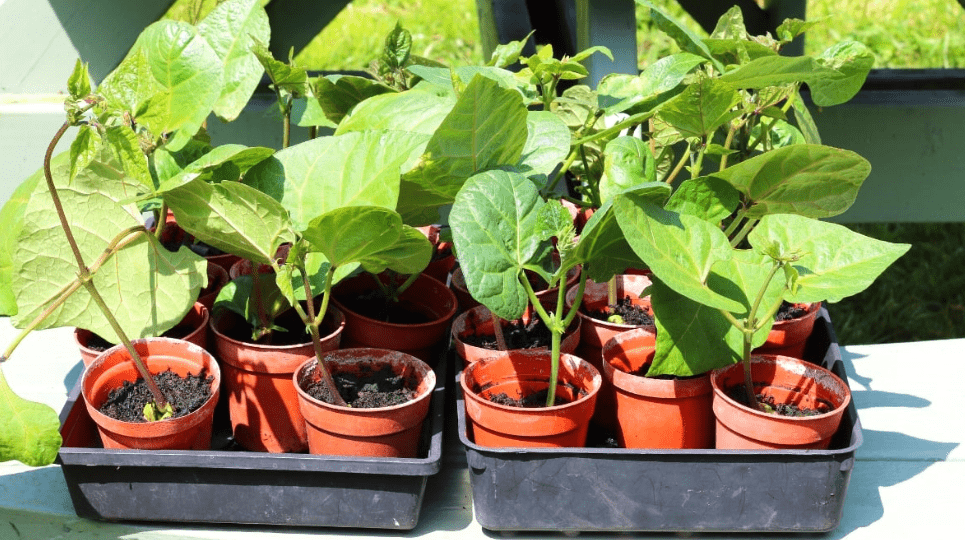

Growing Green Beans in Containers: Tips for Compact Garden Spaces
Growing green beans in containers is a great way to enjoy fresh, homegrown produce even if you have limited garden space. In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know to successfully grow green beans in containers, from choosing the right containers to proper care and maintenance. Whether you’re a beginner gardener or just looking for a space-saving gardening option, these expert tips and techniques will help you grow a bountiful harvest of delicious green beans.
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing the Right Container
A. Discuss the types of containers suitable for green beans (e.g., pots, raised beds, hanging baskets)
When it comes to growing green beans in containers, you have a few options to choose from. Pots, raised beds, and hanging baskets are all suitable containers for green beans. Pots are a good choice for smaller spaces and can be placed on a patio or balcony. Raised beds provide a larger growing area and can be customized to fit your space. Hanging baskets are a great way to save space and add a decorative element to your container garden. Whichever container you choose, make sure it has good drainage to prevent waterlogged soil, and is large enough to accommodate the root system of the green beans. With the right container, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious green beans in even the smallest of spaces.

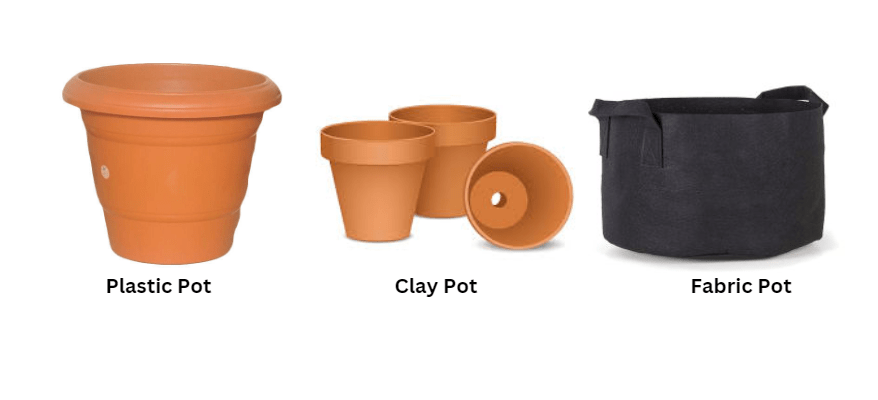
B. Factors to consider: size, material (plastic, clay, fabric), drainage, and mobility
It’s important to consider the size of the container, as green beans need plenty of room to grow. The material of the container is also important, as it should be durable and able to withstand outdoor conditions. Plastic, clay, and fabric containers are all suitable options for growing green beans. Good drainage is essential to prevent waterlogged soil, so make sure the container has drainage holes or add a layer of gravel at the bottom. Finally, consider the mobility of the container, especially if you’re growing green beans in a small space or on a balcony. Choose a container that can easily be moved to optimize sunlight and airflow for your green beans. With these factors in mind, you’ll be well on your way to successfully growing green beans in containers.

Selecting the Ideal Green Bean Variety
A. Best green bean varieties for container gardening (e.g., bush beans, pole beans).
When selecting the ideal green bean variety for container gardening, it’s important to consider the space you have available and the type of support the plants will need. For smaller spaces, bush beans are a great option as they grow in a compact, bushy form and don’t require a trellis or support. On the other hand, pole beans are a good choice if you have a taller container or want to maximize your yield in a smaller space. These varieties will need a trellis, stake, or other support to grow vertically. Ultimately, the best green bean variety for container gardening depends on your specific conditions and preferences.
B. Considerations: growth habit, space requirements, yield, and climate adaptability.
When selecting the ideal green bean variety for container gardening, it’s important to consider several factors. Firstly, consider the growth habit of the variety – whether it is a bush bean or a pole bean. Bush beans are better suited for smaller spaces as they grow in a compact, bushy form and don’t require a trellis or support. On the other hand, pole beans are a good choice if you have a taller container or want to maximize your yield in a smaller space, as they will need a trellis, stake, or other support to grow vertically.
Secondly, consider the space requirements of the variety. Some green bean varieties may take up more space in a container than others, so it’s important to choose a variety that fits within your container’s size constraints.
Next, consider the potential yield of the variety. Some varieties may produce more beans per plant than others, so if maximizing your harvest is a priority, you’ll want to select a high-yielding variety.
Lastly, consider the climate adaptability of the variety. Some green bean varieties are more tolerant of heat, while others may thrive in cooler temperatures. Consider the climate in your area and choose a variety that is well-suited to your local conditions. Ultimately, the best green bean variety for container gardening depends on your specific conditions and preferences.
Preparing the Container
A. Steps to prepare containers for planting: cleaning, adding drainage, and choosing the right soil mix
First, thoroughly clean your containers to remove any dirt, debris, or lingering pathogens that could harm your green bean plants. Next, you’ll want to ensure that your containers have proper drainage to prevent waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot. You can add small rocks or a layer of gravel to the bottom of your containers before adding soil to improve drainage. Lastly, choose a high-quality soil mix that is well-draining and nutrient-rich to provide a healthy growing environment for your green bean plants. These steps will help set the stage for successful container gardening and optimal green bean growth.
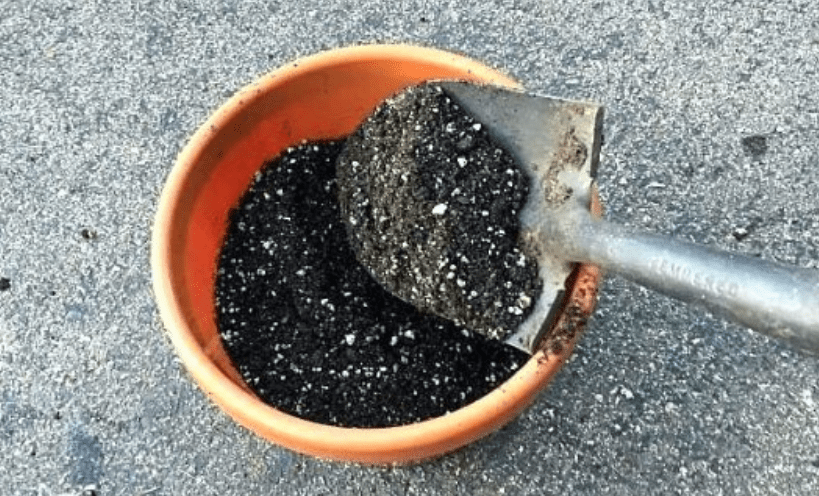

B. Importance of soil quality and amendments (e.g., compost, perlite) for optimal growth.
Soil quality and amendments play a crucial role in the optimal growth of plants. Good soil is essential for providing plants with the necessary nutrients, moisture retention, and aeration for root development. Adding amendments such as compost and perlite can further improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability for plants. Compost adds essential organic matter and beneficial microorganisms to the soil, while perlite helps to improve drainage and aeration. By incorporating these amendments, you can create an ideal growing environment for your green bean plants, leading to healthier and more productive yields.
Planting Green Beans
A. Step-by-step guide to planting green beans in containers: spacing, depth, and seed or seedling options.
Step 1: Choose a container that is at least 12 inches deep and has good drainage holes. A larger container (18-24 inches) is ideal for growing multiple green bean plants.
Step 2: Fill the container with well-draining potting soil, leaving about 1-2 inches of space at the top.
Step 3: For bush green beans, space the seeds or seedlings 4-6 inches apart. For pole green beans, space the seeds or seedlings 6-8 inches apart and provide a trellis or support structure for the vines to climb.
Step 4: Plant the green bean seeds or seedlings about 1 inch deep in the soil and cover lightly with additional soil. Water the container thoroughly after planting.
Step 5: Place the container in a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day.
Step 6: Water the green beans regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Step 7: Fertilize the green beans with a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks to promote healthy growth and production.
By following these steps and providing the proper spacing, depth, and care, you can successfully grow green beans in containers for a bountiful harvest.
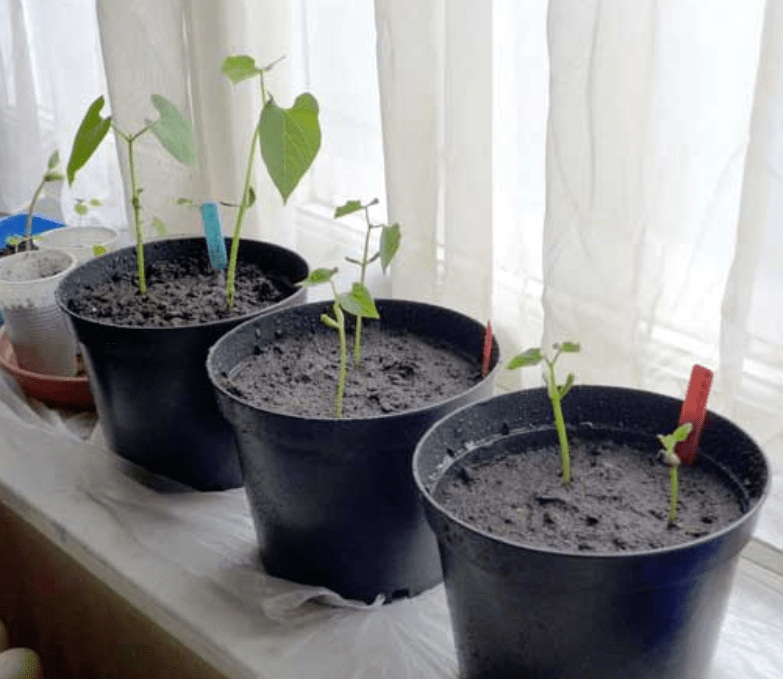

Caring for Green Beans
A. Watering requirements for container-grown green beans: frequency, methods (e.g., drip irrigation, watering cans).
For container-grown green beans, it is important to regularly water the plants to keep the soil consistently moist. This can be done using a watering can or drip irrigation system. The frequency of watering will depend on factors such as the weather and the size of the container, but generally, it is best to water the green beans whenever the top inch of soil feels dry. Avoid overwatering and waterlogging the soil, as this can lead to root rot. By providing the right amount of water and maintaining consistent moisture, you can help ensure healthy growth and a successful harvest of green beans.
B. Fertilization needs: organic vs. synthetic fertilizers, application timing, and nutrient requirements.
When it comes to fertilizing container-grown green beans, there are a few key factors to consider. First, you’ll need to decide between organic and synthetic fertilizers. Organic options, such as compost or manure, can provide slow-release nutrients and improve soil structure, while synthetic fertilizers offer precise nutrient content.
In terms of application timing, it’s best to apply fertilizer when the green beans are actively growing, which is typically after the first set of true leaves has formed. Additionally, be mindful of the nutrient requirements of green beans, which generally need a balanced fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Ultimately, the choice between organic and synthetic fertilizers, as well as the timing and nutrient requirements, will depend on your specific growing situation and preferences. It’s important to monitor the health and growth of your green beans and adjust your fertilization approach accordingly.
Managing Pests and Diseases
A. Common pests and diseases affecting green beans in containers.
Common pests and diseases that can affect green beans in containers include aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies, as well as common diseases such as powdery mildew and bacterial blight. It’s important to regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pest infestations or disease, and take appropriate action to address them. This may involve using organic pest control methods such as insecticidal soaps or neem oil, as well as practicing good sanitation and proper watering techniques to prevent disease. It’s also helpful to choose disease-resistant varieties of green beans when possible, and to rotate your crops to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil. By staying vigilant and taking proactive measures, you can help keep your container-grown green beans healthy and productive.
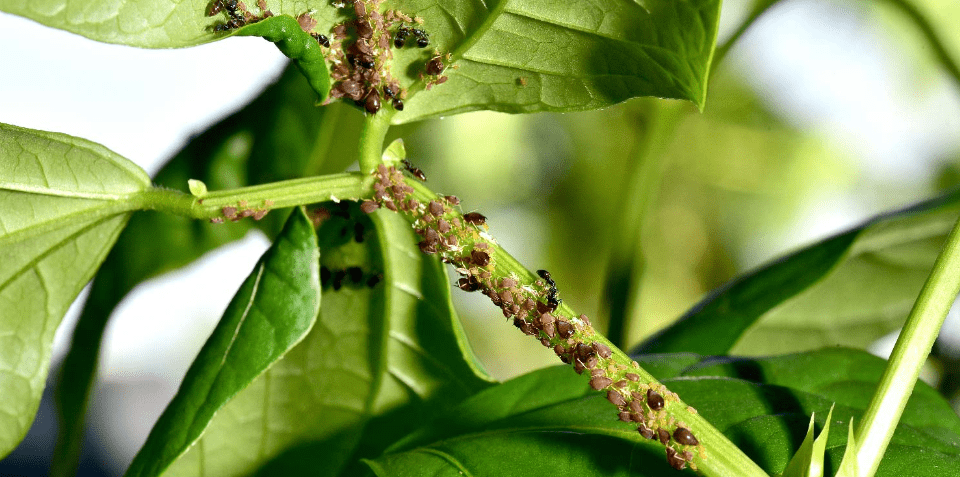

B. Organic pest control methods (e.g., companion planting, neem oil) and preventive measures.
Organic pest control methods for green beans in containers can include companion planting with plants such as marigold, which can repel pests, as well as using neem oil, which is a natural insecticide. Preventive measures such as regularly inspecting your plants, practicing good sanitation, and proper watering techniques can also help prevent pest infestations and diseases. Choosing disease-resistant varieties and rotating your crops can also be effective in reducing the risk of pests and diseases. By incorporating these organic pest control methods and preventive measures, you can help maintain the health and productivity of your container-grown green beans.
Supporting Vertical Growth (if applicable)
A. Techniques for supporting pole beans in containers: trellises, stakes, and other vertical structures.
Supporting pole beans in containers can be achieved through various techniques such as using trellises, stakes, and other vertical structures. Trellises can provide a framework for the beans to climb and grow, while stakes can offer individual support for each plant. Other vertical structures such as teepees or A-frames can also be utilized to support the upward growth of pole beans. By providing these support systems, you can help maximize space, improve air circulation, and make harvesting easier for your container-grown pole beans.
B. Benefits of vertical gardening and maximizing space utilization
Benefits of vertical gardening include maximizing space utilization. Vertical gardening can help maximize space utilization by growing plants upwards instead of outwards, making it a great solution for those with limited space. This method allows for the cultivation of a larger variety of plants in a smaller area, making the most out of available space. It also improves air circulation and sunlight exposure for the plants while minimizing pests and diseases. Additionally, vertical gardening can make it easier to harvest and maintain plants, leading to more efficient and productive gardening. Overall, vertical gardening can be a beneficial and space-saving technique for gardeners looking to make the most out of their available space.
Harvesting and Pruning
A. Signs that green beans are ready for harvest.
Signs that green beans are ready for harvest include the beans being firm and crisp, with a bright green color. They should be about the size of a pencil and snap easily when bent. It’s best to harvest green beans when they are young and tender, as they can become tough and stringy if left on the plant for too long. Regularly checking the plants for mature beans and harvesting them when they reach the appropriate size will ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season.
B. Proper harvesting techniques to promote continuous production.
Proper harvesting techniques for green beans involve gently picking the beans off the plant to avoid damaging the vines. It’s important to harvest the beans frequently, as this will stimulate the plant to produce more beans. Be sure to harvest the beans in the morning when they are at their freshest and have the highest sugar content. To promote continuous production, it’s also important to remove any overripe or damaged beans from the plant to prevent them from inhibiting new growth. Additionally, pruning the plant by removing any old or yellowing leaves can help promote new growth and encourage a higher yield of beans.
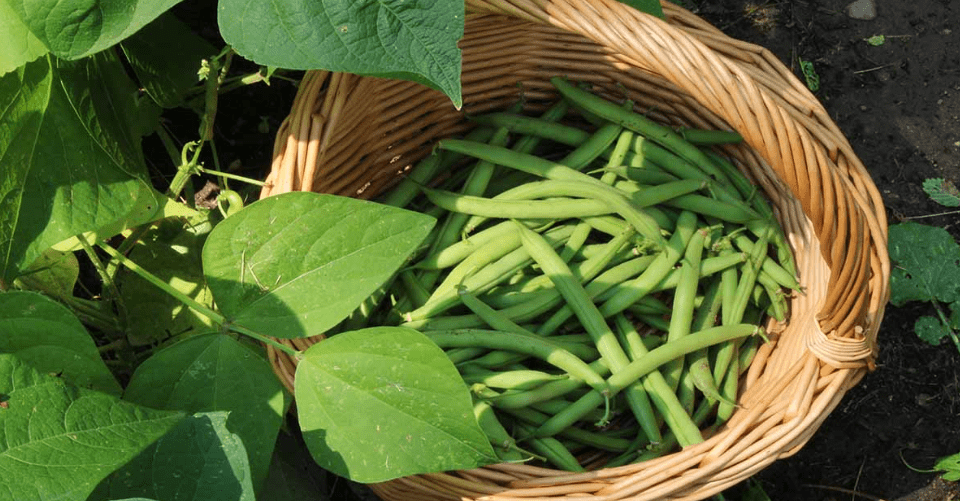

C. Importance of pruning for plant health and productivity
Pruning is important for plant health and productivity as it helps to remove old or yellowing leaves that can inhibit new growth and reduce overall yield. By pruning the plant, you are essentially directing the plant’s energy towards producing new growth and beans. This can lead to a higher yield of beans and also promotes the overall health of the plant. Additionally, pruning helps to improve air circulation and sunlight exposure, which are essential for the plant’s growth and productivity. Overall, proper pruning techniques can greatly contribute to the continuous production of green beans.
Seasonal Care and Maintenance
A. Seasonal care tips: adjusting watering and fertilization based on growth stages
During the growing season, it is important to adjust watering and fertilization based on the plant’s growth stages. In the early stages of growth, it is important to water the plants more frequently to promote strong root development. As the plants mature, you can reduce the frequency of watering, but increase the amount of water given. This will help to support the plant’s larger size and increased water needs.
Similarly, fertilization should also be adjusted based on the plant’s growth stages. In the early stages, a higher nitrogen fertilizer can be used to promote leafy growth. As the plants transition to producing beans, a fertilizer higher in phosphorus can be used to support flower and fruit development.
By adjusting watering and fertilization based on the plant’s growth stages, you can ensure that the plants are receiving the proper nutrients and support for optimal growth and productivity.
B. Overwintering considerations for perennial varieties or cold climates.
In colder climates or for perennial varieties, it’s important to consider overwintering to ensure the plants survive and thrive in the following growing season. Mulching around the base of the plants can help insulate the roots and protect them from freezing temperatures. Additionally, pruning back dead or damaged growth in the fall can help encourage healthy regrowth in the spring. Some gardeners also choose to cover their plants with a protective layer such as burlap or a frost cloth to shield them from harsh winter conditions. By taking these steps, you can help ensure that your perennial plants survive the winter and come back strong in the spring.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
A. Addressing common problems such as yellowing leaves, leggy growth, and nutrient deficiencies.
When addressing common issues in perennial plants, it’s important to identify the specific problem first. Yellowing leaves can be a sign of nutrient deficiencies, such as a lack of nitrogen, iron, or magnesium. Adding a balanced fertilizer or a specific nutrient supplement can help rectify this issue. Leggy growth, where the plant appears stretched and thin, can be a result of inadequate sunlight or overcrowding. Pruning back the plant and providing more space or moving it to a sunnier location can help encourage healthier growth. Nutrient deficiencies can also cause stunted growth or poor flowering. Testing the soil and addressing any deficiencies with the appropriate fertilizer or soil amendment can help improve the overall health of the plant. By troubleshooting these common issues, you can help your perennial plants thrive and flourish in your garden.
B. Solutions for environmental stressors (e.g., heat waves, sudden temperature drops).
To address environmental stressors such as heat waves or sudden temperature drops, providing additional shade or protection during extreme heat can help reduce the stress on the plants. Mulching around the base of the plants can also help keep the soil cooler and more stable during temperature fluctuations. Watering the plants during cooler parts of the day can help prevent heat stress, and covering plants during sudden temperature drops can protect them from damage. Additionally, selecting plant varieties that are more tolerant of extreme temperatures can help mitigate the impact of environmental stressors on your garden. By taking these proactive measures, you can help your perennial plants withstand and recover from environmental challenges.
In conclusion, growing green beans in containers is a great option for those with limited garden space. By following the tips and techniques provided in this post, you can successfully grow green beans and enjoy a bountiful harvest. Remember to choose the right containers, provide proper care and maintenance, and watch your green beans thrive in a compact garden space. Happy gardening!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, green beans can be successfully grown in containers, making them a great option for those with limited garden space.
Choose a container that is at least 8-12 inches deep and has good drainage. You can use plastic or ceramic pots, or even repurpose items like buckets or crates.
Use a well-draining potting mix that is rich in organic matter. Avoid using garden soil, as it can become compacted in containers.
Green beans should be watered regularly, especially during hot and dry weather. Check the soil moisture with your finger and water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
Yes, green beans are climbing plants and will benefit from a trellis, stakes, or a tomato cage for support. This will help prevent the plants from becoming tangled and make harvesting easier.
Yes, green beans can be grown indoors in containers as long as they receive plenty of sunlight, at least 6-8 hours per day.
Green beans typically take 50-60 days to reach maturity and be ready for harvest.
Green beans can be grown alongside other container-friendly vegetables, such as lettuce, radishes, or herbs. Just make sure the container is large enough to accommodate the different plants’ root systems.
