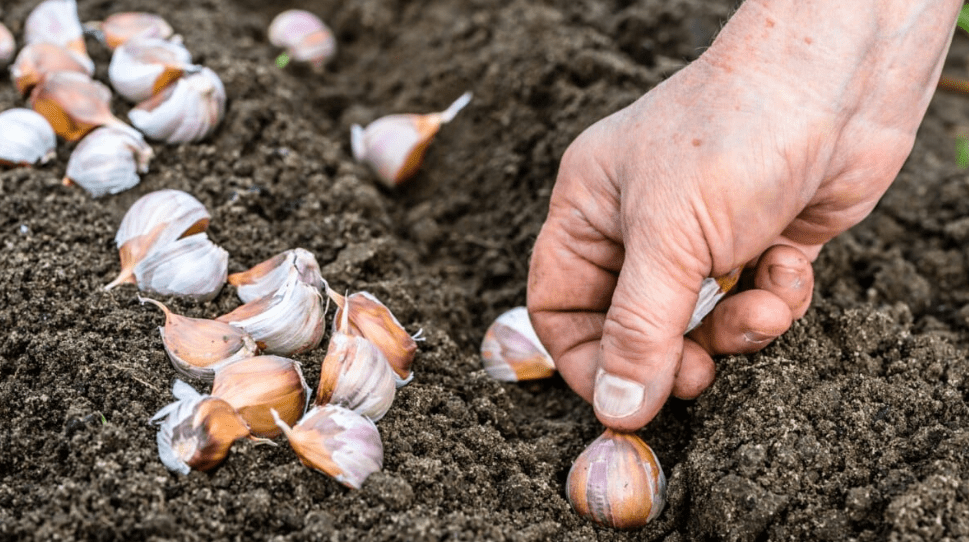

Autumn Planting Garlic: Essential Tips for a Successful Harvest
Garlic is a versatile and flavorful addition to any garden, and planting it in the autumn can lead to a successful harvest the following summer. In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know to ensure that your autumn planting garlic is a success. From selecting the right garlic variety to preparing the soil and caring for your crop, we’ll provide you with essential tips and techniques to help you achieve a bountiful harvest. So, if you’re ready to learn how to plant garlic like a pro, keep reading to discover our top tips for a successful autumn garlic harvest.
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing Garlic Varieties
A. Overview of different garlic types: hardneck, softneck, and elephant garlic.
When choosing garlic varieties, it’s important to consider the unique characteristics of each type. Hardneck garlic varieties tend to have a stronger flavor and are better suited to colder climates, while softneck varieties have a milder taste and are more adaptable to a wider range of growing conditions. Elephant garlic, although not a true garlic, has a mild, sweet flavor and produces large, easy-to-peel cloves. By selecting the right garlic variety for your garden, you can ensure that your plants thrive and produce a successful harvest.

Preparing the Planting Site
A. Soil preparation: optimal pH, drainage, and soil structure.
When preparing the planting site for garlic, it’s important to focus on soil preparation. Garlic grows best in well-drained soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. It’s also important to ensure that the soil has good structure, as garlic bulbs need room to grow and expand. Adding organic matter such as compost or aged manure can help improve soil structure and provide essential nutrients for the garlic plants. By taking the time to properly prepare the planting site, you can create the ideal growing conditions for your garlic crop.
Garlic Planting Techniques
A. Step-by-step guide to planting garlic cloves: depth, spacing, and orientation
When planting garlic cloves, it’s important to follow certain techniques to ensure optimal growth. Start by selecting healthy, large cloves from the garlic bulb. Plant the cloves about 2 inches deep and 4-6 inches apart, with the pointed end facing up and the flat end down. This orientation will encourage proper root development and bulb formation. Space the rows about 12 inches apart to allow for adequate air circulation. After planting, cover the cloves with soil and apply a layer of mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds. Following these techniques will help ensure successful garlic growth and a bountiful harvest.
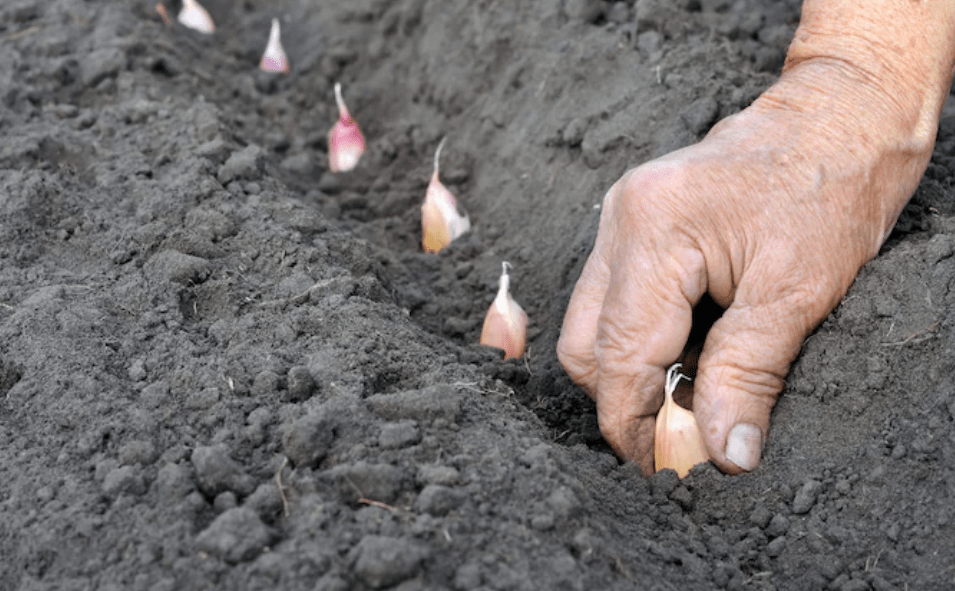

B. Mulching options to regulate soil temperature and moisture levels.
Mulching is a great way to regulate soil temperature and moisture levels for your garlic crop. You can use a variety of materials for mulching, such as straw, hay, or leaves. Applying a layer of mulch over the planted garlic cloves can help retain moisture in the soil and suppress weed growth. This can be especially beneficial during dry periods or in areas with fluctuating temperatures. In addition, mulching can also provide a barrier against extreme temperature changes, which can impact the growth and development of garlic bulbs. Overall, using mulch as a part of your garlic planting process can contribute to a healthier and more successful harvest.
Fertilizing and Nutrient Management
A. Understanding garlic’s nutrient requirements during different growth stages.
Understanding garlic’s nutrient requirements during different growth stages is essential for ensuring a healthy and successful crop. Garlic has specific needs at different points in its growth cycle, and understanding these requirements can help you effectively manage fertilization and nutrient application. For example, during the initial growth stage, garlic benefits from a higher nitrogen content to support leaf and stem development. As the plant matures and begins bulb formation, potassium becomes more important for promoting healthy bulb development. Additionally, ensuring adequate levels of phosphorus throughout the growth cycle can support overall plant health and vigor. By understanding these nutrient needs and implementing a targeted fertilization and nutrient management plan, you can optimize the growth and yield of your garlic crop.
B. Types of fertilizers: organic vs. synthetic options.
When it comes to choosing fertilizers, there are organic and synthetic options to consider. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources such as compost, manure, and other plant and animal materials. They release nutrients slowly and also improve soil structure and water retention. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are manufactured to provide specific nutrients in precise concentrations. They release nutrients quickly and are often used for targeted applications to address specific deficiencies.
Ultimately, the choice between organic and synthetic fertilizers depends on your specific farming practices, soil conditions, and environmental concerns. By understanding the nutrient needs of garlic and considering the pros and cons of different types of fertilizers, you can effectively manage fertilization and nutrient application to optimize the growth and yield of your garlic crop.
C. Application timing and methods to promote healthy bulb development.
When it comes to promoting healthy bulb development in garlic, the timing and method of fertilizer application are important considerations. Both organic and synthetic fertilizers can be effective, but the timing and method of application can vary.
For organic fertilizers, it’s important to apply them well in advance of planting to allow time for the nutrients to break down and become available to the garlic plants. This can be done by incorporating compost or well-rotted manure into the soil several weeks before planting. In addition, side dressing with organic fertilizers during the growing season can provide a continuous source of nutrients to support bulb development.
Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, can be applied at planting or during the growing season as needed. They release nutrients quickly, so it’s important to use them judiciously and follow the recommended application rates to prevent over-fertilization.
In terms of application methods, both organic and synthetic fertilizers can be applied through broadcasting, banding, or as a foliar spray. Banding or side dressing fertilizers near the base of the garlic plants can ensure that the nutrients are available where they are needed most for bulb development.
Ultimately, the key to promoting healthy bulb development in garlic is to understand the nutrient needs of the crop and to apply fertilizers at the right time and in the right way to optimize growth and yield. By considering the specific needs of your garlic crop and the advantages and disadvantages of different fertilizers, you can effectively manage nutrient application to support healthy bulb development.
Managing Weeds and Pests
A. Common weeds that compete with garlic and strategies for weed control.
Common weeds that compete with garlic include grasses, broadleaf weeds, and perennial weeds such as quackgrass and wild garlic. To control weeds, it is important to implement cultural practices such as proper crop rotation and spacing, mulching, and timely cultivation. Additionally, applying pre-emergent herbicides before the garlic emerges and post-emergent herbicides during the growing season can help manage weed competition. It is important to carefully follow label instructions when using herbicides to avoid damage to the garlic plants.
B. Common pests that affect garlic and strategies for pest control.
Common pests that affect garlic include onion thrips, nematodes, aphids, and various diseases such as white rot and downy mildew. To control pests, it is important to implement integrated pest management practices, which may include using pest-resistant varieties, crop rotation, and the use of beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings. Additionally, applying insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils can help manage pest populations. It is important to monitor the garlic crop regularly for signs of pest infestation and to take appropriate action to prevent damage to the plants.

C. Companion planting for natural pest deterrents and beneficial insect attraction.
Companion planting is a great way to naturally deter pests and attract beneficial insects to your garlic crop. Some common companion plants for garlic include marigolds, chives, and alliums, which can help repel pests such as aphids and nematodes. Other beneficial companion plants include dill, fennel, and yarrow, which attract beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps that prey on garlic pests. Planting these companion plants alongside your garlic can help create a more balanced ecosystem and reduce the need for chemical pest control methods. Additionally, intercropping with other crops such as beans and peas can also help deter pests and improve overall garden health.
Caring for Growing Garlic
A. Monitoring garlic growth: signs of nutrient deficiencies and adjustments.
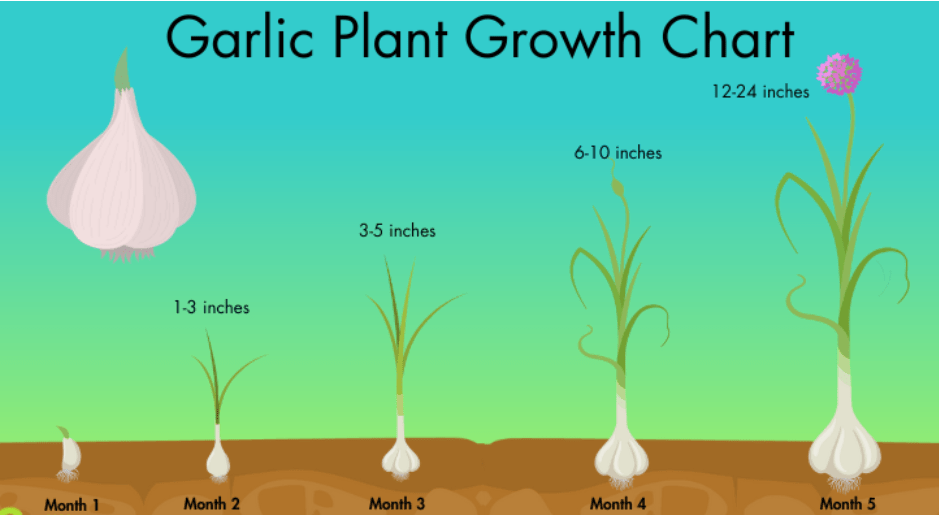
Monitoring the growth of your garlic plants is important for identifying any signs of nutrient deficiencies and making necessary adjustments. Common signs of nutrient deficiencies in garlic include yellowing or browning of the leaves, stunted growth, and poor bulb development. To address nutrient deficiencies, you can conduct a soil test to determine the specific nutrients that may be lacking in your soil. Based on the results, you can then make appropriate adjustments by adding organic fertilizers or soil amendments to improve the nutrient content of the soil. It’s also important to regularly monitor the moisture levels of the soil and ensure that the garlic plants are receiving adequate water and sunlight for healthy growth. By paying close attention to the growth of your garlic plants and addressing any nutrient deficiencies early on, you can promote robust and healthy garlic crops.
B. Proper watering practices throughout the growing season.
Proper watering practices throughout the growing season are essential for the health and growth of garlic plants. Garlic plants require consistent moisture to thrive, but overwatering can lead to issues such as root rot. It’s important to water the plants deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering sessions. This helps promote robust root growth and prevents waterlogged conditions. Additionally, it’s important to water the plants at the base to avoid wetting the foliage, which can lead to fungal diseases. Monitoring the moisture levels of the soil and adjusting your watering schedule based on weather conditions and plant needs will help ensure healthy garlic growth throughout the growing season.
C. Pruning scapes (if applicable) to enhance bulb development.
Pruning scapes is an important practice for promoting maximum bulb development in garlic plants. Scapes are the curly, flower-bearing stems that can emerge from hardneck garlic varieties. By removing the scapes, the plant’s energy is redirected from flower production to bulb growth, resulting in larger and more flavorful garlic bulbs. It’s best to prune the scapes when they have formed a couple of loops or curls, but before they straighten out. Simply snip off the scapes with a pair of garden shears, being careful not to damage the surrounding foliage. By incorporating this practice into your garlic growing routine, you can help ensure a bountiful harvest of well-developed garlic bulbs.
Harvesting Garlic
A. Signs that garlic is ready for harvest: leaf color and bulb size.
When it comes to growing garlic, pruning scapes is a crucial step in maximizing bulb development. Scapes are the curly, flower-bearing stems that can emerge from hardneck garlic varieties. By removing these scapes, you redirect the plant’s energy from flower production to bulb growth, resulting in larger and more flavorful garlic bulbs. It’s best to prune the scapes when they have formed a couple of loops or curls, but before they straighten out. To do this, simply snip off the scapes with a pair of garden shears, being careful not to damage the surrounding foliage. By making this a part of your garlic growing routine, you can help ensure a bountiful harvest of well-developed garlic bulbs. As for signs that garlic is ready for harvest, you can look at the leaf color and bulb size to determine when the garlic is mature and ready to be harvested.
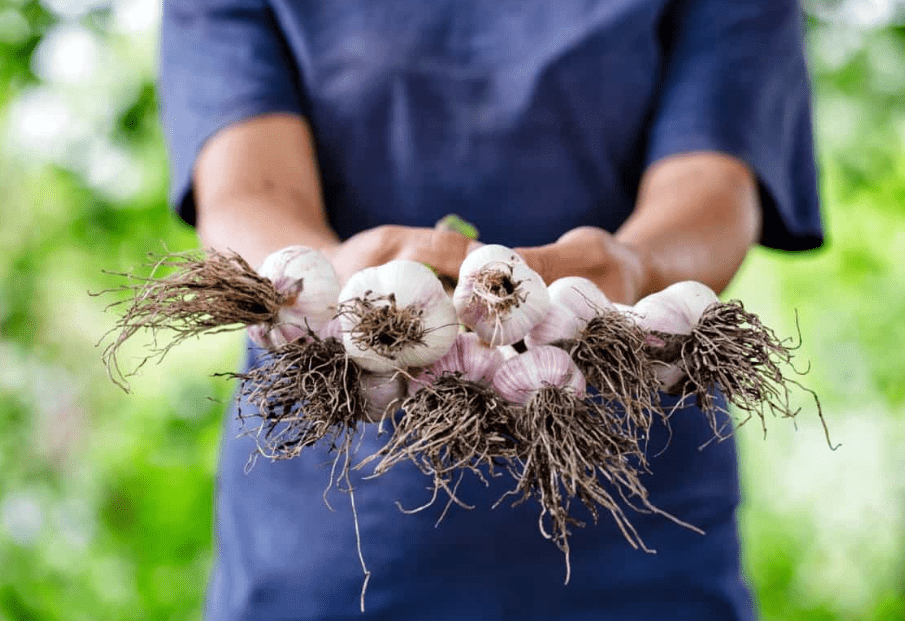
B. Techniques for harvesting, curing, and storing garlic bulbs.
When it comes to harvesting, curing, and storing garlic bulbs, there are a few techniques to keep in mind. First, it’s important to harvest garlic when the lower leaves have turned brown but there are still a few green leaves at the top. To do this, gently loosen the soil around the bulbs with a garden fork and carefully lift them out of the ground.
After harvesting, it’s crucial to cure the garlic to improve its flavor and storage life. To do this, hang the bulbs in a warm, well-ventilated area, out of direct sunlight, for 2-3 weeks. Once the outer skins are dry and the roots are brittle, the garlic is ready for storage.
For long-term storage, it’s best to keep the garlic in a cool, dark, and dry place with good air circulation. Storing the bulbs in a mesh bag or a well-ventilated container will help prevent them from sprouting or rotting.
By following these techniques, you can ensure that your garlic bulbs will keep well and maintain their delicious flavor for several months.

C. Long-term storage options: ideal temperatures and humidity levels.
For long-term storage, it’s best to keep the garlic in a cool, dark, and dry place with good air circulation. Storing the bulbs in a mesh bag or a well-ventilated container will help prevent them from sprouting or rotting. Ideal temperatures for long-term storage range from 60-65°F (15-18°C) with a relative humidity of 60-70%. By following these techniques, you can ensure that your garlic bulbs will keep well and maintain their delicious flavor for several months.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
A. Addressing garlic diseases: fungal infections, rot, and blight.
When it comes to addressing garlic diseases such as fungal infections, rot, and blight, it’s important to take preventive measures to protect your garlic crop. Planting garlic in well-drained soil, rotating crops, and spacing plants properly can help prevent fungal infections and rot. Additionally, keeping the garden free of weeds and debris can also reduce the risk of blight. If you notice any signs of disease, promptly remove and dispose of any affected plants to prevent the spread of the infection. Using organic fungicides and practicing good garden hygiene can also help manage and prevent garlic diseases. It’s important to stay vigilant and take proactive measures to keep your garlic crop healthy and disease-free.
B. Solutions for environmental stressors (e.g., extreme temperatures, inconsistent watering).
When it comes to addressing environmental stressors for garlic, such as extreme temperatures and inconsistent watering, there are several solutions that can help protect your crop.
To mitigate the impact of extreme temperatures, consider using mulch to insulate the soil and regulate temperature, as well as providing shade for your garlic plants during periods of intense heat. Additionally, planting garlic in well-drained soil can help prevent waterlogging during periods of heavy rain, and proper irrigation practices can help ensure consistent watering during dry spells.
Using shade cloth or row covers can also provide protection from extreme temperatures and fluctuations in weather. It’s important to monitor weather patterns and adjust your gardening practices accordingly to protect your garlic crop from environmental stressors. By being proactive and mindful of environmental conditions, you can help your garlic plants thrive and overcome potential challenges.
Seasonal Considerations
A. Special considerations for overwintering garlic in colder climates.
When overwintering garlic in colder climates, it’s important to properly prepare and protect your crop for the harsh winter conditions. One key consideration is to plant your garlic cloves in well-drained soil before the first frost, as waterlogged soil can lead to rot and other issues during the winter months. Additionally, applying a layer of mulch over the garlic bed can help insulate the soil and protect the bulbs from extreme cold. It’s also important to monitor moisture levels and provide supplemental watering if necessary, as winter winds and dry air can dehydrate the soil. Finally, consider using row covers or other protective measures to shield your garlic from snow, ice, and fluctuating temperatures. By taking these precautions, you can help ensure the successful overwintering of your garlic crop in colder climates.
Benefits of Growing Garlic
A. Nutritional benefits and culinary uses of homegrown garlic.
Growing garlic at home can provide a range of nutritional benefits and culinary uses. Freshly harvested garlic has a higher concentration of essential oils and nutrients compared to store-bought garlic, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Garlic is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties, and can be used in a variety of dishes to enhance flavor and provide health benefits. Whether it’s used in salads, soups, stir-fries, or as a seasoning for meat and vegetables, homegrown garlic adds a rich and aromatic flavor to a wide range of recipes. Plus, growing your own garlic allows you to have a ready supply on hand, ensuring that you always have access to this versatile and nutritious ingredient.
B. Economic benefits: cost savings and self-sufficiency.
Growing garlic at home can also provide economic benefits in terms of cost savings and self-sufficiency. By cultivating your own garlic, you can save money on buying it from the store and have a readily available supply in your own garden. This can contribute to a more sustainable and self-sufficient lifestyle, as you can rely on your own garlic harvest rather than purchasing it from external sources. Additionally, growing your own garlic can also be a cost-effective way to ensure that you have a fresh and nutritious ingredient on hand, while reducing your reliance on commercial produce. Overall, growing garlic at home can offer both nutritional and economic benefits, making it a valuable addition to any home garden.
In conclusion, planting garlic in the autumn requires careful attention to detail and proper preparation of the soil. Choosing the right variety of garlic and providing the necessary care throughout the growing season are essential for a successful harvest. By following these essential tips and techniques, you can ensure that your autumn-planted garlic crop thrives and yields a bountiful harvest. Happy planting!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Garlic should be planted in the fall, ideally about 6-8 weeks before the ground freezes. This allows the garlic to establish roots before winter sets in.
Garlic grows best in well-drained, fertile soil with a pH level of 6.0 and 7.0. Adding organic matter such as compost can help improve the soil quality.
Plant the garlic cloves about 2 inches deep, with the pointed end facing up. Space the cloves about 4-6 inches apart in rows that are 12-18 inches apart.
It’s important to water the garlic after planting to help the cloves establish roots. However, be careful not to overwater, as garlic doesn’t like to sit in wet soil.
Mulching the garlic bed with straw or leaves can help insulate the soil and protect the garlic from extreme temperature fluctuations during the winter.
Garlic is typically ready to harvest in late spring or early summer, once the leaves have turned yellow and started to dry out. It’s important to harvest the garlic before the bulbs split open.
Yes, you can save the largest and healthiest cloves from your harvest to plant the following year. Just be sure to store them in a cool, dry place until it’s time to plant them.
Garlic is relatively low-maintenance, but it can be susceptible to pests like aphids and diseases like white rot. Proper crop rotation and good garden hygiene can help prevent these issue
