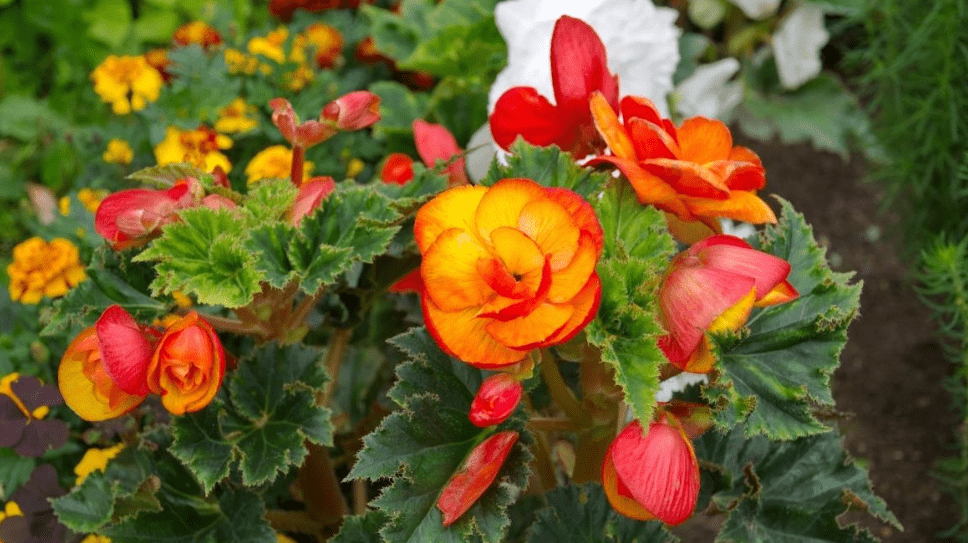

Begonias Perennials: How to Grow and Care for These Stunning Plants
Begonias are a beautiful and popular choice for gardeners looking to add color and vibrancy to their outdoor spaces. In this post, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to grow and care for begonias, including tips on soil, watering, and sunlight requirements. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will help you keep these stunning plants thriving in your garden year after year. So, let’s dive in and learn how to cultivate and care for begonias perennials in your garden.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Begonias as Perennials
A. Definition and characteristics of perennial begonias
Begonias are perennial plants, meaning they can live for more than two years. They are known for their beautiful, vibrant flowers and their ability to thrive in both indoor and outdoor environments. Perennial begonias come in various types, including tuberous begonias, wax begonias, and rex begonias, each with their own unique characteristics and growing requirements. These plants are a popular choice for gardeners due to their long-lasting blooms and low maintenance needs.
B. Types of perennial begonias
1. Hardy begonias
Hardy begonias are a type of perennial begonia that are known for their ability to survive in colder climates. They are often used as ground cover or in shaded areas of the garden.
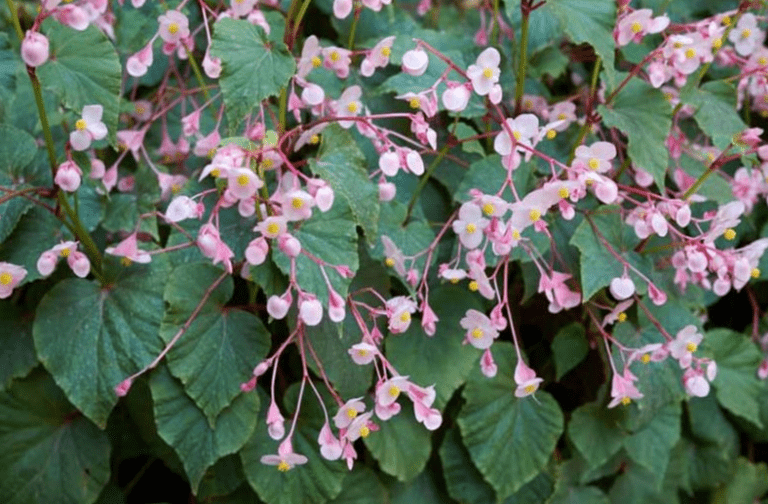

2. Tuberous begonias
Tuberous begonias have large, showy flowers and are often grown in containers or hanging baskets. They require well-drained soil and protection from direct sunlight.
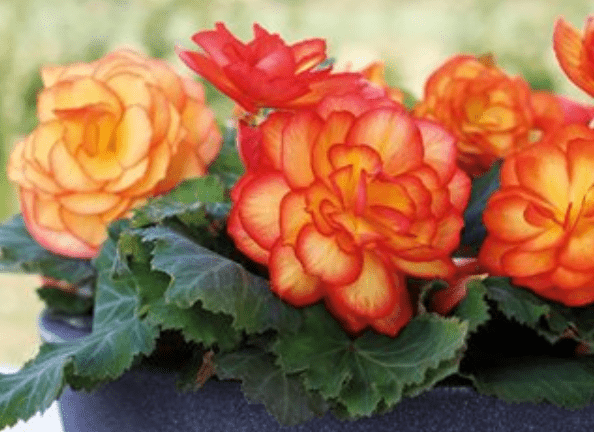

3. Wax begonias
Wax begonias, also known as bedding begonias, are popular for their low maintenance and ability to bloom in full sun or partial shade. They are often used as edging plants or in mass plantings.
4. Rex begonias
Rex begonias are known for their colorful and patterned leaves, making them a popular choice for indoor plants. They require high humidity and indirect sunlight.
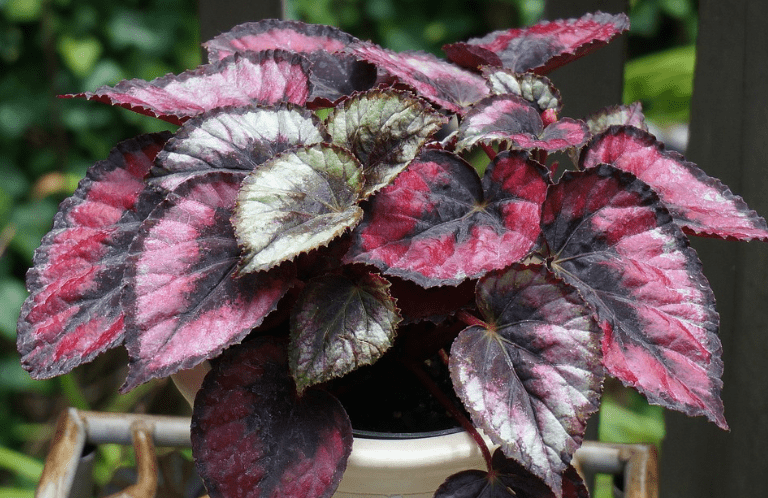

Overall, perennial begonias are a versatile and beautiful addition to any garden, providing long-lasting blooms and a range of options for different growing conditions.
Choosing the Right Begonia Varieties
A. Factors to consider when selecting begonias
1. Climate compatibility
When selecting begonias, it’s important to consider climate compatibility. Perennial begonias are best suited for mild climates in hardiness zones 6-11. They thrive in well-drained soil and prefer protection from direct sunlight. It’s important to choose begonia varieties that are suitable for the specific growing conditions in your garden to ensure their success and longevity.
2. Sunlight requirements
Another factor to consider when selecting begonias is their sunlight requirements. Some begonia varieties prefer shade or partial shade, while others can tolerate full sun. It’s important to choose begonias that are compatible with the amount of sunlight available in your garden to ensure their healthy growth and development.
3. Soil preferences
Begonias have specific soil preferences that should be taken into consideration when selecting them for your garden. They thrive in well-drained, rich soil that is slightly acidic. It’s important to choose begonias that are compatible with the soil conditions in your garden to ensure their optimal growth and health. Adding organic matter to the soil can also help improve its texture and fertility for begonias.
4. Size and growth habit
When selecting begonias for your garden, it’s important to consider their size and growth habit. Some begonia varieties are compact and low-growing, making them suitable for borders and containers, while others are larger and more upright, ideal for filling in larger spaces in the garden. It’s important to choose begonias that are the right size and growth habit for the area in which you plan to plant them to ensure a visually pleasing and well-balanced garden.
B. Popular varieties of perennial begonias
Popular varieties of perennial begonias are include tuberous, rex, and semperflorens begonias. Tuberous begonias are known for their showy, brightly colored flowers and are often grown in containers or hanging baskets. Rex begonias have uniquely patterned foliage and are prized for their ornamental value. Semperflorens begonias, also known as wax begonias, are popular for their long-lasting blooms and are often used as bedding plants or in mass plantings. Each variety has its own unique characteristics and can bring a different look and feel to your garden.
Planting Begonias
A. Best time to plant begonias
The best time to plant begonias varies depending on the variety. Tuberous begonias are typically planted in the spring after the last frost, while rex begonias can be planted in the spring or fall. Semperflorens begonias are best planted in the spring after the danger of frost has passed. It’s important to choose the right time to plant based on the specific needs of the variety you are working with.
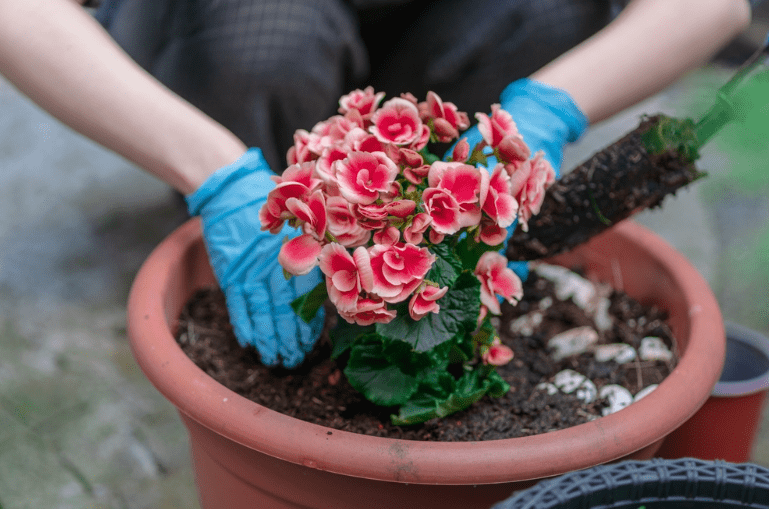

B. Site selection
When planting begonias, it’s important to choose a site that meets the specific needs of the variety you are working with. Most begonias prefer partial shade, although some varieties can tolerate full sun. It’s important to choose a site with well-drained soil and good air circulation to prevent disease. Consider the specific light and soil requirements of the begonia variety you are planting to ensure its success in your garden.
C. Step-by-step planting guide
Step 1: Choose a site with the right light and soil conditions for the begonia variety you are planting.
Step 2: Prepare the soil by adding organic matter and ensuring good drainage.
Step 3: Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball of the begonia.
Step 4: Gently remove the begonia from its container and place it in the hole, making sure the top of the root ball is level with the surface of the soil.
Step 5: Backfill the hole with soil and gently pat it down to remove any air pockets.
Step 6: Water the begonia thoroughly after planting.
Step 7: Provide ongoing care and maintenance based on the specific needs of the begonia variety, including watering, fertilization, and pest control.
Care and Maintenance
A. Watering guidelines
Begonias prefer moist, well-drained soil. Water the plants consistently, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. Be sure to water the plants at the base to avoid getting the foliage wet, which can lead to disease. In general, begonias need about 1 inch of water per week, but this can vary depending on the specific variety and the climate in which they are grown. Be sure to adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
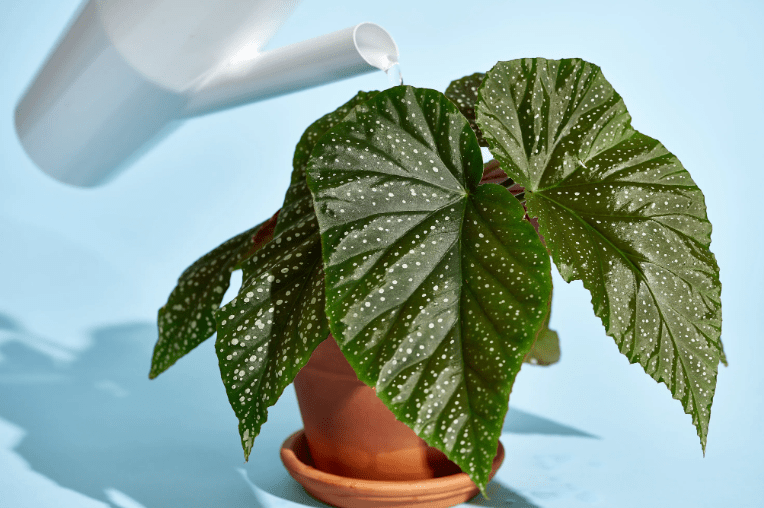

B. Fertilizing begonias
It is important to fertilize begonias regularly to promote healthy growth and abundant blooms. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer with a formula such as 10-10-10 or 20-20-20, and apply it every 2-4 weeks during the growing season. Be sure to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for proper dilution and application. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of blooms. Stop fertilizing in the fall as the plants enter dormancy.
C. Pruning and deadheading
Pruning and deadheading are important maintenance tasks for keeping begonias looking their best. Deadheading, or removing spent blooms, encourages the plant to produce more flowers and prevents the plant from putting energy into seed production. Pruning helps to shape the plant and remove any dead or diseased growth. Use clean and sharp pruners to make clean cuts, and be sure to remove any yellowing or brown leaves as well. Prune and deadhead as needed throughout the growing season to keep begonias healthy and tidy.
Managing Pests and Diseases
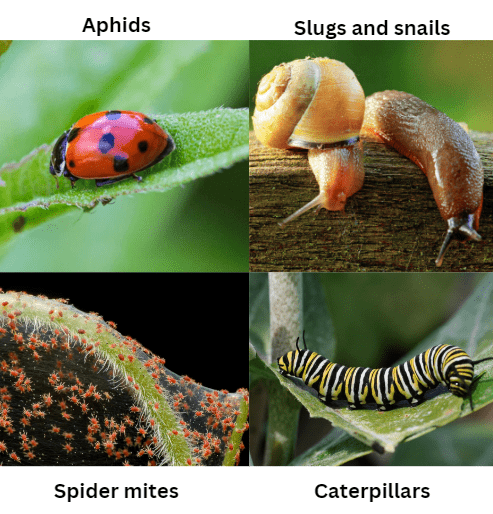
A. Common pests affecting begonias
Common pests that can affect begonias include aphids, mites, caterpillars, and slugs. These pests can damage the foliage and flowers of the plant if left untreated. It’s important to regularly inspect your begonias for any signs of pest infestation and take appropriate measures to control and eliminate them. This can include using insecticidal soaps, neem oil, or natural predators like ladybugs to manage pests. Additionally, practicing good garden hygiene, such as removing any debris or weeds that can harbor pests, can help prevent infestations. Be sure to monitor your begonias for any signs of disease as well, such as powdery mildew or botrytis, and take necessary steps to treat and prevent these issues. By proactively managing pests and diseases, you can help ensure the health and vitality of your begonias.
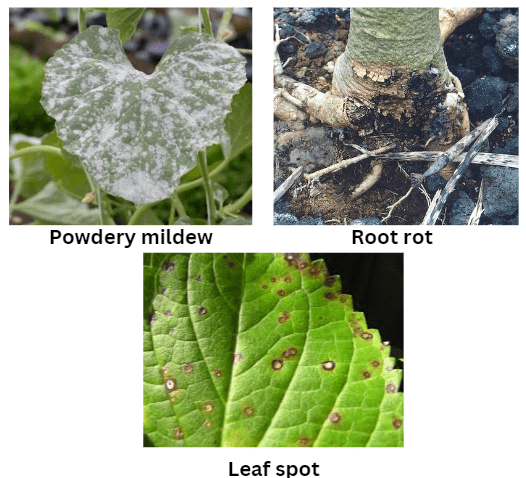
B. Common diseases in begonias
Common diseases include powdery mildew, botrytis, and bacterial leaf spot. It is important to regularly inspect your begonias for any signs of these diseases and take appropriate steps to treat and prevent them. This can include using fungicides, practicing good garden hygiene, and ensuring proper air circulation and watering practices. By being proactive in managing both pests and diseases, you can help keep your begonias healthy and thriving.
C. Organic and chemical control methods
Organic control methods for managing pests and diseases in begonias include using natural predators and beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, to control pest populations. You can also use organic sprays and botanical oils to treat and prevent diseases. Chemical control methods, on the other hand, involve using synthetic pesticides and fungicides to manage pests and diseases. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions on any chemical products and to use them sparingly to minimize potential harm to beneficial insects and the environment. Ultimately, the best approach to managing pests and diseases in begonias will depend on your specific situation and preferences for organic or chemical treatments.
Overwintering Perennial Begonias
A. Preparing begonias for winter
Preparing begonias for winter involves cutting back the foliage and storing the tubers or rhizomes in a cool, dry location. You can also bring potted begonias indoors before the first frost and place them in a sunny spot. Additionally, it’s important to mulch the soil around outdoor begonias to protect the roots from freezing temperatures. It’s important to monitor the temperature and humidity levels to ensure the begonias survive the winter dormant period and can thrive again in the spring.
B. Indoor overwintering techniques
Indoor overwintering techniques for begonias involve bringing potted begonias indoors before the first frost and placing them in a sunny spot. Make sure to water the begonias sparingly during the winter months and avoid overwatering. Keep an eye on the temperature and humidity levels to ensure the begonias stay healthy and dormant during the winter. You can also consider treating the begonias with a fungicide or insecticide before bringing them indoors to prevent any pests or diseases from spreading. Ultimately, the best approach to overwintering perennial begonias will depend on your specific situation and preferences.
C. Replanting in spring
In the spring, when the danger of frost has passed, you can replant your overwintered begonias outdoors. Make sure to gradually acclimate them to the outdoor conditions by exposing them to sunlight and increasing their time outside over the course of a few days. Before replanting, you may want to prune any dead or leggy growth and refresh the soil in the pots. When selecting a location for replanting, choose a spot with well-draining soil and partial shade to protect the begonias from harsh sun exposure. Water the newly planted begonias thoroughly and continue to monitor their growth and health as the spring and summer progress. With proper care and attention, your begonias should flourish and provide beautiful blooms throughout the growing season.
Propagating Begonias
A. Methods of propagation
There are a few different methods for propagating begonias. One common method is by taking leaf or stem cuttings and placing them in a moist, well-draining growing medium. Another method is by dividing the rhizomes or tubers of the begonia plant and replanting them separately. You can also propagate begonias by planting their seeds, although this method may take longer to see results. Whichever method you choose, it’s important to provide the right growing conditions, such as warmth and humidity, to encourage successful propagation. With a little patience and care, you can multiply your begonia plants and enjoy even more beautiful blooms in your garden.
B. Step-by-step propagation guide
- Taking leaf or stem cuttings: Select a healthy, mature leaf or stem from the begonia plant. Cut it at a 45-degree angle and place it in a moist, well-draining growing medium. Keep the soil consistently moist and provide indirect light.
- Dividing rhizomes or tubers: Carefully lift the begonia plant from the soil and separate the rhizomes or tubers. Replant each division separately in a new pot with fresh growing medium. Water thoroughly and provide the right growing conditions.
- Planting seeds: Collect seeds from the begonia plant and sow them in a seed-starting mix. Keep the soil consistently moist and provide warmth and indirect light to encourage germination.
Remember to monitor the progress of your propagation and provide the necessary care to ensure the success of the new begonia plants. With these methods, you can easily propagate begonias and expand your collection of these beautiful plants.
Designing with Begonias
A. Garden design ideas incorporating begonias
When designing a garden with begonias, consider their unique colors and textures to create a visually appealing display. Begonias can be used in flower beds, borders, or containers to add a pop of color and interest to your garden. They also work well in shaded areas, making them versatile for different garden designs. Additionally, begonias can be paired with other shade-loving plants to create a harmonious and eye-catching arrangement. By incorporating begonias into your garden design, you can create a beautiful and vibrant outdoor space.
B. Complementary plants and companions for begonias
When selecting companion plants for begonias, consider shade-loving options such as ferns, hostas, and impatiens. These plants thrive in similar growing conditions and can complement the colors and textures of begonias. Additionally, incorporating foliage plants like caladiums or coleus can add contrast and interest to your garden design. Consider experimenting with different combinations to find the perfect companions for your begonias. By selecting complementary plants, you can create a cohesive and visually appealing garden display.
Benefits of Growing Perennial Begonias
A. Aesthetic appeal and continuous blooms
Perennial begonias offer aesthetic appeal and continuous blooms, making them a beautiful addition to any garden. Their delicate flowers come in a variety of colors and can bloom throughout the growing season, adding vibrant pops of color to your landscape. Additionally, these plants are low-maintenance, requiring minimal care and attention once established. With their long-lasting blooms and attractive foliage, perennial begonias can enhance the visual appeal of your garden and provide long-lasting beauty.
B. Low maintenance and longevity
Perennial begonias are an excellent choice for gardeners looking for low-maintenance plants that offer long-lasting beauty. Once established, these plants require minimal care and attention, making them a great option for those with busy schedules. Additionally, the longevity of perennial begonias means you can enjoy their vibrant blooms and attractive foliage year after year, without the need for frequent replanting. This makes them a practical and visually appealing choice for any garden.
In conclusion, begonias are a beautiful addition to any garden, and with the right care, they can thrive as perennials. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this post, you can ensure that your begonias continue to bloom and bring beauty to your garden year after year. Remember to provide the right soil, water, and sunlight conditions, and you’ll have stunning begonias in your garden for seasons to come.
Yes, begonias are considered perennials in most climates, meaning they can live for several years if properly cared for.
Begonias thrive in bright, indirect light. They should be protected from direct sunlight, especially during the hottest part of the day.
Begonias prefer slightly moist soil, so it’s important to water them regularly, especially during the growing season. However, it’s important not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot.
Yes, begonias can be grown indoors as long as they receive enough light and are kept in a well-ventilated area. They can also be grown outdoors in containers or in garden beds.
Begonias benefit from regular fertilization during the growing season and may need to be pruned to maintain their shape. It’s also important to keep an eye out for pests and diseases and address any issues promptly.
Yes, begonias are relatively easy to grow and are a good choice for beginner gardeners. They are also available in a wide variety of colors and shapes, making them a popular choice for many gardeners.
Begonias can be planted in the spring after the threat of frost has passed. They can also be planted in the fall in warmer climates.
Yes, begonias can be divided and propagated by taking stem or leaf cuttings. This can be a great way to create new plants and expand your begonia collection.
