
How to Grow Delicious Cherries on Trees in Your Backyard
If you’ve ever dreamed of having your own cherry trees in your backyard, this article is for you. Growing delicious cherries at home can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience, and with the right techniques, you can have a bountiful harvest of fresh, juicy cherries right in your own backyard. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about growing cherry trees, from planting to harvesting, and we’ll provide tips and techniques to ensure your cherry trees thrive and produce an abundance of tasty fruit. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this article will help you grow delicious cherries on trees in your backyard.
Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Cherry Trees
1.Sweet Cherries (Prunus avium)
Sweet cherries are perfect for snacking and making desserts. They come in a variety of colors, including red, yellow, and black, and are typically larger and juicier than sour cherries.
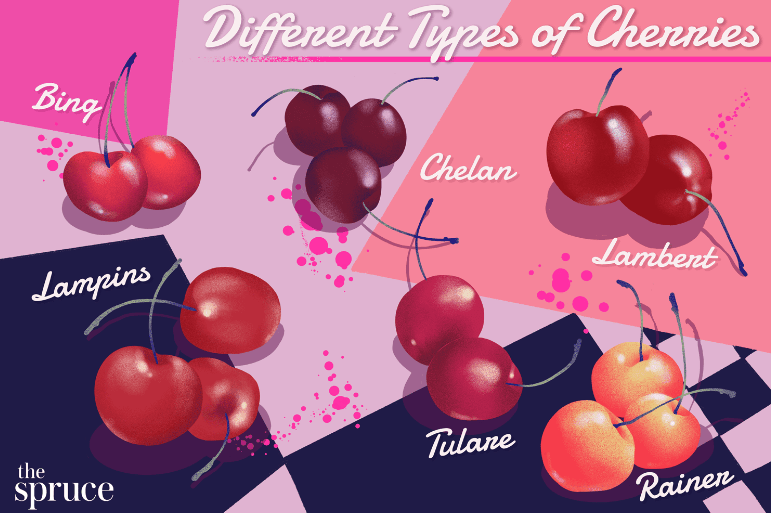
A.Popular varieties: Bing, Rainier, Lambert
Bing, Rainier, Lambert are some popular varieties of sweet cherries that are well-suited for growing in backyard gardens. These varieties are known for their delicious flavor and juicy texture, making them a popular choice for home orchards. When choosing a variety of sweet cherry tree to plant in your backyard, consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and available space in your garden. It’s also important to consider the pollination requirements of sweet cherry trees, as many varieties require a compatible pollinizer tree in order to produce fruit. With the right selection of cherry tree varieties and proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious cherries right in your own backyard.
2.Sour Cherries (Prunus cerasus)
Sour cherries are commonly used for baking and cooking. They’re smaller and tarter than sweet cherries, and they’re great for making pies, jams, and sauces.
A.Popular varieties: Montmorency, Morello
Montmorency and Morello are popular varieties of sour cherries that are often used for baking and cooking. Their tart flavor and smaller size make them perfect for making pies, jams, and sauces. When choosing a variety of sour cherry tree to plant in your backyard, consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and available space in your garden. It’s also important to consider the pollination requirements of sour cherry trees, as many varieties require a compatible pollinizer tree in order to produce fruit. With the right selection of cherry tree varieties and proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious sour cherries right in your own backyard.

Choosing the Right Cherry Tree
1.Climate and hardiness zones
When selecting cherry tree varieties, consider your climate and hardiness zone. Sour cherry trees, for example, are more cold-hardy than sweet cherry trees, so they may be better suited for colder climates.
2.Soil conditions
Consider the soil conditions in your backyard. Sour cherry trees prefer well-drained, fertile soil, so make sure your garden soil meets these requirements.
3.Available space
Consider the available space in your backyard. Sour cherry trees can grow to be quite large, so make sure you have enough space for the tree to mature and produce fruit.
4.Pollination requirements
Many sour cherry tree varieties require a compatible pollinizer tree in order to produce fruit. Be sure to plant the right combination of trees to ensure successful pollination.
With careful consideration of these factors and proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious sour cherries right in your own backyard.
Planting Cherry Trees
1.When to plant (season and timing)
Cherry trees are best planted in the early spring or late fall, when the weather is cool and the tree is dormant. This gives the tree time to establish its roots before the hot summer months.
2. Site selection and preparation
Choose a sunny location with well-drained, fertile soil for planting your cherry trees. Prepare the planting site by removing any weeds and incorporating organic matter into the soil to improve its fertility and drainage.
3. Planting technique
Dig a hole that is twice as wide and just as deep as the tree’s root ball. Place the tree in the hole, making sure the graft union is above the soil level. Fill in the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots to remove any air pockets.
4. Watering and mulching
After planting, water the tree thoroughly to help settle the soil around the roots. Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the tree to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
By selecting the right cherry tree variety and properly planting and caring for it, you can enjoy a beautiful and productive cherry tree in your own backyard.

Caring for Cherry Trees
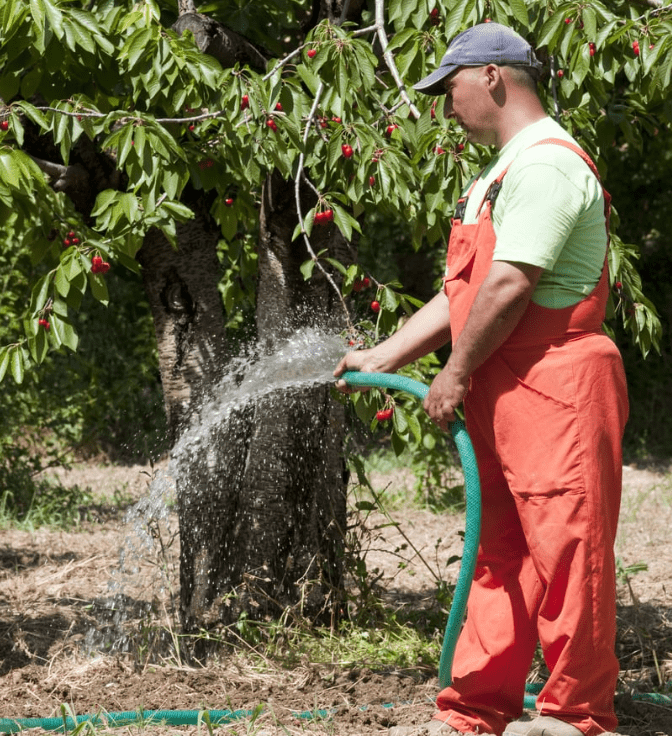
1.Watering schedules and techniques
Water young cherry trees regularly, especially during dry periods, to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Use a soaker hose or drip irrigation to deliver water directly to the root zone. As the tree matures, it will require less frequent watering but may still need supplemental irrigation during hot, dry spells.
2. Pruning and training
Prune cherry trees in late winter or early spring to remove dead or diseased branches, improve air circulation, and shape the tree for optimal fruit production. Train young trees by selecting a central leader and removing competing branches to encourage strong, upward growth.
3. Fertilizing
Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring, just as the tree begins to break dormancy. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of fruit production.
Preventing and Managing Diseases and Pests
1.Common diseases: brown rot, bacterial canker, cherry leaf spot
To prevent common cherry tree diseases such as brown rot, bacterial canker, and cherry leaf spot, practice good sanitation by removing and disposing of infected leaves and fruit. Apply fungicides and bactericides as needed, following label instructions. Proper pruning to improve air circulation can also help prevent disease.
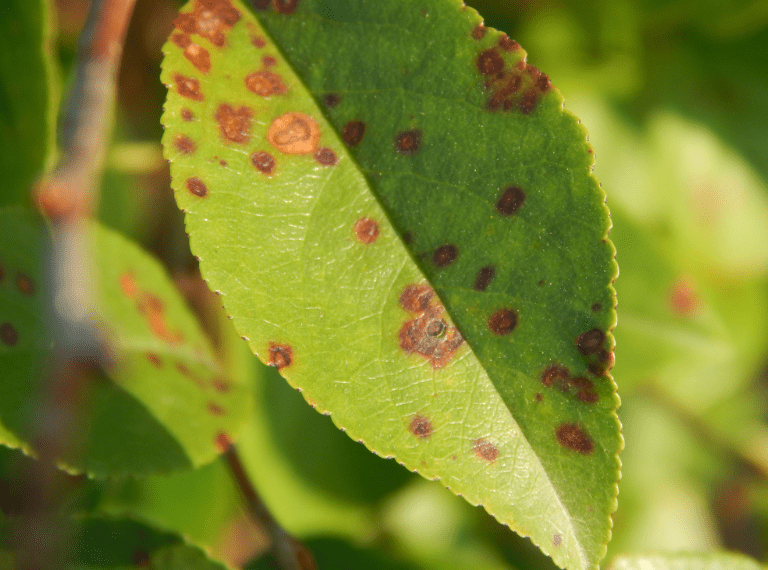

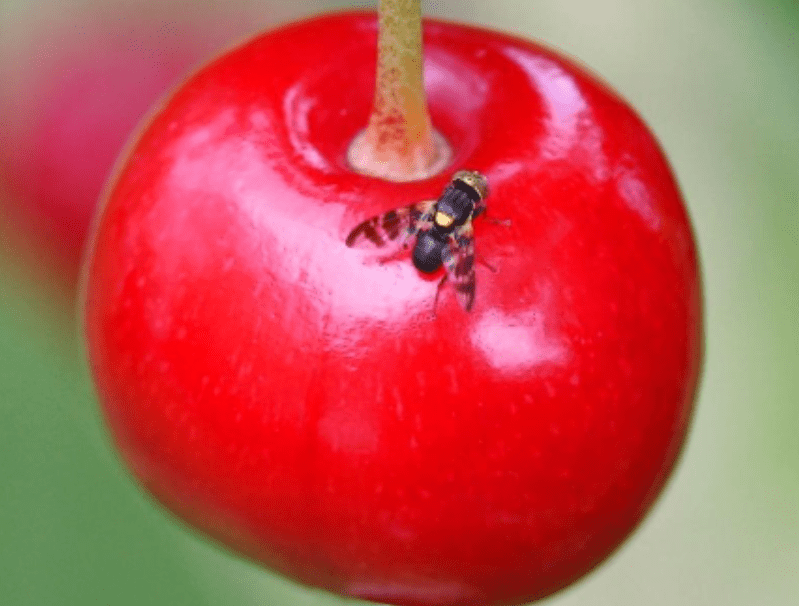
2.Common pests: aphids, cherry fruit fly, birds
To prevent common pests such as aphids, cherry fruit fly, and birds from damaging cherry trees, consider using physical barriers like netting to protect the fruit. Insecticides and repellents can also be used, following label instructions. Regular monitoring for pest activity and taking appropriate action when needed can help to manage these issues.

3.Organic vs. chemical control methods
When it comes to managing diseases and pests in cherry trees, there are both organic and chemical control methods available. Organic methods may include using natural predators, such as ladybugs, to control aphids, or using neem oil to deter pests. Additionally, maintaining healthy soil through organic fertilizers and compost can help prevent diseases. On the other hand, chemical control methods may involve using synthetic pesticides and fungicides to manage pests and diseases. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each method and consider factors such as environmental impact, effectiveness, and cost before choosing a management approach. Additionally, always follow label instructions when using any type of control method to ensure safe and effective application.
Harvesting Cherries
1.When to harvest: signs of ripeness
Cherries are typically ready for harvest when they have reached their full color and size, and their stems easily detach from the tree with a gentle twist. It’s important to regularly check the ripeness of the fruit by sampling a few cherries from different areas of the tree. The best time to harvest cherries is usually in the early morning when the fruit is cool, and the sugar content is at its highest. It’s also important to avoid harvesting cherries after rainfall, as the fruit can become watery and prone to splitting. Once harvested, cherries should be handled carefully to avoid bruising and should be stored in a cool, dry place to maintain their freshness.
2.Harvesting techniques
When harvesting cherries, it’s best to use a pair of sharp pruning shears to clip the stems of the fruit, rather than pulling them off by hand, as this can damage the fruit and the tree. It’s important to handle the cherries gently and avoid placing too much pressure on the fruit to prevent bruising. When picking the cherries, it’s also a good idea to use a basket or bucket lined with a soft material to cushion the fruit and prevent it from getting crushed. It’s important to harvest cherries carefully and efficiently to ensure the best quality fruit for storage and consumption.
3.Post-harvest handling and storage
After harvesting, it’s important to sort the cherries and remove any damaged or overripe fruit. Cherries should be stored in a cool, dry place, ideally in the refrigerator, to maintain their freshness. It’s also a good idea to store cherries in a single layer to prevent them from crushing each other. If you plan to store cherries for a longer period of time, you can also consider freezing them or preserving them in syrup or jam. Proper post-harvest handling and storage will ensure that your cherries remain fresh and delicious for as long as possible.
Benefits of Growing Cherries on Trees
1.Nutritional benefits of cherries
Cherries are a nutritious fruit, rich in antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins such as vitamin C and vitamin A. They also contain important minerals like potassium and calcium. Consuming cherries can help support overall health and wellness, including immune function and digestion. Additionally, cherries are low in calories and a good source of natural sugar, making them a healthy and delicious snack option.
2.Environmental benefits (pollinator attraction, carbon sequestration)
Cherry trees provide important environmental benefits as well. They are attractive to pollinators such as bees, which play a crucial role in the pollination of other plants in the area. Additionally, cherry trees, like all trees, help to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which can contribute to mitigating climate change. Planting and cultivating cherry trees can therefore have positive impacts on both local ecosystems and the global environment.
3.Economic benefits (home gardening, potential for small-scale farming)
Growing cherries on trees can also have economic benefits. For home gardeners, cherries can be a valuable and rewarding crop to grow, providing fresh fruit for personal consumption or for sale at local markets. Additionally, for those interested in small-scale farming, cherries can be a profitable crop, especially in areas with suitable climate and soil conditions for cherry production. Furthermore, cherries are in high demand and can fetch a good price in the market, making them a potentially lucrative option for small-scale farmers. Overall, growing cherries on trees can provide both personal and financial satisfaction.
Common Problems and Solutions
1.Poor fruit set
Poor fruit set in cherry trees can be caused by a variety of factors, such as inadequate pollination, weather conditions, or pests and diseases. To address this issue, ensuring adequate pollination by planting multiple cherry tree varieties to cross-pollinate can help increase fruit set. Additionally, providing proper irrigation and fertilization, and controlling pests and diseases through proactive management practices can also help improve fruit set in cherry trees. Consulting with local agricultural extension services or horticultural experts can provide tailored solutions for specific issues in cherry tree cultivation.
2.Leaf discoloration and drop
Leaf discoloration and drop in cherry trees can be a sign of nutrient deficiencies, pests, diseases, or environmental stress. To address this issue, it is important to regularly monitor the health of the cherry trees and address any potential problems promptly. Providing proper fertilization to ensure the trees have the necessary nutrients, and implementing pest and disease control measures can help prevent leaf discoloration and drop. It is also important to consider environmental factors such as proper watering and suitable growing conditions to minimize stress on the trees. Consulting with local experts or agricultural extension services can provide guidance on specific solutions for addressing leaf discoloration and drop in cherry trees.
3.Fruit cracking
Fruit cracking in cherry trees can be caused by fluctuations in water availability, leading to rapid fruit growth and skin splitting. To address this issue, it is important to maintain consistent and adequate watering practices, especially during dry periods, to prevent rapid changes in fruit size. Using mulch around the base of the trees can help retain soil moisture and reduce water stress on the fruit. Additionally, ensuring proper pruning and thinning of the fruit can help reduce overcrowding and pressure on the skin, minimizing the risk of cracking. Consulting with local horticultural experts or agricultural extension services can provide tailored advice for addressing fruit cracking in cherry trees.
Recipes and Uses for Homegrown Cherries
1.Fresh eating
One of the most popular and delicious ways to enjoy homegrown cherries is to simply eat them fresh. Cherries are a sweet and juicy fruit that can be enjoyed on their own as a tasty and healthy snack. They can also be added to fruit salads or used as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal for a nutritious and flavorful breakfast. Additionally, fresh cherries can be used in smoothies, added to baked goods such as muffins or scones, or incorporated into savory dishes like salads or salsas for a burst of flavor. The possibilities are endless when it comes to enjoying homegrown cherries fresh from the tree.
2.Cooking and baking (pies, jams, sauces)
Homegrown cherries can also be used in a variety of cooking and baking recipes. Cherry pies are a classic favorite, and homemade cherry jam or sauce can be a delicious addition to pastries, pancakes, or ice cream. Cherries can also be used to make a flavorful glaze for meats or added to savory dishes like pork tenderloin or chicken. When it comes to baking, cherries can be folded into batter for cakes, cupcakes, or breads, or used as a filling for turnovers or hand pies. With their sweet and tart flavor, homegrown cherries are a versatile ingredient that adds a burst of deliciousness to a wide range of recipes.
3.Preserving and canning
Preserving and canning homegrown cherries is a great way to enjoy them year-round. Cherries can be preserved by canning them in a sugar syrup or by making cherry preserves or compote. These can be enjoyed on toast, as a topping for ice cream, or as a filling for pastries. Cherries can also be frozen for future use in smoothies, baked goods, or as a topping for yogurt. By preserving and canning homegrown cherries, you can savor their delicious flavor even when they are out of season.
4.Beverage recipes (cherry juice, cocktails)
Cherries are also a versatile ingredient in beverage recipes. Cherry juice can be made at home by blending fresh cherries and straining the pulp. It can be enjoyed on its own or used as a base for cocktails, mocktails, or mixed with sparkling water for a refreshing drink. Cherries can also be muddled and used as a flavoring for cocktails, such as in a classic cherry mojito or cherry margarita. Their sweet and tangy flavor adds a unique twist to a variety of beverage recipes.

Cherry Tree Varieties for Different Regions
1.Best varieties for cold climates
In colder climates, the best cherry tree varieties to consider are Montmorency, North Star, and Balaton. These varieties are well-suited to withstand harsh winter temperatures and produce delicious tart cherries that are perfect for baking, cooking, and preserving. Their hardiness and ability to thrive in colder climates make them ideal choices for home gardeners and commercial growers in regions with harsh winter weather.
2.Best varieties for mild/warm climates
In mild or warm climates, you may want to consider varieties such as Bing, Rainier, or Stella. These varieties thrive in warmer temperatures and produce sweet, juicy cherries that are perfect for eating fresh or using in a variety of recipes. Their ability to tolerate warmer weather makes them well-suited for regions with milder or warmer climates.
3.Regional considerations and recommendations
When selecting cherry tree varieties for different regions, it’s important to consider the climate and weather conditions of your specific area. In colder climates, Montmorency, North Star, and Balaton are great choices for their ability to withstand harsh winter temperatures. In mild or warm climates, Bing, Rainier, and Stella are ideal options as they thrive in warmer temperatures. Considering regional climate and weather conditions when selecting cherry tree varieties can help ensure a successful and bountiful harvest.
In conclusion, growing cherry trees in your backyard can be a rewarding and delicious experience. By following the tips and techniques outlined in this article, you can enjoy the benefits of fresh, homegrown cherries and create a beautiful and fruitful addition to your backyard. With proper care and attention, you can have a bountiful harvest of delicious cherries to enjoy with your family and friends. Happy growing up!
Frequently Asked Question
t’s best to choose a cherry tree that is suited for your specific climate and soil conditions. Some popular varieties include Bing, Rainier, and Stella.
The best time to plant a cherry tree is in the early spring, before the tree starts to bud.
Cherry trees thrive in full sunlight, so it’s best to plant them in an area that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day.
Cherry trees require regular watering, especially during the first few years of growth. It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Yes, cherry trees should be pruned annually to remove dead or diseased branches and to promote healthy growth. It’s best to prune in late winter or early spring while the tree is still dormant.
Regularly inspect your cherry tree for signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to control them. Using organic pest control methods is recommended to avoid harmful chemicals.
Cherries are typically ready to be harvested in the early summer, around June or July, depending on the variety. They should be picked when they are fully ripe and have a deep, rich color.
Ripe cherries are firm, plump, and have a deep, dark color. They should come off the tree easily when gently pulled. If they are still hard and pale, they need more time to ripen.
