
Fertilizing Asparagus: Tips and Tricks for Healthier Plants
Asparagus is a delicious and nutritious vegetable that can thrive in your garden with the right care and attention. One crucial aspect of maintaining healthy asparagus plants is proper fertilization. In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about fertilizing asparagus, including the best fertilizers to use and expert tips for ensuring your plants grow strong and vibrant. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will help you keep your asparagus plants healthy and thriving.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Asparagus Needs
A. Growth stages of asparagus
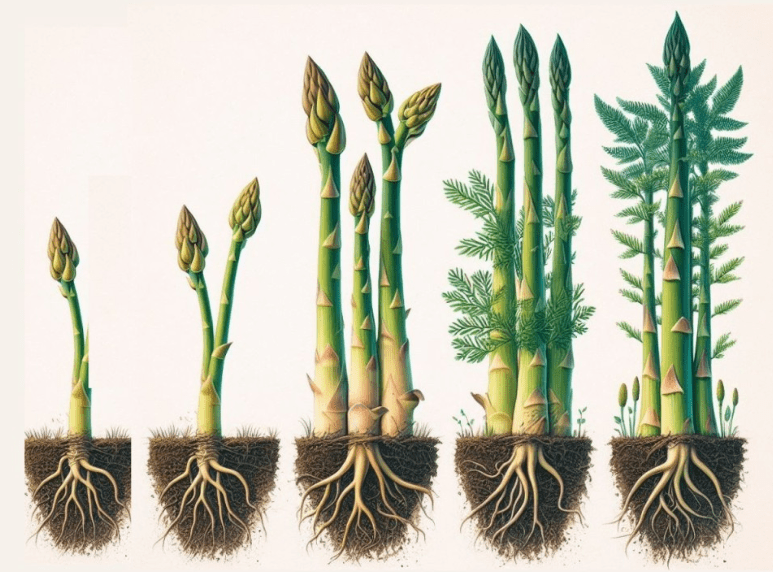
Asparagus has three main growth stages: establishment, production, and fern growth. During the establishment stage, it’s important to focus on building strong roots and healthy foliage. In the production stage, the focus shifts to developing healthy, robust spears. Finally, the fern growth stage is when the plant focuses on storing energy for the next growing season.

B. Nutrient requirements at each stage
During the establishment stage, it’s important to provide the asparagus plants with a balanced fertilizer that is high in phosphorus to promote strong root development. In the production stage, asparagus plants require a fertilizer high in nitrogen to support spear growth. Finally, during the fern growth stage, it’s important to provide a balanced fertilizer that promotes overall plant health and energy storage for the next growing season. It’s also important to ensure that the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter to support the nutrient needs of the asparagus plants throughout their growth stages.
Preparing the Soil
A. Soil testing and amendments
Before planting asparagus, it’s important to conduct a soil test to determine the pH and nutrient levels of the soil. This will help to identify any deficiencies or imbalances that need to be addressed. Based on the results of the soil test, you may need to amend the soil with lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower the pH. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can also improve the soil structure and fertility. By properly preparing the soil, you can create the ideal growing environment for your asparagus plants.

B. PH levels and adjustments
The pH level of the soil is an important factor to consider when preparing for asparagus planting. Asparagus plants prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 6.5 and 7.5. If your soil test reveals that the pH is too low (acidic), you can add lime to raise the pH. Conversely, if the pH is too high (alkaline), you can add sulfur to lower the pH. Adjusting the pH to the appropriate range will help ensure that your asparagus plants can access the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer
A. Types of fertilizers (organic vs. inorganic)
When it comes to choosing the right fertilizer for your asparagus plants, you have a couple of options to consider: organic and inorganic. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources such as compost, manure, and bone meal, and they release nutrients slowly over time. They also improve the overall soil structure and microbial activity. Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, are synthetic and release nutrients quickly. They are often more concentrated and provide a rapid boost of nutrients to the plants. Depending on your gardening preferences and the specific needs of your asparagus plants, you can choose the type of fertilizer that best suits your situation.

B. Essential nutrients for asparagus (NPK ratio)
When it comes to providing essential nutrients for your asparagus plants, it’s important to consider the NPK ratio. NPK stands for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are the three main nutrients that plants need in large quantities. For asparagus, the ideal NPK ratio is typically around 1-1-2 or 1-1-1. This means the fertilizer should have equal or slightly higher amounts of phosphorus and potassium compared to nitrogen. These nutrients are crucial for asparagus growth, root development, and overall health. By selecting a fertilizer with the appropriate NPK ratio, you can ensure that your asparagus plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and yield.
C. Recommended brands and formulations
Recommended brands and formulations may vary, so it’s best to consult with a local gardening expert or agricultural extension office to determine the best fertilizer for your specific growing conditions. It’s also important to follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging to ensure proper application and avoid over-fertilization. Remember to always water your asparagus plants after fertilizing to help the nutrients penetrate the soil and reach the roots effectively. With the right NPK ratio and proper care, you can help your asparagus plants thrive and produce a bountiful harvest
Fertilizing Asparagus: Year-by-Year Guide
A. Year 1: Establishing the Bed
In the first year of establishing an asparagus bed, it’s important to focus on preparing the soil and providing the necessary nutrients for the young plants. A balanced fertilizer with a lower nitrogen content, such as a 5-10-10 or 5-10-5 NPK ratio, can help promote strong root development and overall plant health. It’s important to avoid over-fertilization in the first year, as too much nitrogen can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of root development. Water the plants well after fertilizing to help the nutrients reach the roots effectively. It’s also important to remove any weeds or competing vegetation to give the young asparagus plants the best chance for success.
B. Year 2: Promoting Growth
In the second year, asparagus plants will need more nutrients to support their growth and development. A balanced fertilizer with a slightly higher nitrogen content, such as a 10-10-10 NPK ratio, can help promote healthy foliage and stem growth. It’s important to apply the fertilizer early in the spring before the spears emerge, and then again after the harvest to replenish the nutrients used during the growing season. Be sure to water the plants well after fertilizing to help the nutrients reach the roots and promote strong growth. It’s also important to continue removing weeds and competing vegetation to give the asparagus plants the best chance to thrive. With the right NPK ratio and proper care, you can help your asparagus plants thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
C. Year 3 and Beyond: Maintaining Productivity
In the third year and beyond, it’s important to continue providing the necessary nutrients and care to maintain the productivity of your asparagus plants. You can continue using a balanced fertilizer with a slightly higher nitrogen content to promote healthy foliage and stem growth. It’s also important to ensure that the plants receive adequate water and sunlight to support their growth. Additionally, you should continue to remove weeds and competing vegetation to give the asparagus plants the best chance to thrive. By maintaining proper care and providing the necessary nutrients, you can help your asparagus plants continue to produce a bountiful harvest for years to come.
Application Techniques
A. How to apply fertilizer (granular vs. liquid)
When applying fertilizer to your asparagus plants in their third year and beyond, you can choose between granular or liquid fertilizers. Granular fertilizers can be spread evenly around the base of the plants and then watered in, ensuring that the nutrients are released slowly over time. Liquid fertilizers, on the other hand, can be diluted with water and applied directly to the soil for faster absorption by the plants. Both methods can be effective, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your preference and the specific needs of your plants. Whichever method you choose, make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and frequency to ensure that your asparagus plants receive the proper nutrients for continued productivity.
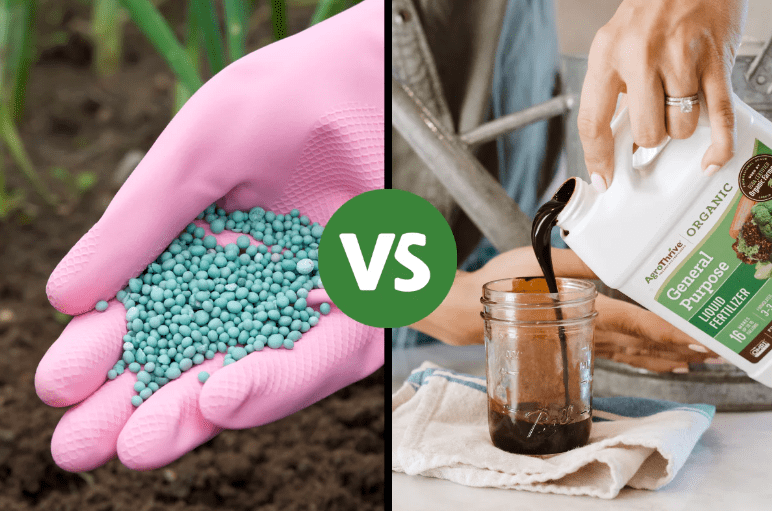
B. Timing and frequency of applications
Granular fertilizer is usually applied once or twice a year, typically in the spring and summer. However, it’s important to spread it evenly and avoid over-application to prevent burning the plants. Liquid fertilizers, on the other hand, can be applied more frequently, typically every 2-4 weeks during the growing season. It’s important to water the plants after applying liquid fertilizer to ensure that the nutrients are absorbed properly. Additionally, it’s important to avoid applying fertilizer during periods of drought or extreme heat, as this can stress the plants. Ultimately, the timing and frequency of fertilizer applications will depend on the specific needs of your asparagus plants and the type of fertilizer you choose to use.
C. Avoiding common mistakes
Avoiding common mistakes when applying fertilizer to asparagus plants is essential for their health and growth. One common mistake is over-applying fertilizer, which can result in burning the plants and damaging their roots. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and use the appropriate amount for your specific plant needs. Additionally, it’s important to avoid applying fertilizer during periods of drought or extreme heat, as this can stress the plants and lead to damage. Another mistake to avoid is applying fertilizer too close to the base of the plants, as this can also cause burning and damage. Instead, it’s best to spread the fertilizer evenly around the plants to ensure proper absorption. By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can help ensure the health and growth of your asparagus plants.
Organic Fertilizing Options
A. Benefits of organic fertilizers
Organic fertilizers have several benefits compared to synthetic fertilizers. They are made from natural materials such as compost, manure, and other plant and animal sources, making them environmentally friendly and sustainable. Organic fertilizers also contain a wide range of nutrients that are released slowly, providing a steady and consistent source of nutrition for plants. They improve soil structure, increase microbial activity, and promote long-term soil health. Organic fertilizers are also less likely to cause burning or damage to plants, as the nutrients are released more slowly and in a more balanced way. Additionally, they are safe for use around children and pets and do not contribute to chemical runoff or pollution. Overall, organic fertilizers are a great option for promoting the health and vitality of plants while being mindful of the environment.
B. Homemade compost and manure
Homemade compost and manure are excellent options for organic fertilizers. They are sustainable, environmentally friendly, and provide a wide range of nutrients for plants. Using homemade compost and manure can improve soil structure, increase microbial activity, and promote long-term soil health. They are also less likely to cause burning or damage to plants and are safe for use around children and pets. Overall, homemade compost and manure are great choices for promoting the health of plants while being environmentally conscious.

C. Green manure and cover crops
Green manure and cover crops are both effective ways to improve soil fertility and health. Green manure refers to crops that are grown specifically to be turned into the soil to improve its nutrient content, while cover crops are grown to cover and protect the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Both options help to prevent soil erosion, increase organic matter, and suppress weeds. They also add nitrogen and other essential nutrients to the soil, making them excellent choices for sustainable and organic farming practices. Overall, green manure and cover crops are valuable tools for promoting soil health and increasing the productivity of farmland.
Troubleshooting and Tips
A. Identifying nutrient deficiencies
If you’re experiencing issues with your plants and suspect a nutrient deficiency, there are a few things you can do to identify the problem. Start by observing the symptoms of your plants, such as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or poor fruit production. You can also conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels in your soil. Once you’ve identified the specific nutrient that is lacking, you can address the deficiency by applying the necessary fertilizer or amendments to the soil. It’s important to address nutrient deficiencies promptly to ensure healthy plant growth and maximize crop yield.
B. Addressing common problems (yellowing, poor spear growth)
If you’re noticing common problems such as yellowing leaves or poor spear growth in your plants, there are a few steps you can take to address these issues. Yellowing leaves can be a sign of nutrient deficiency, water stress, or pest infestation. Conduct a soil test to determine nutrient levels and adjust your watering schedule if necessary. If pests are the issue, you can use organic or chemical treatments to control the infestation.
For poor spear growth in plants, it could be due to inadequate sunlight, overcrowding, or improper soil conditions. Make sure your plants are receiving adequate sunlight and have enough space to grow. You can also amend the soil with organic matter or fertilizers to improve its quality.
It’s important to address these common problems promptly to ensure the health and productivity of your plants. Observation, analysis, and timely action are key in maintaining a thriving garden.
C. Tips for maximizing yield and plant health
Here are some tips for maximizing yield and plant health in your garden. If pests are the issue, you can use organic or chemical treatments to control the infestation. For poor spear growth in plants, it could be due to inadequate sunlight, overcrowding, or improper soil conditions. Make sure your plants are receiving adequate sunlight and have enough space to grow. You can also amend the soil with organic matter or fertilizers to improve its quality. It’s important to address these common problems promptly to ensure the health and productivity of your plants. Observation, analysis, and timely action are key in maintaining a thriving garden. By addressing these issues, you can help your plants reach their full potential and maximize yield.
In conclusion, fertilizing asparagus is an essential part of maintaining healthy plants. By using the right fertilizers and following proper techniques, you can ensure that your asparagus plants grow strong and produce a bountiful harvest. It’s important to pay attention to the specific needs of your plants and provide them with the necessary nutrients to thrive. With the right care and attention, your asparagus plants will reward you with delicious, healthy spears for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is best to fertilize asparagus in the early spring before the spears emerge and then again after the harvest in mid-summer.
A balanced fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 or 12-12-12 is recommended for asparagus plants.
For established asparagus plants, apply about 1-4.5 pounds of fertilizer per 100 square feet of the asparagus bed.4.
Yes, organic fertilizers such as compost, well-rotted manure, or fish emulsion can also be used to fertilize asparagus plants.
Yes, asparagus plants benefit from annual fertilization to promote healthy growth and a bountiful harvest.
Yellowing or stunted growth of the asparagus ferns can be a sign that the plants need fertilizing.
Yes, over-fertilizing can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of the asparagus spears, so it’s important to follow recommended guidelines for fertilization.
For newly planted asparagus crowns, it’s best to wait until the second year before starting a regular fertilization schedule. In the first year, focus on establishing a healthy root system.
