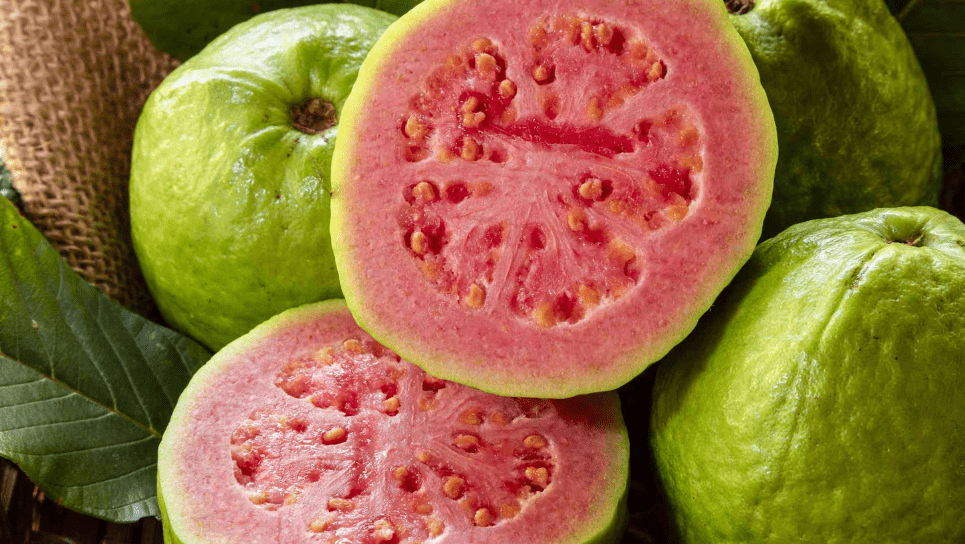

Pink Guava Tree: A Guide to Growing and Care
Pink guava trees are a popular fruit tree for home gardeners, known for their delicious and nutritious fruit. Whether you’re a beginner or experienced gardener, growing and caring for a pink guava tree can be a rewarding experience. In this post, we’ll provide a comprehensive guide to help you successfully cultivate and care for your pink guava tree, covering everything from planting and watering to pruning and harvesting. By following these tips, you’ll be on your way to enjoying a bountiful harvest of sweet and juicy pink guavas.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Pink Guava Tree
A. Botanical Information
The pink guava tree, also known as Psidium guajava, is a tropical fruit tree that is native to Central and South America. It is a small to medium-sized tree with a spreading canopy, and it can reach heights of 15 to 30 feet. The leaves are evergreen, oval-shaped, and smooth, and they emit a strong fragrance when crushed. The fruit of the pink guava tree is round or pear-shaped, with pink or yellow flesh and a strong, sweet aroma. It is rich in vitamin C, dietary fiber, and antioxidants, making it a popular choice for juicing, snacking, and cooking.
1. Common varieties of pink guava
There are several common varieties of pink guava, including the Ruby Supreme, Red Malaysian, and Thai Maroon. Each variety has its own unique flavor profile, with some being more sweet and others more tangy. It’s important to research which variety is best suited to your climate and growing conditions before planting

B. Nutritional and Health Benefits
Pink guava is known for its high vitamin C content, with just one fruit providing more than 200% of the recommended daily intake. It also contains dietary fiber and antioxidants, which can help improve digestion and support overall health. The fruit is also low in calories and contains a variety of essential nutrients, making it a healthy choice for snacking and juicing. Some studies have also suggested that the antioxidants in pink guava may have potential health benefits, such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Preparing to Plant Your Pink Guava Tree
A. Selecting the Right Variety
When selecting the right variety of pink guava to plant, it’s important to consider the unique flavor profiles of each variety and how they will thrive in your specific climate and growing conditions. Some varieties may be more sweet or tangy, so it’s important to research which variety will best suit your preferences and environment. By taking the time to choose the right variety, you can ensure a successful and fruitful harvest of pink guavas.
B. Choosing the Right Location
When choosing a location to plant your pink guava tree, it’s important to consider the tree’s need for full sunlight and well-drained soil. Pink guava trees thrive in tropical and subtropical climates, so it’s important to find a location that provides the right conditions for growth. Additionally, ensure that the location has enough space for the tree to spread out and grow without obstruction. By selecting the right location, you can help your pink guava tree thrive and produce bountiful fruit.
Planting Your Pink Guava Tree
A. Obtaining a Pink Guava Tree
Once you have selected the right location for your pink guava tree, the next step is to obtain a healthy tree from a reputable nursery or garden center. Look for a tree that is free from any signs of disease or pest damage, with a strong and well-developed root system. It’s also important to choose a tree that is the right size for your space and will fit well in your chosen location. Taking the time to select a healthy and suitable tree will set you up for success in growing a thriving pink guava tree.

B. Soil Preparation
Before planting your pink guava tree, it’s important to prepare the soil to create the ideal growing conditions. Pink guava trees prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. Start by testing the pH of the soil to ensure it falls within the optimal range of 5.5 to 7.0. If the pH is too high or too low, you can make adjustments with the addition of lime to raise the pH or elemental sulfur to lower it.
C. Planting Process
Once you have prepared the soil, it’s time to plant your pink guava tree. Choose a location that receives full sunlight and has plenty of space for the tree to spread its roots. Dig a hole twice as wide and just as deep as the tree’s root ball. Gently remove the tree from its container and place it in the hole, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding ground. Backfill the hole with the soil you removed, pressing it down firmly to remove any air pockets. Water the tree thoroughly after planting to help settle the soil and provide essential moisture for the roots. With proper soil preparation and planting techniques, your pink guava tree will have the best chance of thriving and producing delicious fruit.
Caring for Your Pink Guava Tree
A. Watering
Watering is a crucial part of caring for your pink guava tree. It’s important to ensure that the tree receives enough water, especially during its first few years of growth. Be sure to water the tree regularly, especially during dry periods, to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. However, be careful not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot. It’s also important to water the tree at the base, rather than from overhead, to prevent fungal diseases. As the tree matures, you can adjust your watering schedule based on the weather and soil conditions. Overall, proper watering is essential for the health and growth of your pink guava tree.
B. Fertilizing
Fertilizer is also important for the health and growth of your pink guava tree. You can provide the tree with a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 formula, in the early spring and late summer. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the correct application and dosage of the fertilizer. Fertilizing will help provide the tree with essential nutrients it needs to thrive and produce healthy fruit. It’s important to monitor the tree’s growth and adjust the fertilizing schedule as necessary based on its needs. Overall, proper fertilizing, along with regular watering, will contribute to the overall health and success of your pink guava tree.
C. Pruning and Training
Pruning and training are important tasks to help maintain the health and shape of your pink guava tree. Pruning involves removing any dead, damaged, or overgrown branches to encourage new growth and improve air circulation. This can be done in the late winter or early spring before the tree starts to produce new growth. Training involves shaping the tree to a desired form, such as an open center or central leader structure, to promote better fruit production and overall health. It’s important to use clean, sharp tools when pruning and to avoid over-pruning, as this can stress the tree. Regular pruning and training will help ensure a strong and productive pink guava tree.
Managing Pests and Diseases
A. Common Pests and Diseases
and diseases that can affect pink guava trees include fruit flies, aphids, scales, and fungal diseases such as anthracnose and powdery mildew. To manage pests, it’s important to regularly inspect the tree for any signs of infestation and to take appropriate measures, such as using insecticidal soaps or natural predators, to control the population. For fungal diseases, it’s important to maintain good air circulation around the tree and to avoid overhead watering, as this can create a moist environment that is favorable for fungal growth. Additionally, applying fungicides as a preventative measure can help protect the tree from fungal diseases. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help to keep pests and diseases at bay and ensure the health of your pink guava tree.
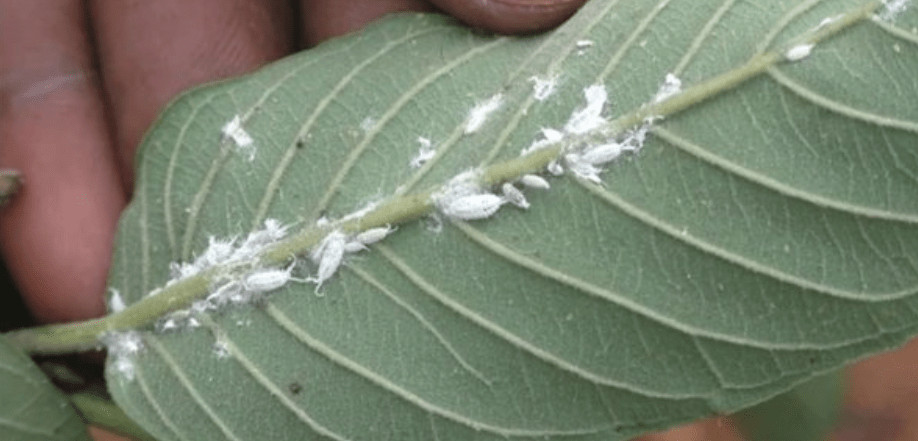

B. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to managing pests and diseases that focuses on prevention, monitoring, and control. It involves using a combination of cultural, biological, mechanical, and chemical methods to address pest and disease issues. This can include practices such as crop rotation, using resistant plant varieties, introducing beneficial insects, and using pesticides only as a last resort. By combining these different strategies, IPM aims to minimize the impact of pests and diseases while also reducing the reliance on chemical treatments. It’s an effective and environmentally sustainable approach to managing pests and diseases in agricultural and horticultural settings.
Flowering and Fruit Production
A. Flowering Cycle
The flowering cycle refers to the process by which a plant produces flowers. This cycle typically begins with the formation of buds, followed by the development and opening of flowers. Once the flowers have been pollinated, they may produce fruits or seeds. The exact timing and duration of the flowering cycle can vary depending on the specific plant species and environmental conditions. Understanding the flowering cycle is important for both plant cultivation and pollination, as it can impact the timing of harvest and the reproductive success of the plant.
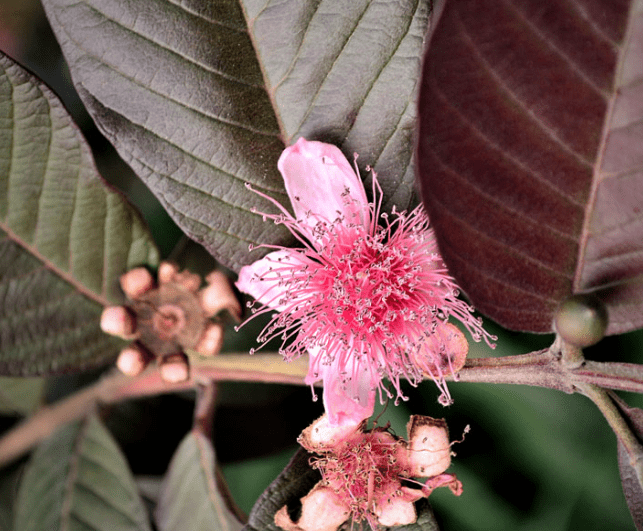
B. Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male reproductive organs of a flower to the female reproductive organs, leading to fertilization and the production of seeds or fruits. This transfer of pollen can occur through wind, insects, birds, or other natural agents. Pollination is crucial for the reproduction and survival of many plant species, as it allows for genetic diversity and the production of new plant offspring. Understanding the process of pollination is important for maintaining healthy ecosystems and promoting the growth of crops and other agricultural plants.
C. Fruit Development and Harvesting
Fruit development and harvesting are key stages in the flowering cycle of a plant. After successful pollination and fertilization, the ovary of the flower develops into a fruit, which contains seeds for new plant growth. The timing of fruit development and harvesting is significant for farmers and gardeners, as it directly impacts the quality and quantity of the crop. Understanding the factors that influence fruit development, such as temperature, humidity, and pollination, can help optimize harvest time and ensure a successful crop yield. Additionally, proper harvesting techniques are important for preserving the fruit’s quality and maximizing its shelf life. Overall, a thorough understanding of fruit development and harvesting is essential for successful plant cultivation and agricultural practices.
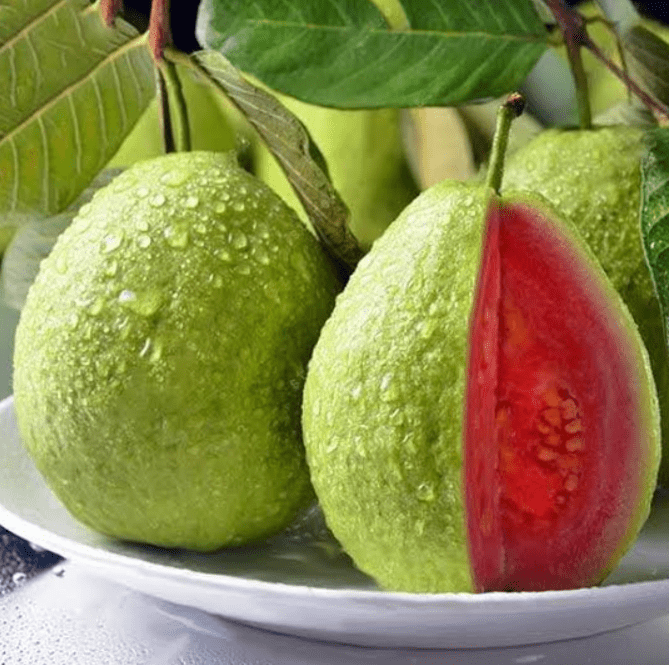

Maximizing Your Harvest
A. Enhancing Fruit Yield
There are several ways to enhance fruit yield during the harvesting process. One method is to ensure proper soil fertility by regularly testing and amending the soil with necessary nutrients. Providing adequate water and maintaining proper irrigation practices can also help promote healthy fruit development. Additionally, managing pests and diseases through integrated pest management techniques can protect the fruit from damage and improve overall yield. Pruning and thinning fruit trees and plants can also help optimize the size and quality of the fruit. Lastly, timing the harvest based on the specific ripening characteristics of each fruit variety can help ensure a bountiful yield. By implementing these strategies, farmers and gardeners can effectively maximize their harvest and produce high-quality fruits.
B. Dealing with Common Issues
Dealing with common issues in fruit production involves utilizing various strategies to promote healthy growth and maximize yield. Some common issues include soil fertility, water and irrigation, pests and diseases, pruning and thinning, and timing of harvest. By addressing these issues, farmers and gardeners can enhance the quality and quantity of their fruit production.
Using Your Pink Guava Harvest
A. Culinary Uses
Pink guava can be used in a variety of culinary applications due to its sweet and tropical flavor. It can be eaten fresh, juiced, or used in smoothies, cocktails, and desserts. The fruit can also be used to make jams, jellies, and sauces. Additionally, pink guava can be added to fruit salads and salsas for a refreshing and tangy flavor. The versatility of pink guava makes it a popular choice for both sweet and savory dishes.
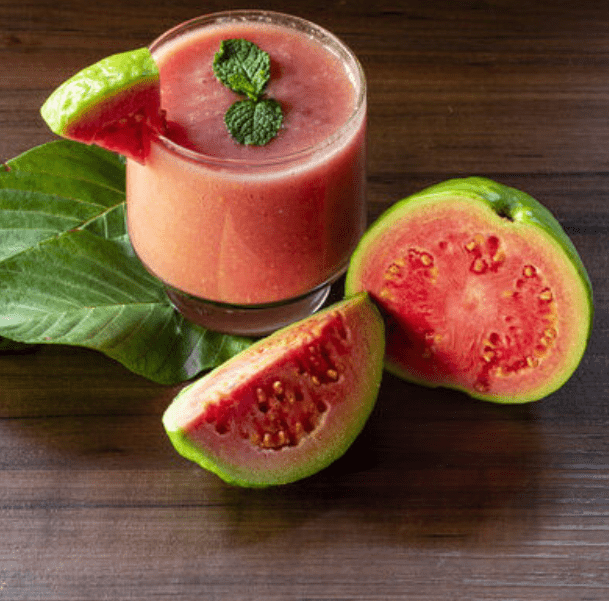

B. Health and Wellness
Pink guava is a nutritious fruit that is rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, and fiber. Consuming pink guava can help support the immune system, improve digestion, and promote overall health and wellness. The fruit can also aid in weight management and promote healthy skin. Additionally, pink guava is low in calories and contains no cholesterol, making it a great choice for those looking to maintain a healthy diet. Whether eaten fresh or used in recipes, pink guava can be a delicious and beneficial addition to a well-rounded diet.
In conclusion, growing and caring for a pink guava tree requires patience, attention to detail, and regular maintenance. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this post, you can ensure that your pink guava tree thrives and produces delicious, juicy fruit for years to come. Remember to provide adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients, and to monitor the tree for any signs of pests or disease. With proper care, your pink guava tree will be a beautiful and productive addition to your garden.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Pink guava trees thrive in tropical or subtropical climates with warm temperatures and high humidity. They prefer temperatures between 68-82°F (20-28°C).
Pink guava trees require full sun, so it’s best to plant them in a location where they will receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Pink guava trees need regular watering, especially during dry periods. It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. They may require more frequent watering during the fruiting season.
Pink guava trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. A sandy loam or loamy soil is ideal for their growth.
Fertilize pink guava trees with a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 NPK fertilizer, three times a year – in early spring, early summer, and early fall. Be sure to follow the recommended dosage on the fertilizer package.
Pink guavas are typically ready for harvest 4-6 months after flowering. The fruit should be firm and have a strong, sweet aroma when ripe. Simply twist the fruit gently to harvest it from the tree.
To protect pink guava trees from pests like fruit flies and diseases like anthracnose, it’s important to keep the area around the tree clean and free of fallen fruit and debris. Additionally, applying organic pesticides and fungicides can help prevent infestations and infections.
Yes, pink guava trees can be grown in containers, but it’s important to choose a large container with good drainage. They will need regular watering and fertilizing, and may require repotting as they grow.
