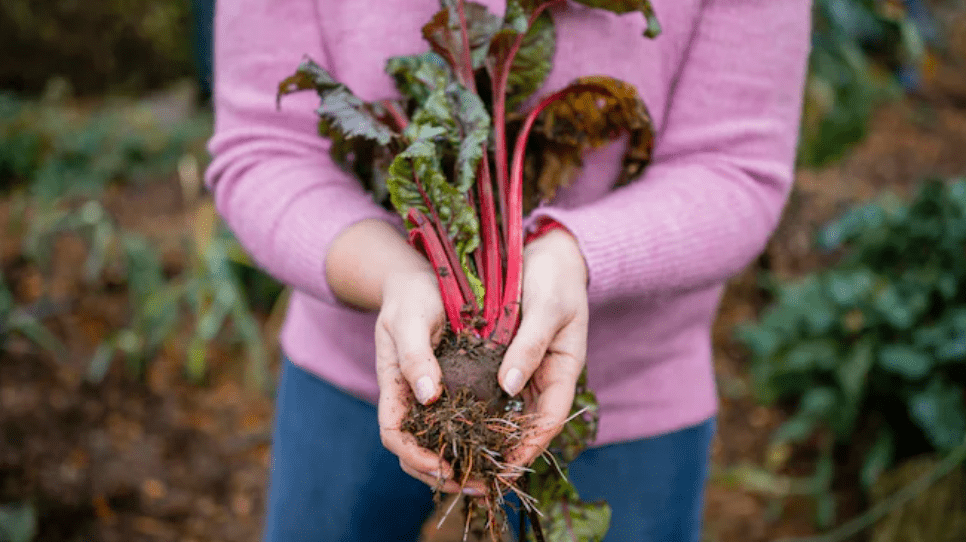

Rhubarb Roots: How to Grow and Care for Your Own Rhubarb Plants
Rhubarb is a popular and versatile plant that can be grown in your own garden, providing you with a delicious and nutritious crop. In this post, we will walk you through the process of growing and caring for your own rhubarb plants, from planting the roots to harvesting the stalks. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to successfully cultivate and maintain healthy rhubarb plants in your garden. So, let’s get started and learn how to grow and care for your very own rhubarb roots!
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Rhubarb
A. What is Rhubarb?
Rhubarb is a perennial plant known for its large, edible leaf stalks. It is often used in cooking and baking to make pies, jams, and other desserts. Rhubarb is also known for its tart flavor and is often paired with sweet fruits to balance out its taste.
1. Varieties of rhubarb (e.g., Victoria, Canada Red, Crimson Red)
There are several varieties of rhubarb, including Victoria, Canada Red, and Crimson Red. Each variety may have slightly different characteristics, such as color and flavor, so you may want to explore different varieties to find the one that best suits your preferences and growing conditions.
B. Rhubarb Roots and Their Importance
Rhubarb roots are essential for the growth and reproduction of the plant. They are used to propagate new plants and can also be used for medicinal and culinary purposes. The roots contain compounds that have been used in traditional medicine for their potential health benefits. Additionally, rhubarb roots can be harvested and divided to create new plants, making them an important part of the plant’s life cycle.
1. Role of roots in rhubarb growth
The roots of rhubarb play a crucial role in its growth and development. They provide stability for the plant and absorb nutrients and water from the soil, which are essential for its overall health. The roots also store energy and nutrients during the dormant winter months, allowing the plant to survive until the next growing season. Additionally, rhubarb roots can be divided and replanted to propagate new plants, making them an important factor in the plant’s reproduction and spread.
Preparing to Grow Rhubarb
A. Choosing the Right Variety
There are several varieties of rhubarb to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics. When selecting a variety to grow, it’s important to consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and desired harvest time. For example, some varieties are better suited for colder climates, while others are more tolerant of heat. Additionally, some varieties are known for their earlier or later harvest times, so it’s important to choose a variety that aligns with your growing season. It’s also important to consider the flavor and color of the stalks, as different varieties may offer different taste and appearance. By selecting the right variety for your specific growing conditions and preferences, you can ensure a successful and bountiful rhubarb harvest.
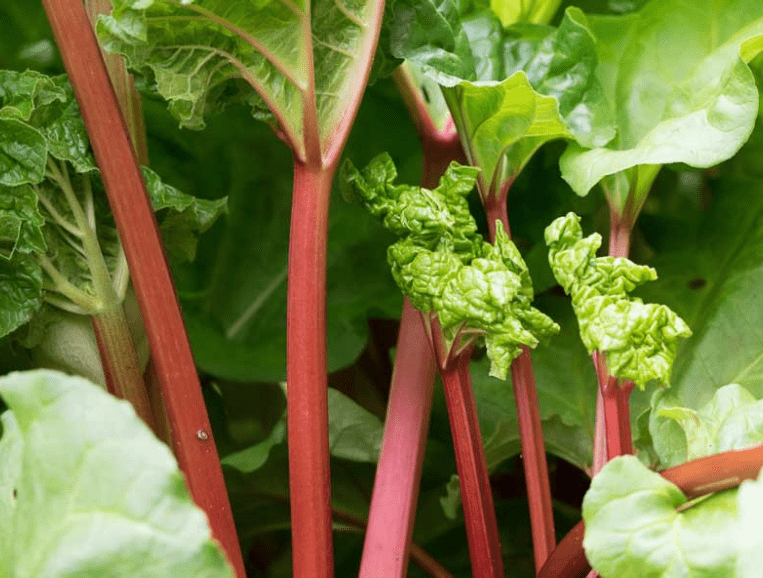

1. Factors to consider (climate, space, taste preference)
When choosing a variety of rhubarb to grow, it’s important to consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and desired harvest time. Some varieties are better suited for colder climates, while others are more tolerant of heat. Additionally, some varieties are known for their earlier or later harvest times, so it’s important to choose a variety that aligns with your growing season. It’s also important to consider the flavor and color of the stalks, as different varieties may offer different taste and appearance. By selecting the right variety for your specific growing conditions and preferences, you can ensure a successful and bountiful rhubarb harvest.
2. Popular rhubarb varieties and their characteristics.
There are several popular varieties of rhubarb, each with its own unique characteristics. For example, Victoria rhubarb is known for its bright red stalks and tart flavor, making it a popular choice for cooking and baking. MacDonald rhubarb, on the other hand, is known for its large, greenish-red stalks and milder flavor. Other popular varieties include Canada Red, Cherry Red, and Valentine, each offering their own distinct flavor and appearance. It’s important to research and choose a variety that best suits your specific growing conditions and taste preferences.
B. Selecting and Preparing the Site
1. Ideal soil conditions (well-drained, fertile soil)
Rhurbarb thrives in well-drained, fertile soil. It’s important to choose a location with soil that does not get waterlogged, as this can be detrimental to the plants. Adding compost or well-rotted manure to the soil can help improve its fertility and drainage, providing a better environment for rhubarb to grow.
2. Sunlight requirements (full sun to partial shade)
Rhubarb plants require full sun to partial shade, so it’s important to choose a site that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day. Planting rhubarb in an area with too much shade can result in leggy, weak growth and smaller harvests. It’s best to find a location that offers a good balance of sunlight throughout the day.
3. Preparing the soil (testing pH, adding compost or manure)
Before planting rhubarb, it’s important to test the pH of the soil to ensure it falls within the ideal range of 6.0-6.8. If necessary, you can amend the soil with lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it. Adding compost or well-rotted manure to the soil can also help improve its fertility and drainage, providing a better environment for rhubarb to grow. It’s important to thoroughly mix these amendments into the soil before planting to ensure even distribution.
Planting Rhubarb Roots
A. When to Plant
Rhubarb roots should be planted in early spring, as soon as the ground can be worked. This is typically around March or April, depending on your location. It’s important to plant the roots as soon as possible after purchasing to prevent them from drying out. When planting, be sure to space the roots about 3-4 feet apart to allow for their large size at maturity. Dig a hole deep enough to accommodate the roots and cover them with about 2 inches of soil. Water the newly planted roots thoroughly to help them establish in their new location.
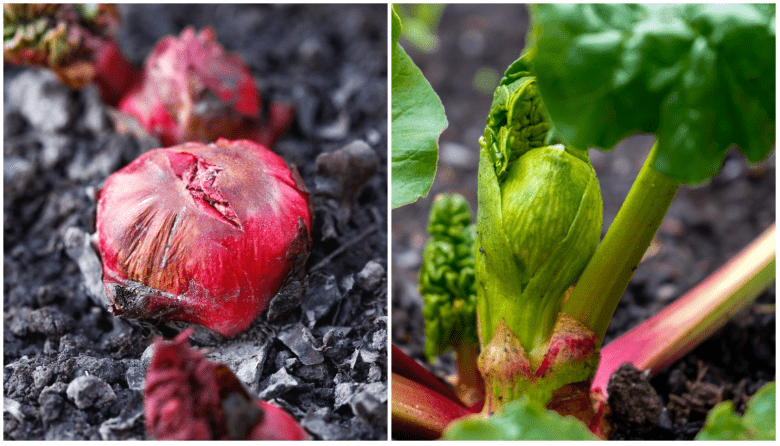

B. Watering and Initial Care
It’s best to water the newly planted rhubarb roots regularly, especially during dry periods, to help them establish and grow strong. Once the plants are established, they typically require about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation. It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adding a layer of mulch around the plants can help retain moisture and prevent weeds from competing with the rhubarb. Additionally, you may want to consider applying a balanced fertilizer in early spring to help the plants thrive. Overall, providing consistent moisture and proper care will help ensure a successful rhubarb harvest.
Caring for Rhubarb Plants
A. Watering and Feeding
Watering and feeding are important aspects of caring for rhubarb plants. It’s important to water newly planted rhubarb roots regularly, especially during dry periods, to help them establish and grow strong. Once the plants are established, they typically require about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation. It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adding a layer of mulch around the plants can help retain moisture and prevent weeds from competing with the rhubarb.
In addition to watering, applying a balanced fertilizer in early spring can help the plants thrive. This will provide the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and a successful rhubarb harvest. Overall, providing consistent moisture and proper care will help ensure the health and productivity of your rhubarb plants.
B. Mulching and Weed Control
Mulching and Weed Control are essential for maintaining the health of your rhubarb plants. Adding a layer of mulch around the plants will help retain moisture and prevent weeds from competing with the rhubarb. This will ensure that the plants receive the necessary nutrients and water without being hindered by surrounding vegetation. By taking these steps, you can help your rhubarb plants thrive and produce a successful harvest.
C. Pruning and Dividing Rhubarb Plants
Pruning and dividing rhubarb plants is an important part of maintaining their health and productivity. Pruning helps to remove any old or damaged leaves and stalks, allowing the plant to focus its energy on producing new growth. Dividing the plants every few years can also help rejuvenate them and promote healthier growth. By taking the time to prune and divide your rhubarb plants, you can ensure that they continue to thrive and provide a bountiful harvest for years to come.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
A. Common Pests and Diseases
Dealing with pests and diseases is crucial for the overall health and productivity of your rhubarb plants. Common pests that can affect rhubarb include aphids, snails, and slugs, which can damage the leaves and stems. It is important to regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pest infestation and take appropriate measures to control them, such as using organic insecticides or hand-picking the pests.
In terms of diseases, rhubarb plants are susceptible to fungal diseases such as crown rot and leaf spot. To prevent these diseases, it is important to ensure proper air circulation around the plants and avoid overwatering. If any signs of disease are observed, it is crucial to promptly remove and destroy any infected plant parts to prevent the spread of the disease.
By taking proactive measures to prevent and control pests and diseases, you can help ensure that your rhubarb plants remain healthy and productive. This will ultimately lead to a successful and bountiful harvest.
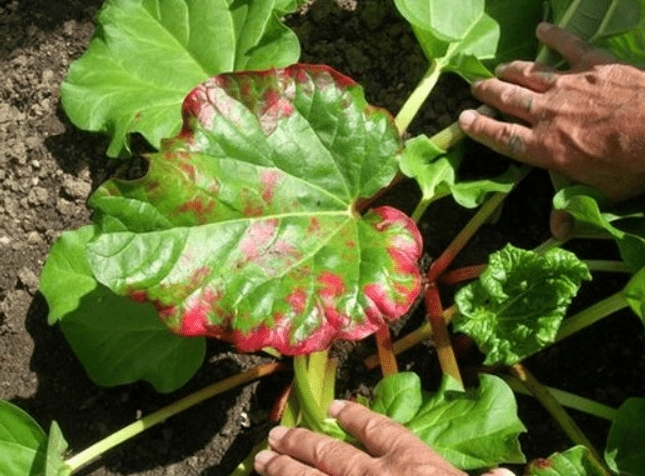

B. Organic and Chemical Solutions
It is important to regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pest infestation and take appropriate measures to control them, such as using organic insecticides or hand-picking the pests. In terms of diseases, rhubarb plants are susceptible to fungal diseases such as crown rot and leaf spot. To prevent these diseases, it is important to ensure proper air circulation around the plants and avoid overwatering. If any signs of disease are observed, it is crucial to promptly remove and destroy any infected plant parts to prevent the spread of the disease. By taking proactive measures to prevent and control pests and diseases, you can help ensure that your rhubarb plants remain healthy and productive. This will ultimately lead to a successful and bountiful harvest.
Harvesting Rhubarb
A. When to Harvest
Rhubarb can be harvested once the stalks are about 10-15 inches long. It is best to harvest in the early spring or late summer when the stalks are at their peak. To harvest, simply grasp the stalk near the base and gently pull it upward and away from the plant. It is important to leave at least a third of the stalks on the plant to ensure continued growth and vitality. Enjoy your fresh rhubarb in pies, jams, and other delicious recipes!
B. Post-Harvest Care
After harvesting your rhubarb, it’s important to properly care for the plant to ensure continued growth and a successful harvest next season. Remove any leaves or stalks that are damaged or diseased, and trim off any flower stalks that have formed. This will help redirect the plant’s energy back into the roots for future growth. Additionally, it’s a good idea to fertilize the soil around the plant with a balanced fertilizer to give it a boost of nutrients. Keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged, to support healthy growth. With proper post-harvest care, your rhubarb plant will continue to produce a bountiful harvest for years to come.
Winter Care and Long-Term Maintenance
A. Preparing Rhubarb for Winter
As winter approaches, it’s important to prepare your rhubarb for the colder months ahead. Once the plant has stopped producing new growth, it’s time to cut back the remaining leaves and stalks to ground level. This will help protect the plant from the harsh winter weather and encourage new growth in the spring. Additionally, you can apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to help insulate the roots and prevent frost damage. Throughout the winter, be sure to monitor the soil moisture and water the plant if necessary, as dry winter weather can still cause stress to the plant. With proper winter care and long-term maintenance, your rhubarb will continue to thrive year after year.
B. Long-Term Maintenance
Long-Term Maintenance of your rhubarb plant is important for its overall health and productivity. In addition to winter preparation, it’s recommended to divide and replant mature rhubarb plants every 4-5 years to promote new growth and prevent overcrowding. Regularly fertilizing the soil with well-balanced nutrients and keeping the area around the plant weed-free will also contribute to its long-term success. By following these maintenance steps, you can ensure that your rhubarb plant remains healthy and continues to provide delicious stalks for years to come.
In conclusion, growing and caring for rhubarb plants can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this post, you can ensure that your rhubarb plants thrive and produce an abundant harvest. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, growing your own rhubarb can be a fun and fulfilling endeavor. So, roll up your sleeves and get ready to enjoy the delicious rewards of your own home grown rhubarb.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is possible to grow rhubarb from seeds, but it is not recommended as it can take several years for the plant to mature and produce edible stalks. It is best to start with rhubarb crowns or divisions from an established plant.
Rhubarb plants thrive in full sun, so it is best to plant them in a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day.
Rhubarb plants prefer consistently moist soil, so it is important to water them regularly, especially during dry periods. However, be careful not to overwater, as rhubarb does not like to sit in waterlogged soil.
Rhubarb stalks can be harvested in the spring, once they have reached a sufficient size. It is best to wait until the second year after planting before harvesting any stalks, to allow the plant to establish a strong root system.
Yes, rhubarb plants can be divided every 4-5 years to rejuvenate the plant and increase its productivity. Dividing the plant also allows you to propagate new rhubarb plants for your garden or to share with others.
Rhubarb plants are relatively low-maintenance and are not commonly affected by pests or diseases. However, it is important to keep the area around the plants free of weeds and debris to prevent any potential issues.
No, the leaves of the rhubarb plant are toxic and should not be consumed. Only the stalks of the plant are edible, and they should be harvested and prepared with caution.
With proper care, rhubarb plants can live for many years, often producing abundant harvests for up to 15-20 years. It is important to continue dividing and rejuvenating the plants to ensure their longevity and productivity.
