
Rootstock Selection for Grafting Fruit Trees: A Complete Guide for Successful Grafting
Grafting fruit trees is a rewarding and effective way to enhance tree growth, improve fruit quality, and increase yields. 🌿 However, one of the most crucial steps in this process is rootstock selection for grafting fruit trees. Choosing the right rootstock can significantly influence the health, productivity, and longevity of your tree. 🌳 Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, understanding how to select the ideal rootstock is key to successful grafting. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the factors that matter most in rootstock selection, helping you make informed choices for healthier, more productive fruit trees. 🍏🍎
Table of Contents
Toggle🌱 What is Rootstock in Grafting? 🌳
In simple terms, rootstock is the part of a plant that provides the roots in grafting. It serves as the foundation for the grafted tree, providing essential nutrients, water, and stability to the top part, called the scion (the branch or shoot you want to propagate). 🌳

Rootstocks are carefully selected based on factors like soil type, climate, and the desired tree size. They determine how the tree will grow—whether it will be a dwarf tree for small spaces or a full-sized tree for larger orchards. 🍏
Rootstocks also impact the tree’s resistance to diseases, pests, and environmental stress, making them a key player in the tree’s overall health. Choosing the right rootstock ensures a successful graft and a thriving fruit tree! 🍊
🌿 Factors to Consider When Choosing Rootstock 🌱
Selecting the right rootstock is crucial for the success of your grafted fruit tree. Here are the key factors to keep in mind when making your choice: 🌿

1. 🌞🌧️ Climate and Soil Conditions 🌱
- Rootstocks are adapted to different climates and soil types. Some rootstocks are better suited to cold climates ❄️, while others thrive in warmer areas ☀️. It’s essential to pick one that matches your local environment for healthy growth. 🌻
2. 🌳 Tree Size and Growth Habit 🍏
- Rootstocks influence the size and shape of the tree. Dwarfing rootstocks keep trees small and compact, perfect for smaller spaces or easier harvesting 🧑🌾. Full-size rootstocks allow for larger, more vigorous trees with higher fruit production 🍎.

3. 🦠 Disease Resistance 🐛
- Some rootstocks are resistant to specific soil-borne diseases and pests 🐛. For example, certain rootstocks can protect against root rot or fungal infections, ensuring your tree stays healthy and strong. 🌱
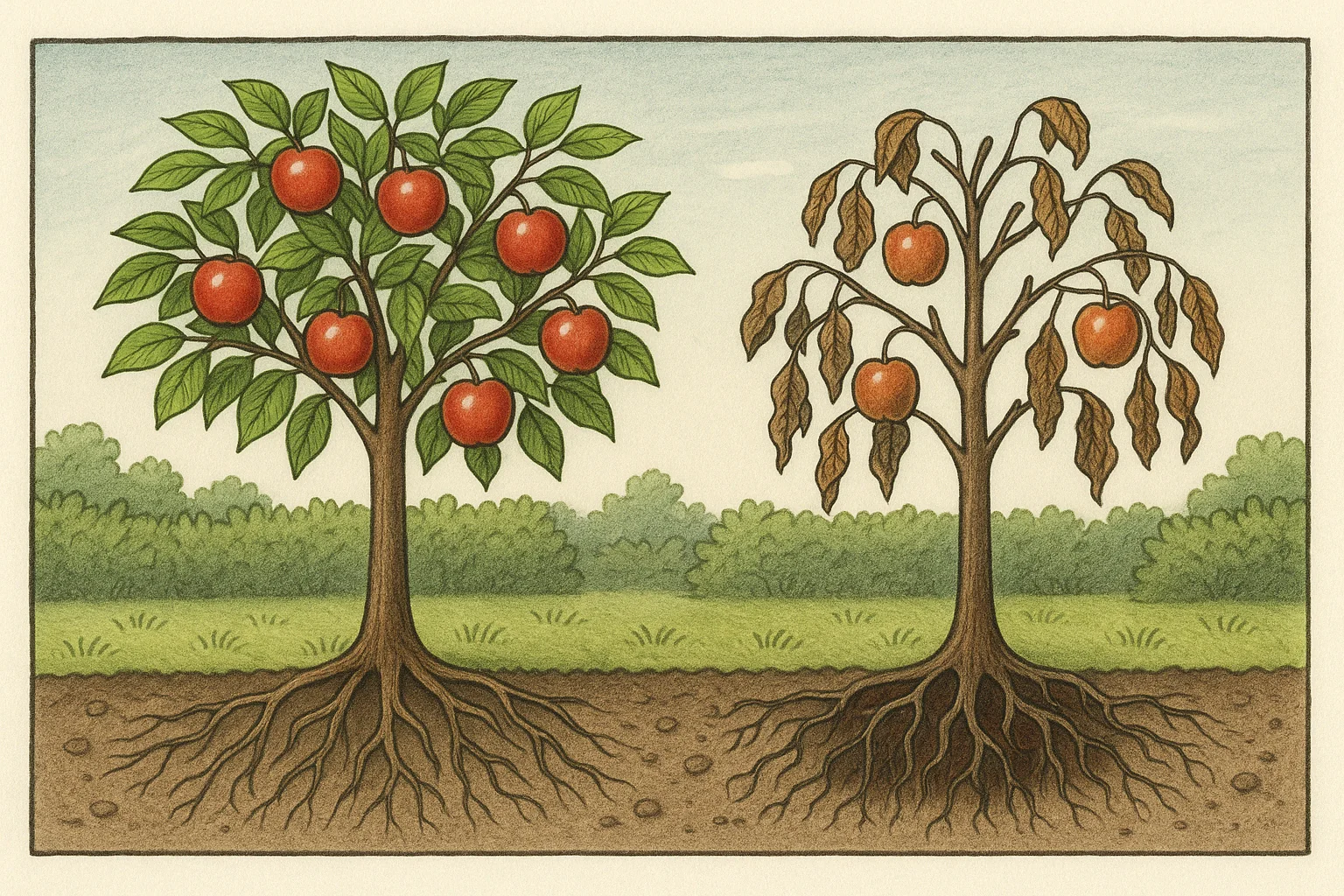
4. 🌿 Compatibility with Scion 🌱
- Not all rootstocks work well with every fruit variety. Ensure your rootstock is compatible with the scion you plan to graft. Compatibility affects graft success, tree health, and fruit quality 🍐.
5. 🍒 Fruit Production and Quality 🌟
- Rootstocks can affect the size, flavor, and overall yield of your fruit. For high-quality fruit, select rootstocks that promote strong growth and good fruit development 🌟.

By carefully considering these factors, you’ll set your grafted fruit tree up for long-term success and a bountiful harvest! 🌳🍏
🍏 Types of Rootstocks for Different Fruit Trees 🍑
Choosing the right rootstock depends on the type of fruit tree you’re grafting. Different fruit trees require specific rootstocks to thrive. Here’s a quick guide to some of the most popular rootstocks for common fruit trees: 🍏
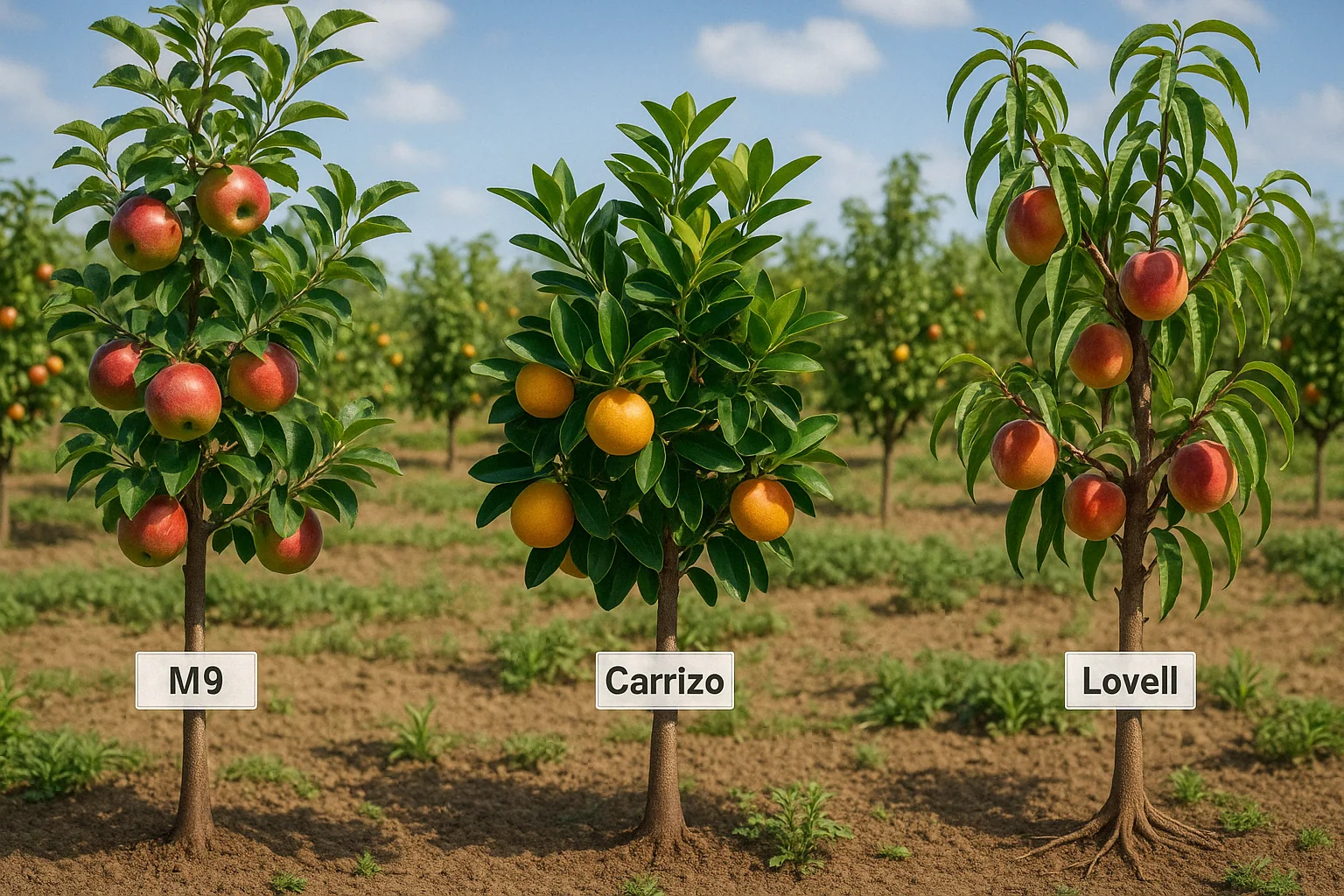

1. 🍎 Apple Rootstocks 🌳
- M9: A dwarfing rootstock that keeps apple trees small, perfect for limited spaces or container gardening. It produces high-quality fruit but may require more care.
- MM106: A semi-dwarf rootstock, ideal for those who want a balance between tree size and fruit production. It’s known for good disease resistance and adaptability to different soil types.
- M26: Another semi-dwarf option that offers moderate growth and is less susceptible to root rot.
2. 🍊 Citrus Rootstocks 🌿
- Carrizo: Popular for citrus trees, Carrizo provides strong disease resistance, good fruit production, and adaptability to different soil types.
- Swingle: Best suited for citrus trees in sandy soils, this rootstock improves vigor and overall growth.
- Trifoliate Orange: Known for its cold tolerance, this rootstock is great for citrus in cooler climates and offers good disease resistance.
3. 🍑🍐🍒 Peach, Pear, and Plum Rootstocks 🌳
- Lovell (Peach): Ideal for peach trees, Lovell is strong and provides good growth while tolerating a wide range of soil conditions.
- Pyrus (Pear): Used for pear trees, Pyrus rootstocks provide resistance to fire blight and improve overall tree health.
- Myrobalan (Plum): Great for plums, this rootstock ensures strong growth and good disease resistance, especially for trees in heavier soils.
4. 🍒🍋 Other Fruit Trees 🌿
- Cherry Rootstocks: Gisela rootstocks are commonly used for cherries and provide compact growth while enhancing fruit quality.
- Almond Rootstocks: Rootstocks like GF677 are used for almonds, offering excellent resistance to nematodes and ensuring strong growth.
By choosing the appropriate rootstock for your fruit tree, you can ensure better growth, higher yields, and a more successful grafting experience! 🌿🍓 Careful attention to Rootstock Selection for Grafting Fruit Trees will greatly influence the long-term health and productivity of your plants. 🍋🍊🍎
🌳 How to Select the Right Rootstock for Your Fruit Trees 🌿
Choosing the right rootstock is essential for the health and productivity of your fruit trees. Here are some practical tips to guide you in making the best selection: 🍏

1. 🏡 Match Rootstock to Your Space and Goals 🌱
- Dwarf Rootstocks: If you’re working with limited space or want smaller trees for easier harvesting, choose dwarfing rootstocks like M9 for apples or Trifoliate Orange for citrus. These will keep your trees compact while still producing delicious fruit. 🍊
- Full-Size Rootstocks: If you have ample space and want larger trees with a higher yield, opt for rootstocks like MM106 (apple) or Lovell (peach). These will encourage vigorous growth and a larger tree size. 🌳
2. 🌡️ Consider Your Climate 🌞
- Some rootstocks are better suited to specific climates. For example, if you live in a colder area, choose rootstocks with cold tolerance, like Trifoliate Orange for citrus. For warmer regions, rootstocks like Carrizo work well, as they’re adaptable to a variety of soil types and climates. 🌞🌧️
3. 🦠 Think About Disease Resistance 🌱
- Rootstocks can offer protection against diseases such as root rot or fire blight. If your area is prone to certain diseases, look for rootstocks with built-in resistance. For example, MM106 for apples is known for its resistance to common apple tree diseases. 🦠
4. 🌱 Factor in Tree Health and Long-Term Maintenance 🌳
- Some rootstocks require more care than others. Semi-dwarf rootstocks like MM106 might need less maintenance compared to dwarfing types. If you’re looking for a tree that’s low-maintenance, choose rootstocks known for resilience and adaptability to various soil conditions. 🌿
5. 🧑🌾 Consult Local Experts 🌿
- Local nurseries or gardening experts can provide valuable insights into which rootstocks perform best in your region. Don’t hesitate to ask for advice on which rootstock would thrive in your area for optimal fruit production. 🌸
By considering these factors, you’ll be well on your way to selecting the right rootstock for a healthy, thriving fruit tree! 🍏🌿 Understanding the importance of Rootstock Selection for Grafting Fruit Trees is key to achieving strong growth and abundant harvests. 🌳🪴
🌱 Steps for Grafting Fruit Trees with the Selected Rootstock 🍏
Grafting can be an incredibly rewarding process, and once you’ve selected the right rootstock, it’s time to get started. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide to grafting fruit trees: 🌳
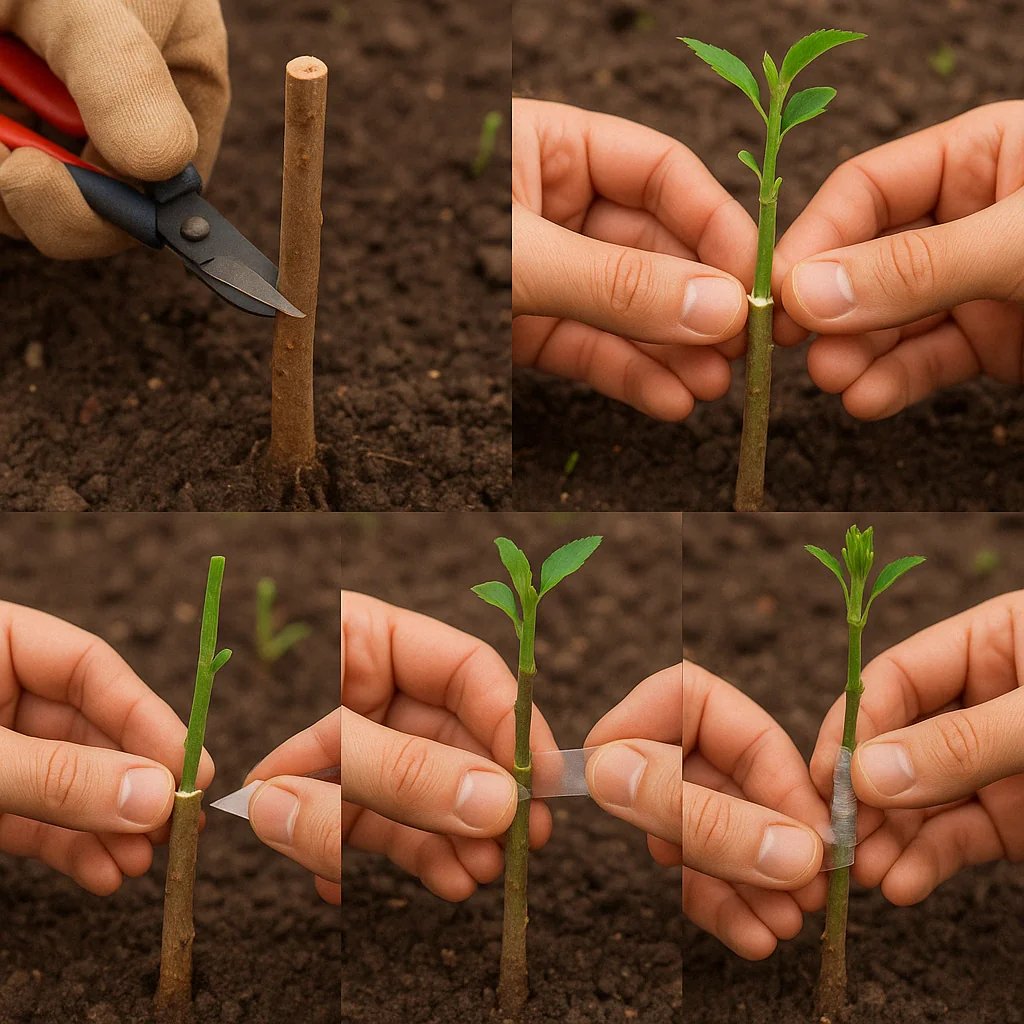

1. 🌿 Prepare the Rootstock and Scion 🍊
- Rootstock: Start by cutting the rootstock just above the soil line to expose a clean, fresh surface for grafting. Make sure it’s healthy and free from pests or disease. 🌱
- Scion: Choose a healthy scion (the fruit variety you want to propagate). It should be a young, vigorous branch from the previous year’s growth. 🍒
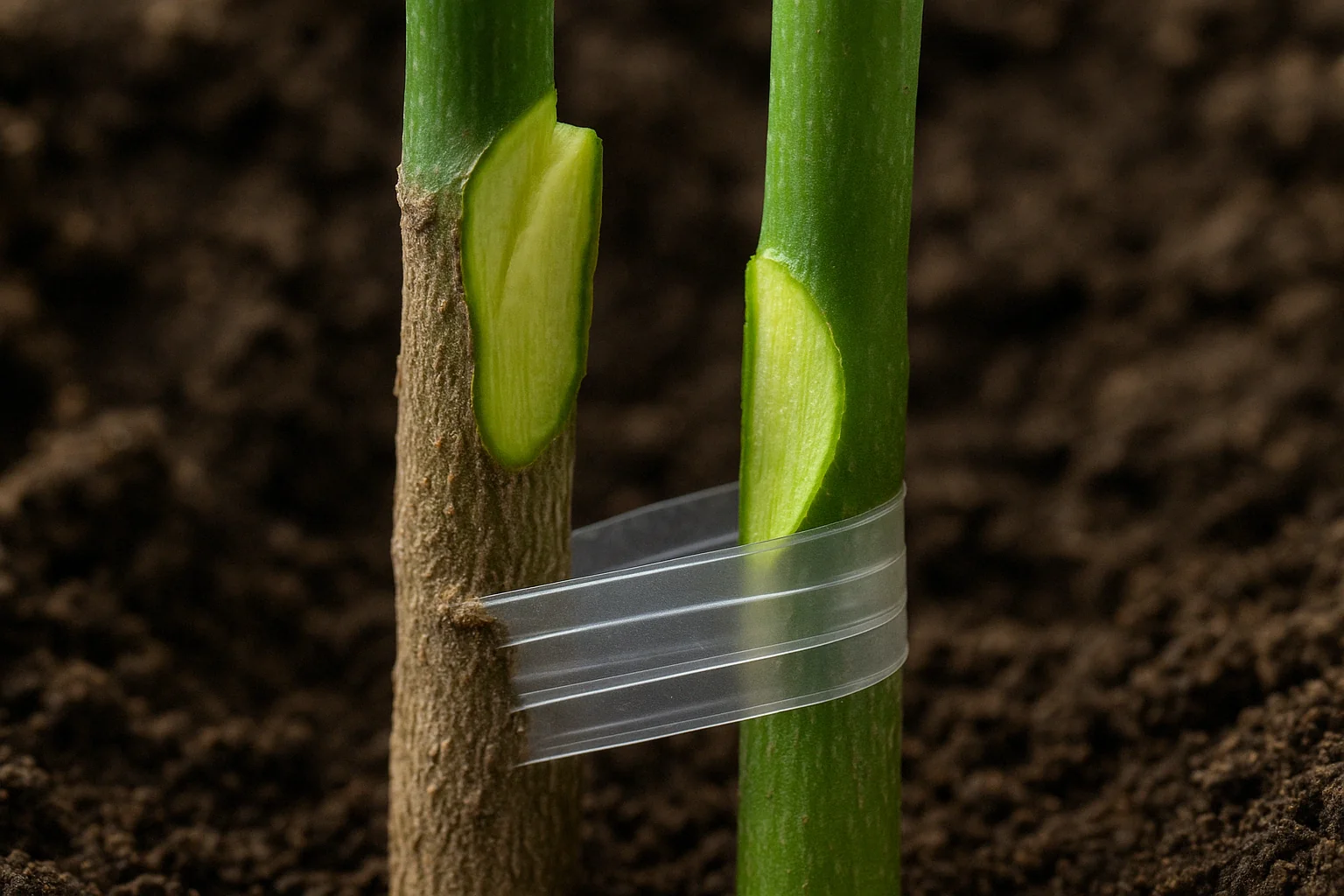
2. ✂️ Choose the Right Grafting Method 🔪
- There are several grafting techniques to choose from, including whip-and-tongue, cleft, or bark grafting. The whip-and-tongue method is ideal for matching similar-sized scions and rootstocks, while cleft grafting works best for larger rootstocks. 🌿
3. 🔪 Make the Grafting Cut ✂️
- For whip-and-tongue grafting, make a diagonal cut on both the rootstock and the scion, ensuring that the cuts align perfectly. For cleft grafting, split the rootstock down the center and place the scion into the split. 🌱
4. 🌳 Join the Scion and Rootstock 🌿
- Carefully align the cambium layers (the green tissue just beneath the bark) of the rootstock and scion. This is the part that needs to be in contact for a successful graft. Press them together firmly to ensure a good connection. 🌿
5. 🪢 Secure the Graft with Grafting Tape or Ties 🎀
- Wrap the grafting area with tape, grafting wax, or ties to hold the scion and rootstock together. This will help protect the graft from drying out and ensure a stable union. 🎋
6. 🌬️ Protect the Graft 🌱
- Cover the graft with a plastic bag or moisture-retaining wrap to keep the grafting area warm and humid. Be sure to remove it after a few weeks once the graft has healed and the scion begins to show signs of growth. 🌳
7. 💧 Post-Grafting Care 🌱
- Water the grafted tree regularly but avoid overwatering. Keep an eye on the graft for any signs of stress or infection. Once the graft is successful and the scion begins to grow, remove the grafting tape and plastic cover. 🌿
By following these steps carefully, you can ensure a successful graft and watch your fruit tree flourish! 🌳🍒 Proper Rootstock Selection for Grafting Fruit Trees is essential to support healthy growth and maximize your harvest.🌿🪴
❌🌿 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Rootstock Selection 🌱
Selecting the right rootstock is crucial for the success of grafting fruit trees. However, it’s easy to make mistakes that can affect the growth and health of your tree. Here are some common mistakes to avoid: 🚫

1. 🚫 Choosing Incompatible Rootstocks and Scions 🍏
- Not all rootstocks are compatible with every scion. Using a mismatched rootstock and scion can result in poor grafting success or weak tree growth. 🌳 Always ensure that the rootstock and scion are compatible for a healthy graft. 🌿
2. 🌞❄️ Ignoring Local Climate and Soil Conditions 🌱
- Failing to choose a rootstock suited to your local climate and soil conditions can lead to poor tree performance. For example, rootstocks that thrive in hot, dry climates may not do well in colder, wetter regions. 🌦️ Do your research to select a rootstock that matches your environmental conditions. 🌍
3. 🦠 Overlooking Disease Resistance 🍂
- Some rootstocks are more resistant to diseases than others. Neglecting to choose a rootstock with good disease resistance could lead to tree health problems, like root rot or fungal infections. 🌿 Always consider disease-resistant rootstocks, especially if your region is prone to specific soil-borne diseases. 🦠
4. 🍎🍐 Focusing Only on Fruit Variety 🍒
- While the fruit variety (scion) is important, the rootstock plays an equally vital role in the tree’s success. Don’t focus solely on the type of fruit you want to grow; make sure the rootstock complements your goals in terms of tree size, vigor, and health. 🌳
5. 🌳 Choosing a Rootstock Without Considering Tree Size 🍏
- Rootstocks control the size of your tree. If you want a dwarf tree for small spaces or easier harvesting, choose a dwarfing rootstock. 🍋 Conversely, if you want a larger tree with a bigger yield, select a full-size rootstock. Choosing the wrong size can affect your tree’s growth and overall fruit production. 🍊
6. 🧑🌾 Neglecting Long-Term Maintenance 🌿
- Some rootstocks require more maintenance than others. For example, certain dwarfing rootstocks might need more frequent care and support, like staking or extra watering. Don’t overlook the long-term care requirements when making your choice. 🌱
By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll set yourself up for success and grow healthy, productive fruit trees! 🍊🍓🌿
🌳🍎 Final Thoughts 🍏
Choosing the right rootstock for grafting fruit trees is essential to ensure the health, size, and productivity of your tree. 🌱 By understanding the different types of rootstocks and considering factors like climate, soil, disease resistance, and tree size, you can make an informed decision that sets your fruit trees up for long-term success. 🌿

With the right rootstock in place, you’ll not only enhance the growth and resilience of your fruit trees but also enjoy a bountiful harvest for years to come. 🍏🍑 So, take your time, do the research, and watch your grafted fruit trees flourish! 🌳🌿 Choosing the right Rootstock Selection for Grafting Fruit Trees plays a crucial role in ensuring the long-term success and productivity of your orchard. 🌳🍎
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best rootstock for apple trees?
The best rootstock for apple trees depends on your space and needs. For smaller spaces, M9 is a dwarfing rootstock, while MM106 is a semi-dwarf that balances tree size and fruit production.
Can I graft any fruit onto any rootstock?
No, not all rootstocks are compatible with every type of fruit. It’s essential to choose a rootstock that works well with your specific scion to ensure successful grafting and healthy growth.
How do I know which rootstock is best for my climate?
Climate is key in choosing the right rootstock. For example, Trifoliate Orange works well in cold climates, while Carrizo is suitable for warmer areas. Consider local growing conditions and consult with experts to make the right choice.
What happens if I choose the wrong rootstock?
Choosing the wrong rootstock can result in poor tree health, slow growth, or even graft failure. It may also affect the tree’s fruit quality and its ability to withstand pests or diseases.
Can rootstock affect the size and growth rate of my tree?
Yes, rootstock significantly influences tree size. Dwarfing rootstocks, like M9, create smaller trees, while full-size rootstocks, like Lovell for peaches, encourage larger, more vigorous trees.
How do I select the right rootstock for disease resistance?
Look for rootstocks known for their resistance to common diseases in your area. For example, MM106 offers resistance to apple tree diseases, while Pyrus rootstocks provide fire blight resistance in pears.
Can rootstock affect the fruit's taste and yield?
Yes, rootstock selection can influence the fruit’s size, flavor, and yield. Some rootstocks improve fruit quality, while others focus more on boosting tree size or overall productivity.
How long does it take for a grafted tree to start producing fruit?
It typically takes a few years for grafted fruit trees to mature and begin producing fruit, depending on the rootstock and scion. Dwarfing rootstocks may speed up fruit production, while full-sized trees may take longer to bear fruit.
