
Sorghum Seeds for Planting: How to Grow Your Own Crop
Sorghum seeds for planting are readily available and can be a great addition to your garden. If you’re looking to grow your own crop of sorghum, it’s important to start with high-quality seeds. When selecting your seeds, look for varieties that are well-suited to your climate and soil conditions. Once you have your seeds, it’s time to start planting. Prepare the soil by loosening it and removing any debris. Plant the seeds at the appropriate depth and spacing, and water them thoroughly. As your sorghum crop begins to grow, be sure to provide it with the necessary care, including regular watering and protection from pests and diseases. When it comes time to harvest your sorghum, be sure to do so at the right time to ensure the best quality crop. By following these steps and tips, you can successfully grow your own sorghum crop and enjoy the many benefits it has to offer.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Sorghum Plants
Sorghum plants are a great crop to grow, whether for food, animal feed, or biofuel. When growing sorghum, it’s important to start with good quality seeds that are well-suited to your climate and soil conditions. When planting, make sure to prepare the soil by loosening it and removing any debris, then plant the seeds at the appropriate depth and spacing. It’s important to provide the necessary care for your sorghum crop, including regular watering and protection from pests and diseases. When it’s time to harvest, make sure to do so at the right time to ensure the best quality crop. By following these steps and tips, you can successfully grow your own sorghum crop and enjoy the many benefits it has to offer.
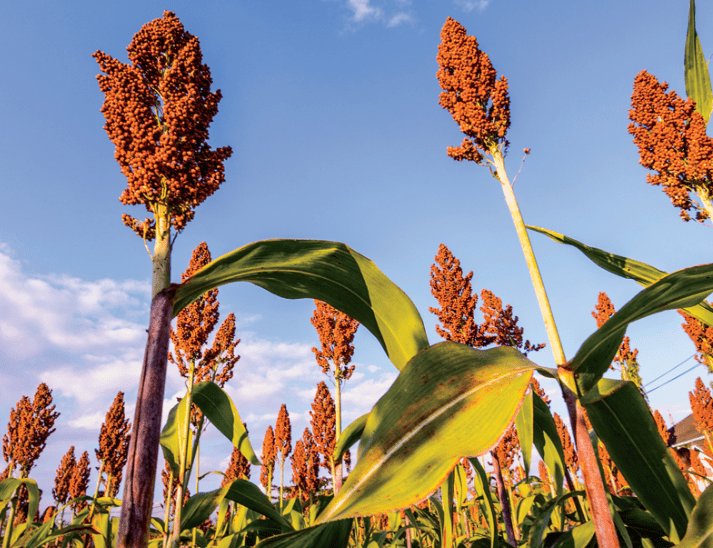

Describe the sorghum plant, its characteristics, and its importance as a cereal grain.
Sorghum is a versatile plant that is an important cereal grain in many parts of the world. It is a warm-season grass that can grow up to 15 feet tall and has large, corn-like leaves. Sorghum comes in many different varieties, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. It is drought-tolerant and can thrive in dry, arid conditions, making it an important crop for areas with limited water resources.
Sorghum is used for a variety of purposes, including human consumption, animal feed, and biofuel production. As a cereal grain, sorghum is a staple food for many people and is used to make flour, porridge, and other food products. It is also a valuable source of nutrients, including protein, fiber, and antioxidants. In addition to its uses as a food crop, sorghum is also fed to livestock and is used in the production of ethanol and other biofuels.
Discuss the various types of sorghum, including grain sorghum, sweet sorghum, and forage sorghum.
Sorghum is a versatile and important crop with many different varieties, each serving various purposes. Grain sorghum is primarily used as a cereal grain for human consumption, animal feed, and biofuel production. It is a valuable source of nutrients and is a staple food for many people, used to make flour, porridge, and other food products. Sweet sorghum, on the other hand, is primarily used for the production of syrup and biofuels due to its high sugar content. It is also used as animal feed and forage. Forage sorghum is mainly used as feed for livestock and is known for its high biomass production and adaptability to various environmental conditions. Each type of sorghum has its own unique characteristics and uses, making it a valuable and versatile crop for both human and animal consumption, as well as for biofuel production.
Benefits of Growing Sorghum from Seeds
Detail the economic, nutritional, and environmental benefits of growing sorghum.
Growing sorghum offers a range of economic, nutritional, and environmental benefits. From an economic standpoint, sorghum is a valuable crop due to its versatility and multiple uses. Grain sorghum can be sold for human consumption, animal feed, or used in biofuel production, providing income opportunities for farmers. Sweet sorghum, with its high sugar content, can be used to produce syrup and biofuels, further adding to its economic value. Additionally, forage sorghum serves as a valuable feed for livestock, contributing to the agricultural economy.

Nutritionally, sorghum is a rich source of nutrients and serves as a staple food for many people around the world. It is used to make flour, porridge, and other food products, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and energy. Forage sorghum also contributes to the nutritional needs of livestock, supporting their health and well-being.
From an environmental perspective, growing sorghum can have positive impacts. It is a drought-tolerant crop, requiring less water than other grains, which can help conserve water resources. Additionally, sorghum has a deep root system that helps prevent soil erosion and improve soil quality. By growing sorghum, farmers can contribute to sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
Discuss its drought tolerance, versatility, and sustainability compared to other crops.
Sorghum is a highly versatile and sustainable crop with excellent drought tolerance compared to other crops. It is a staple food in many parts of the world and is used to make flour, porridge, and other food products that provide essential nutrients and energy. Forage sorghum also plays a crucial role in providing nutrition for livestock, supporting their health and well-being.
From an environmental perspective, sorghum is a sustainable choice for farmers. Its drought tolerance means that it requires less water than other grains, which can help conserve water resources, especially in arid regions. Additionally, sorghum has a deep root system that helps prevent soil erosion and improves soil quality, making it an environmentally friendly option for crop production.
Selecting the Right Sorghum Seeds
Provide tips on selecting high-quality sorghum seeds for planting.
When selecting high-quality sorghum seeds for planting, there are a few key factors to consider. First, look for seeds that are certified by a reputable seed supplier. Certified seeds are rigorously tested and proven to have high germination rates and genetic purity, ensuring that you are starting with the best possible foundation for your crop.
Next, consider the specific characteristics of the sorghum variety you want to plant. Different varieties have different traits, such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and yield potential. Choose a variety that aligns with your specific growing conditions and farming goals.
Additionally, pay attention to the seed size, shape, and color. Healthy, high-quality seeds should be uniform in size and shape, with a consistent color and no signs of damage or disease. Avoid seeds that are discolored, misshapen, or show any signs of mold or pest damage.

Finally, consider the source of the seeds and their handling and storage conditions. It’s important to purchase seeds from a reputable supplier who follows proper storage and handling practices to ensure the viability and quality of the seeds.
By carefully selecting high-quality sorghum seeds for planting, you can set yourself up for a successful and productive growing season.
Discuss factors to consider, such as climate, soil type, and intended use.
When choosing sorghum seeds for planting, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure a successful growing season. Climate plays a crucial role in the success of your sorghum crop, so it’s important to select a variety that is well-suited to your specific growing conditions. Consider the average temperature, precipitation, and length of the growing season in your area when choosing your seeds.
Soil type is another important factor to consider when selecting sorghum seeds. Different sorghum varieties thrive in different soil types, so it’s important to choose seeds that are well-adapted to the soil on your farm. Consider the texture, fertility, and drainage of your soil when making your selection.
In addition to climate and soil type, it’s important to consider your intended use for the sorghum crop. Whether you plan to use it for grain, forage, biofuel, or other purposes, there are specific varieties that are best suited for each use. Be sure to select a variety that aligns with your specific farming goals and intended use for the crop.
When choosing sorghum seeds, pay attention to the seed size, shape, and color. Healthy, high-quality seeds should be uniform in size and shape, with a consistent color and no signs of damage or disease. Avoid seeds that are discolored, misshapen, or show any signs of mold or pest damage.
Preparing for Planting
Detail the steps to prepare the soil and planting area for sorghum seeds.
Step 1: Clear the planting area of any debris, rocks, or large clumps of soil. This will provide a clean and even surface for planting the sorghum seeds.
Step 2: Test the soil to determine its pH levels and nutrient content. Sorghum thrives in slightly acidic to neutral soil with good fertility. If necessary, amend the soil with organic matter or fertilizers to improve its nutrient content and pH levels.
Step 3: Till the soil to a depth of 4-6 inches to create a loose, well-aerated seedbed. This will allow the sorghum seeds to establish strong root systems and access nutrients and water more easily.
Step 4: Create rows for planting by using a hoe or garden rake to make furrows in the soil. Space the rows according to the recommended planting distance for the specific sorghum variety you have chosen.
Step 5: Plant the sorghum seeds at the appropriate depth, typically around 1-2 inches deep. Space the seeds according to the recommended seeding rate for the specific variety.
Step 6: Cover the seeds with soil and lightly pack the soil to ensure good seed-to-soil contact. Water the planting area thoroughly to promote germination and establishment of the sorghum seeds.
By following these steps, you can effectively prepare the soil and planting area for sorghum seeds, setting the stage for successful growth and development of your sorghum crop.
Discuss the ideal climate and growing conditions for sorghum, including temperature and rainfall requirements.
Sorghum is a versatile and resilient crop that can thrive in a variety of climates and growing conditions. However, the ideal climate for sorghum cultivation is a warm and dry environment. Sorghum requires temperatures between 75-85 degrees Fahrenheit for optimal growth. It is also important to note that sorghum is a drought-tolerant crop, making it well-suited for areas with low rainfall. In fact, sorghum can withstand dry conditions and still produce a good yield, making it a valuable crop in regions with limited water resources. When it comes to rainfall requirements, sorghum typically needs around 18-24 inches of rainfall throughout the growing season. However, sorghum can still grow in areas with lower rainfall, as long as there is access to irrigation or other water sources. Overall, sorghum is adaptable to a range of climate and growing conditions, making it a valuable crop for farmers around the world.
How to Plant Sorghum Seeds
Step-by-step guide on planting sorghum seeds, including seedbed preparation and planting methods.
Planting sorghum seeds requires careful preparation and attention to detail. The first step is to prepare the seedbed by plowing and harrowing the soil to create a smooth, level surface. It’s important to ensure that the soil is well-drained and free of any clods or debris. Once the seedbed is prepared, you can begin planting the sorghum seeds. There are several methods for planting sorghum, including broadcasting, drilling, and using a precision planter. Broadcasting involves spreading the seeds evenly across the seedbed, while drilling involves planting the seeds in rows using a seed drill. Precision planters are also available for more controlled and accurate planting. Whichever method you choose, it’s important to ensure that the seeds are planted at the appropriate depth and spacing for optimal germination and growth. After planting, it’s important to provide the sorghum seeds with adequate water and nutrients to support their growth. With proper care and attention, you can expect a successful sorghum harvest.
Discuss spacing, seeding rates, and depth for optimal germination and growth.
When planting sorghum, it’s important to consider spacing, seeding rates, and depth for optimal germination and growth. The spacing between sorghum seeds should be around 12-36 inches, depending on the variety and planting method. The seeding rates can vary, but a common recommendation is to plant around 75,000-100,000 seeds per acre. As for the depth of planting, sorghum seeds should be planted at a depth of 1-2 inches in well-prepared soil. This will ensure that the seeds have adequate contact with the soil for germination.
It’s also important to consider the planting method, whether it’s broadcasting, drilling, or using a precision planter. Broadcasting involves spreading the seeds evenly across the seedbed, while drilling plants the seeds in rows using a seed drill. Precision planters are also available for more controlled and accurate planting.
After planting, it’s crucial to provide the sorghum seeds with adequate water and nutrients to support their growth. Proper irrigation and fertilization practices are essential for ensuring the health and productivity of the crop.
By paying attention to spacing, seeding rates, and depth, and providing proper care and attention, you can expect to see optimal germination and growth in your sorghum crop.
Caring for Sorghum Plants
Detailed care guide for sorghum plants, including watering, fertilizing, and weed control.

When caring for sorghum plants, it’s important to ensure that the seeds have adequate contact with the soil for germination. The planting method, whether it’s broadcasting, drilling, or using a precision planter, should be carefully considered. Broadcasting involves spreading the seeds evenly across the seedbed, while drilling plants the seeds in rows using a seed drill. Precision planters are also available for more controlled and accurate planting. After planting, it’s crucial to provide the sorghum seeds with adequate water and nutrients to support their growth. Proper irrigation and fertilization practices are essential for ensuring the health and productivity of the crop. Additionally, it’s important to pay attention to spacing, seeding rates, and depth to ensure optimal germination and growth. In addition to watering and fertilizing, weed control is also an important aspect of caring for sorghum plants. By following a detailed care guide and providing proper care and attention, you can expect to see healthy and productive sorghum crops.
Discuss common pests and diseases affecting sorghum and strategies for prevention and management.
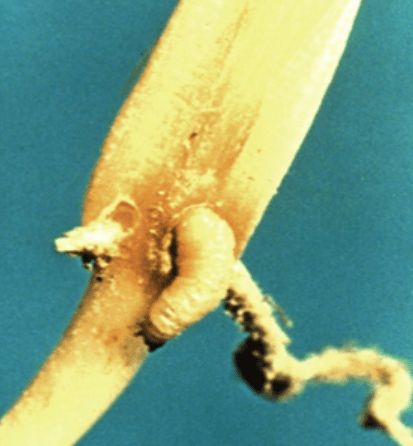
Sorghum crops can be affected by several pests and diseases, including aphids, armyworms, mites, and sorghum midge. It’s important to monitor for these pests and take preventive measures to manage their populations. This can include using insecticidal treatments, implementing crop rotation, and using natural predators to control pest populations. In terms of diseases, common issues for sorghum crops include smut, ergot, and leaf blight. Proper crop rotation, sanitation, and selecting disease-resistant varieties can help prevent and manage these diseases. Additionally, practicing good irrigation practices and providing proper air circulation can help prevent the development and spread of diseases. Overall, it’s crucial to regularly monitor sorghum crops for signs of pests and diseases and take proactive measures for prevention and management. By being proactive and implementing sound agricultural practices, farmers can ensure the health and productivity of their sorghum crops.
Pollination and Fertilization
Are essential processes in the reproductive cycle of plants. Pollination occurs when pollen from the male part of the flower (the stamen) is transferred to the female part of the flower (the pistil), leading to the fertilization of the ovule and the development of seeds. This process can occur through various means, including wind, water, and most commonly, through the activity of pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds.
Fertilization, on the other hand, occurs when the male gametes (pollen) combine with the female gametes (ovule) to form a zygote, which eventually develops into a seed. This process is crucial for the growth and development of plants, as it leads to the production of offspring and the continuation of the plant species.
It’s important for farmers and gardeners to understand the importance of pollination and fertilization in order to ensure the successful growth and reproduction of their plants. By providing a favorable environment for pollinators, such as planting native flowers and minimizing pesticide use, and by ensuring proper soil fertility and nutrient levels, they can promote healthy pollination and fertilization processes. This, in turn, will lead to better crop yields and the overall health of their plants.
Harvesting Sorghum

Is an important part of the farming process. Sorghum is typically harvested when the grain reaches the hard dough stage, which is when the seeds are fully developed and have a hard, starchy endosperm. The timing of the harvest is crucial to ensure high-quality grain and maximum yield.
When harvesting sorghum, it is important to use the right equipment, such as a combine harvester, to efficiently and effectively harvest the crop. The crop should be harvested when the moisture content is around 20-25% to prevent shattering of the grain and to facilitate proper drying and storage.
After harvesting, the grain should be properly dried and stored to maintain its quality and prevent spoilage. Proper storage conditions, such as adequate ventilation and moisture control, are essential to preserve the grain and prevent mold and insect infestations.
Uses of Sorghum
Explore the diverse uses of sorghum, including food, feed, and industrial applications.
Sorghum is a versatile crop with diverse uses, including food, feed, and industrial applications. In terms of food, sorghum can be used to make flour, porridge, and even alcoholic beverages. It is a gluten-free grain, making it a great option for those with gluten sensitivities. In addition, sorghum can be used as a feed for livestock, providing essential nutrients for animals. In terms of industrial applications, sorghum can be used to produce biofuels, paper products, and even building materials. Its versatility and resilience make it a valuable crop for farmers and a sustainable option for various industries.
Common Problems and Solutions
Proper storage conditions, such as adequate ventilation and moisture control, are essential to preserve the grain and prevent mold and insect infestations. When storing sorghum, it’s important to keep it in a dry and well-ventilated area to prevent moisture from causing mold or attracting insects. Using airtight containers or bags can also help protect the grain from pests and contaminants.
In terms of uses, sorghum is a versatile crop with diverse applications. It can be used to make flour, porridge, and alcoholic beverages, making it a valuable food source. Sorghum is also used as a feed for livestock, providing essential nutrients for animals. Additionally, it can be used in industrial applications to produce biofuels, paper products, and building materials.
Overall, sorghum’s resilience and versatility make it a valuable crop for farmers and a sustainable option for various industries. By addressing common problems such as storage and maximizing its diverse uses, sorghum can continue to be an important and sustainable crop for the future.
In conclusion, growing sorghum from seeds can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this post, you can successfully grow your own crop of sorghum and enjoy the satisfaction of harvesting your own homegrown grains. Whether you’re looking to expand your gardening skills or simply enjoy the process of growing your own food, growing sorghum can be a great addition to your gardening endeavors. Happy planting!
Frequently asked questions And Answer
Sorghum is a type of cereal grain that is grown for its edible seeds and used for a variety of purposes, including human consumption, animal feed, and biofuel production.
Sorghum thrives in warm climates with temperatures between 75-85°F. It is also drought-tolerant and can grow in areas with limited rainfall.
Sorghum typically takes 90-120 days to reach maturity, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
Sorghum plants should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods. Fertilizer can also be applied to promote healthy growth. Additionally, weeds should be kept under control to prevent competition for nutrients and water.
Sorghum is ready to harvest when the seeds have turned hard and the plant has dried out. Cut the stalks close to the ground and allow them to dry further before threshing the seeds.
Harvested sorghum seeds can be used for making flour, syrup, animal feed, or even popped like popcorn. They can also be saved for planting in the next growing season.
Sorghum is susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases, including aphids, mites, and fungal infections. Proper crop management and pest control measures can help prevent and manage these issues.
