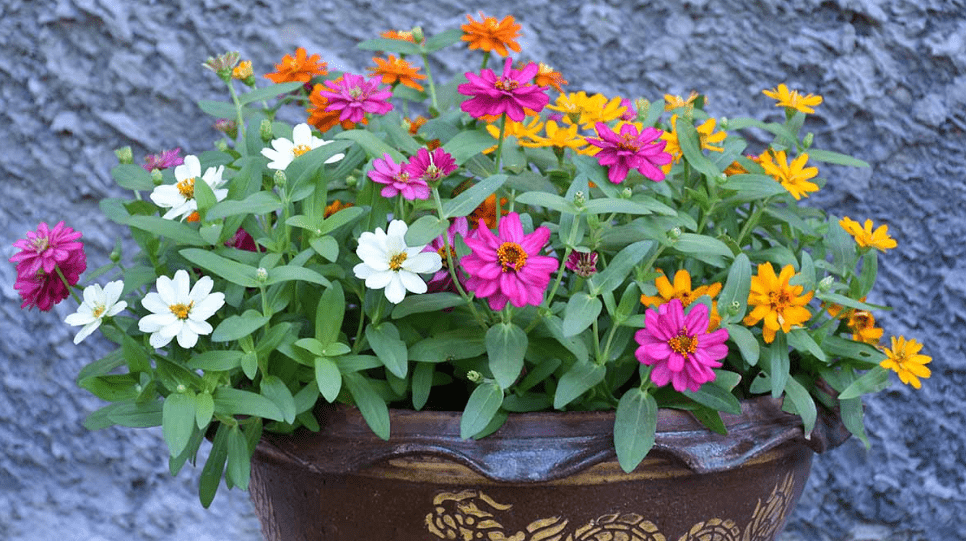

Grow Zinnias in Containers: Easy Steps for Vibrant Garden Beauty
Zinnias are a beautiful and vibrant addition to any garden, and growing them in containers can be a great way to add color and beauty to your outdoor space. In this article, we will provide you with easy, step-by-step instructions on how to successfully grow zinnias in containers, from selecting the right containers to proper care and maintenance. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, these tips will help you create a stunning display of zinnias in your garden.
Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing the Right Container
A. Types of containers suitable for growing zinnias (e.g., pots, hanging baskets)
When it comes to growing zinnias in containers, it’s important to choose the right type of container. Pots and hanging baskets are both great options for growing zinnias. Pots are ideal for smaller zinnia varieties and can be placed on the ground or elevated on a patio or deck. Hanging baskets are perfect for creating a cascading effect with trailing zinnias, adding a beautiful touch to your garden. Whichever type of container you choose, make sure it has good drainage to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Additionally, consider the size of the container – zinnias need space to grow, so choose a container that allows for proper root development and growth. By selecting the right container, you can create a stunning display of zinnias that will add vibrant beauty to your garden.
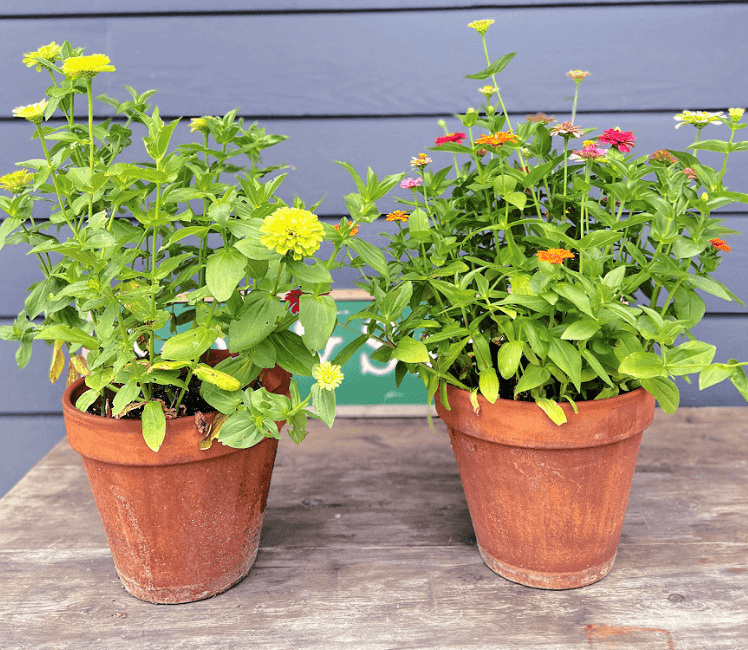

B. Material options and their benefits.
When it comes to growing zinnias in containers, there are a few material options to consider, each with its own benefits. One popular option is terracotta pots, which are not only visually appealing but also allow for good air circulation and drainage. Another option is plastic pots, which are lightweight and durable, making them easy to move around and resistant to breakage. Hanging baskets are also a great choice for growing zinnias, as they provide a cascading effect and can add a beautiful touch to your garden. Whichever material you choose, make sure the container has good drainage to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Additionally, consider the size of the container – zinnias need space to grow, so choose a container that allows for proper root development and growth. With the right material and size, you can create a stunning display of zinnias that will add vibrant beauty to your garden.
Selecting Zinnia Varieties
A. Overview of zinnia varieties suitable for container gardening (e.g., dwarf, compact).
When selecting zinnias for container gardening, it’s important to choose varieties that are well-suited for smaller spaces. Dwarf and compact zinnia varieties are ideal for containers, as they have a more confined growth habit and won’t overwhelm the container. Some popular zinnia varieties for container gardening include the Zinnia angustifolia ‘Crystal White’ and ‘Crystal Orange’, as well as the Zinnia marylandica ‘Zahara’ series, which are all known for their compact size and prolific blooming. When choosing zinnia varieties for containers, look for those that are labeled as suitable for compact or container gardening, as these will be the best options for creating a stunning display in your containers.
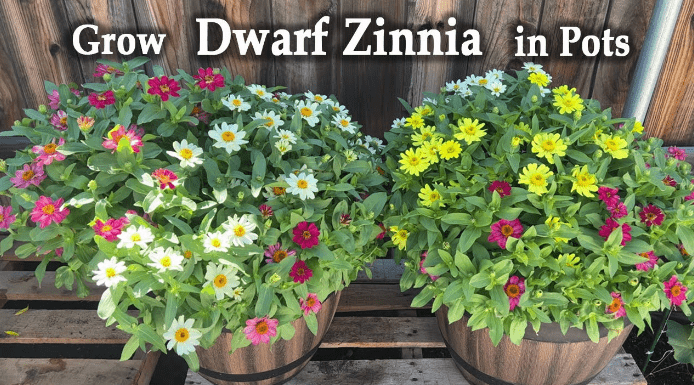
B. Considerations based on climate and space constraints
When growing zinnias in containers, it’s important to consider your climate and space constraints. Make sure to choose zinnia varieties that are well-suited for smaller spaces, such as dwarf and compact varieties. These types of zinnias won’t overwhelm the container and will be easier to maintain. Additionally, take into account your climate and choose zinnia varieties that are suitable for the weather conditions in your area. Some zinnia varieties are more tolerant to heat, while others are better suited for cooler climates. By considering these factors, you can ensure that your zinnias will thrive and add beauty and color to your garden.
C. Color options and aesthetic considerations.
When choosing zinnias for your container garden, consider the color options and aesthetic considerations. Zinnias come in a wide range of vibrant colors, from soft pastels to bold, bright hues. Think about the color scheme of your garden or outdoor space and choose zinnias that complement it. You can also mix and match different zinnia varieties to create visually stunning arrangements. Additionally, consider the height and shape of the zinnia plants, as well as the size of the container. Taller zinnias can add dimension and interest to your container garden, while shorter, bushier varieties can create a more compact, lush look. By carefully selecting zinnias based on their color, height, and shape, you can create a beautiful and cohesive container garden.
Preparing the Container and Soil
A. Steps for preparing the container (cleaning, adding drainage)
Before planting your zinnias in a container, it’s important to properly prepare the container and soil. Start by choosing a container that is large enough to accommodate the zinnias and has drainage holes at the bottom. If the container has been used for planting before, make sure to thoroughly clean it with soap and water to remove any dirt and debris. Once the container is clean, add a layer of gravel or broken pottery to the bottom to improve drainage and prevent waterlogging. Then, fill the container with a high-quality potting mix that is well-draining and nutrient-rich. Avoid using regular garden soil, as it can become compacted and hinder root growth in a container. Once the container and soil are prepared, you can proceed with planting your zinnias and watch them thrive in your container garden.
B. Choosing the right potting mix for zinnias (well-draining, nutrient-rich)
When choosing a potting mix for planting zinnias in a container, it’s important to select a well-draining and nutrient-rich option. Regular garden soil can become compacted in a container, which can hinder root growth and overall plant health. Look for a high-quality potting mix specifically designed for containers, as these mixes are formulated to provide good drainage and ample nutrients for your plants. Avoid using soil that may contain garden pests or diseases. With the right potting mix, your zinnias will have the best chance of thriving in your container garden.
C. Importance of soil amendments and fertilizers
Soil amendments and fertilizers play a crucial role in the success of your container garden, especially when planting zinnias. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can improve soil structure and fertility. Additionally, incorporating a balanced fertilizer can provide the necessary nutrients for healthy plant growth. These amendments and fertilizers help ensure that your zinnias have the essential elements for strong roots and vibrant blooms. It’s important to follow the recommended application rates and timing for the specific needs of zinnias in containers to promote their overall health and longevity.
Planting Zinnias
A. Best practices for planting zinnia seeds or transplants in containers
When planting zinnias in containers, it’s best to start with a high-quality potting mix that is well-draining and nutrient-rich. Make sure to sow the zinnia seeds or transplant the seedlings at the appropriate depth and spacing according to the plants’ specific requirements. Water the zinnias thoroughly after planting and continue to provide consistent moisture throughout the growing season. It’s also important to place the containers in a location that receives at least six hours of sunlight per day. Lastly, consider using supports or trellises for taller zinnia varieties to help them grow upright and prevent them from bending or breaking. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your zinnias have the best chance of thriving in your container garden.
B. Proper spacing and depth guidelines
When planting zinnias in containers, it’s important to follow the recommended spacing and depth guidelines for the specific variety of zinnia you are planting. Typically, zinnia seeds should be planted at a depth of 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch in the potting mix, while transplants should be placed at the same depth as they were in their original container. As for spacing, smaller zinnia varieties can be planted 6-12 inches apart, while larger varieties may need 12-18 inches of space between plants. Following these guidelines will ensure that the zinnias have enough room to grow and thrive in the container.
C. Watering techniques to establish healthy roots
When it comes to watering zinnias in containers, it’s important to establish a healthy root system. Zinnias prefer well-drained soil, so it’s best to water them deeply and infrequently rather than shallowly and frequently. This will encourage the roots to grow deeper into the soil in search of water, creating a stronger and more resilient plant. It’s also important to water the zinnias at the base of the plant rather than from above, as moisture on the leaves can lead to disease. Additionally, it’s best to water in the morning to allow any excess moisture to evaporate during the day, reducing the risk of fungal issues. By following these watering techniques, you can ensure that your zinnias develop healthy and robust root systems in their container garden.
Caring for Zinnias in Containers
A. Watering schedule and moisture management
Zinnias in containers require a specific watering schedule and moisture management to ensure healthy growth. It’s best to water them deeply and infrequently, rather than shallowly and frequently, to encourage the roots to grow deeper into the soil. Water the zinnias at the base of the plant to avoid moisture on the leaves, which can lead to disease. It’s also recommended to water in the morning to allow for evaporation throughout the day, reducing the risk of fungal issues.
B. Fertilization tips for promoting blooming
To promote blooming, it’s important to fertilize your zinnias in containers. Choose a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer and apply it every 2-4 weeks during the growing season. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for the proper dilution and application method. Additionally, deadheading or removing spent flowers can also encourage more blooms to form. With the right fertilization and maintenance, you can enjoy vibrant and long-lasting zinnia blooms in your container garden.
C. Deadheading and pruning to encourage continuous flowering
To encourage continuous flowering in your zinnias, it’s important to regularly deadhead or remove spent flowers. This will redirect the plant’s energy into producing new blooms. Additionally, pruning the plant by cutting back any leggy or overgrown stems can also help to promote new growth and flowering. By implementing these maintenance techniques, you can enjoy a prolonged and abundant display of beautiful zinnia blooms in your garden.
Managing Pests and Diseases
A. Common pests and diseases affecting zinnias in containers.
Common pests that may affect zinnias in containers include aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. These pests can be managed by regularly inspecting your plants and using organic or chemical insecticides as necessary. Additionally, zinnias are susceptible to diseases such as powdery mildew and botrytis. To prevent these diseases, it’s important to avoid overwatering, provide good air circulation, and remove any infected plant material. By staying vigilant and managing pests and diseases, you can keep your zinnia container garden healthy and thriving.
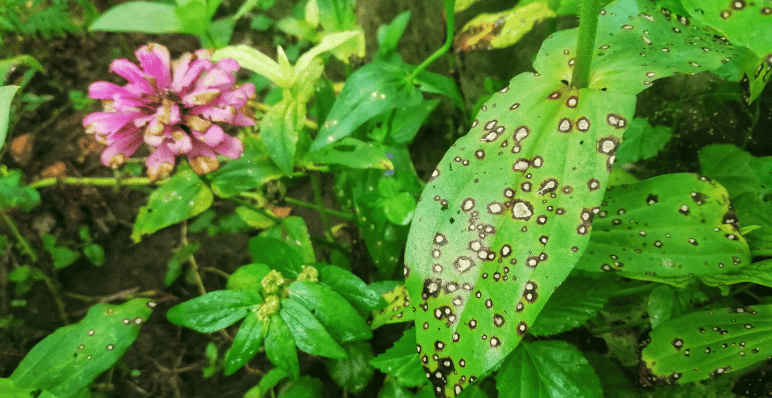
B. Organic pest control methods and preventive measures
Organic pest control methods and preventive measures for zinnias in containers include using natural predators such as ladybugs and lacewings to control aphids and mites, as well as regularly spraying plants with a mixture of water, soap, and oil to keep pests at bay. In terms of preventing diseases, using well-draining soil, avoiding overhead watering, and providing proper spacing between plants can help reduce the likelihood of powdery mildew and botrytis. By incorporating these organic pest control methods and preventive measures, you can maintain a healthy and vibrant zinnia container garden.
C. Recognizing symptoms and early intervention strategies
Recognizing symptoms and early intervention strategies are crucial for maintaining a healthy zinnia container garden. Keep an eye out for signs of pest infestations such as yellowing or distorted leaves, as well as symptoms of diseases like powdery mildew and botrytis, which may manifest as white or gray powdery spots on the leaves. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to take early intervention measures such as removing infected plant material, improving air circulation, and using organic pest control methods to prevent further spread. By being vigilant and taking proactive steps, you can effectively address issues before they become more severe and keep your zinnia container garden in optimal condition.
Supporting Zinnia Growth
A. Providing adequate sunlight and temperature conditions
Providing adequate sunlight and temperature conditions is essential for supporting zinnia growth in a container garden. Zinnias thrive in full sunlight, so be sure to place your container in a location where they can receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Additionally, zinnias prefer warm temperatures, so aim to keep your container garden in an area with temperatures between 70-90°F (21-32°C). By providing the right environmental conditions, you can help your zinnias grow healthy and vibrant.
B. Importance of proper air circulation in container gardening
Proper air circulation is also important for supporting zinnia growth in a container garden. Good air circulation helps prevent diseases and pests, as well as promotes strong and sturdy plant growth. To ensure proper air circulation, avoid overcrowding your container with too many plants and make sure there is some space between them. Additionally, consider placing your container in an area with a gentle breeze or use a small fan to help circulate the air. By maintaining proper air circulation, you can help your zinnias thrive and stay healthy.
C. Using stakes or supports for taller zinnia varieties
Using stakes or supports for taller zinnia varieties is important to prevent the plants from leaning or falling over as they grow. This can help promote straight and upright growth, as well as prevent damage to the stems and flowers. To support taller zinnia varieties, use stakes or cages that can be placed in the container and gently tied to the plant for added support. This will help keep the zinnias looking their best and prevent any potential damage as they continue to grow.
Harvesting and Enjoying Zinnias
A. Signs of readiness for harvesting zinnia flowers
Signs of readiness for harvesting zinnia flowers include fully opened petals, a strong stem, and vibrant color. It’s best to harvest zinnia flowers in the morning when they are at their peak freshness. Use sharp scissors or pruning shears to cut the stem at a 45-degree angle, and immediately place the cut stem in a container of water. This will help prolong the life of the zinnia flowers and allow you to enjoy them for a longer period of time.
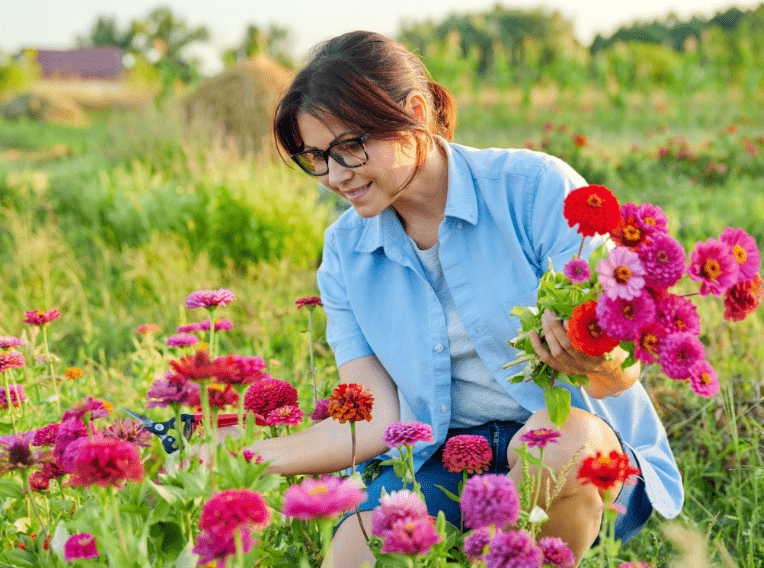

B. Tips for prolonging vase life
- Change the water in the vase every 2-3 days to keep it fresh and prevent bacterial growth
- Trim the stems every few days to remove any decaying or slimy parts and help the flowers absorb water more efficiently
- Keep the vase out of direct sunlight and away from any drafts to prevent wilting and drying out
- Consider adding a floral preservative to the water to extend the vase life even further
- Enjoy your beautiful zinnias and the vibrant color they bring to your home!
C. Creative ways to display zinnias in indoor and outdoor settings
Displaying zinnias in indoor and outdoor settings can add a pop of color and beauty to your space. In indoor settings, consider arranging zinnias in a vase with other complementary flowers or greenery for a stunning centerpiece. You can also create a simple and elegant display by placing a few zinnias in small bud vases and scattering them throughout your home.
In outdoor settings, zinnias can be used in a variety of ways to enhance your garden or patio. Planting them in flower beds or containers will create a vibrant and eye-catching display. Additionally, you can also use zinnias to create a unique and colorful border along pathways or garden beds.
For a more creative approach, consider drying zinnias and using them in craft projects such as making wreaths, pressed flower art, or potpourri. The vibrant colors of zinnias make them perfect for adding a touch of natural beauty to any DIY project.
No matter how you choose to display your zinnias, their cheerful colors and long vase life will bring joy and beauty to any space.
In conclusion, growing zinnias in containers is a great way to add vibrant beauty to your garden with minimal effort. By following these easy steps and providing the proper care, you can enjoy beautiful, colorful zinnias all season long. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, container gardening with zinnias is a great way to add a pop of color to your outdoor space. So go ahead and give it a try!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, you can definitely grow zinnias in containers. In fact, they are well-suited for container gardening and can add vibrant beauty to any garden or patio space.
Use a well-draining potting mix for growing zinnias in containers. This will help prevent waterlogging and promote healthy root growth.
Zinnias in containers should be watered regularly, especially during hot and dry weather. Keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged.
Yes, zinnias thrive in full sunlight, so make sure to place your containers in a sunny spot to promote healthy growth and vibrant blooms.
Yes, you can fertilize zinnias in containers with a balanced, all-purpose fertilizer. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for best results.
Keep an eye out for common pests such as aphids and caterpillars, and treat them with insecticidal soap if necessary. Also, make sure the containers have good air circulation to prevent fungal diseases.
Deadhead your zinnias regularly to promote continuous blooming. Simply remove faded blooms to encourage the plant to produce new flowers.
Zinnias are annual plants, so they typically do not survive the winter. However, you can collect their seeds and start new plants in the following growing season.
