
How Long Do Pecan Trees Produce? A Complete Guide to Maximizing Pecan Tree Yield and Lifespan
If you’ve ever planted a pecan tree or dreamt of growing your own nut harvest, you’ve likely asked, How long do pecan trees produce? Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just getting started, the longevity and productivity of your tree are crucial to achieving a successful harvest year after year. 🌰
Pecan trees are known for their impressive lifespan, but their peak production years can vary. Knowing when to expect a bountiful harvest, and how to maximize your tree’s yield, can save you time, effort, and frustration. Unfortunately, many new growers aren’t sure how to maintain a steady pecan supply, or how to keep their trees healthy for the long haul. That’s where this guide comes in.
In the following sections, we’ll break down everything you need to know about pecan tree production—from how long they produce, to tips on boosting yield, and how to care for your tree throughout its life. Stick with us, and you’ll be well on your way to becoming a pecan-growing pro! 🌱
Table of Contents
Toggle🧑🌾🌳 The Lifespan of Pecan Trees 🌳🧑🌾
When you plant a pecan tree, you’re planting for the long haul. 🌱 These majestic trees can live for over 100 years under the right conditions! 🌳 But here’s the catch: the productive lifespan—the number of years they bear nuts—doesn’t last that long. 🌰 So, how long do pecan trees produce? Let’s break it down! 📋

🌱How Long Do Pecan Trees Live? 🌱
Pecan trees are incredibly hardy and long-lived. 🌳 In the wild or with optimal care, they can survive for more than a century. 💪 However, as with any tree, their productivity starts to decline after a certain point. ⏳
🌿 Maximum lifespan:
100+ years
🌰 Most productive years:
30 to 50 years
After this, trees may still live for many more years, but their nut production will decrease significantly. 🍂
🧐Factors That Affect Pecan Tree Lifespan 🧐
Several factors influence how long a pecan tree remains healthy and productive. 🌿
🌱 Soil quality:
Healthy, well-draining soil ensures strong root systems. 🌍
💧 Watering:
Regular, deep watering during dry spells helps trees thrive. 🌊
🌞 Climate:
Pecan trees prefer warm, subtropical climates. 🌞 Extreme cold or droughts can shorten their lifespan. ❄️
🌿 Care:
Regular pruning, disease control, and pest management can all extend your tree’s life. 🌱
🌰 When Does a Pecan Tree Start to Produce Nuts? 🌰
A pecan tree typically starts producing nuts when it’s about 6-10 years old if grafted, and 15-20 years if grown from seed. 🌳 However, full yields usually don’t come until the tree reaches around 12-20 years. 🌱 Keep in mind that early nut production varies depending on tree variety and care. 🌿
📋 In Summary 📋
Pecan trees are long-lived, but their most fruitful years typically last 30-50 years. 🌳 Proper care can help ensure your tree produces quality nuts for decades, while neglect can shorten both its lifespan and productivity. 🍃 Now that you know the lifespan basics, let’s dive into how to make the most of your pecan tree’s productive years! 🌰
🌱🌰 When Do Pecan Trees Start Producing? 🌰🌱
One of the most common questions new pecan growers ask is, “When will my pecan tree start producing nuts?” 🌳 The answer depends on several factors, such as the tree’s variety, how it’s planted, and how well it’s cared for. 🌱 But don’t worry—we’re here to break it down! 🍂

🌳 The Early Years of Pecan Trees 🌳
Pecan trees are relatively slow starters. ⏳ They don’t produce nuts right away, but they will eventually reward your patience. 🌿
🌳 Grafted trees:
These are typically hybrids of different pecan varieties and start producing in 6-10 years. 🌱
🌰 Seedling trees:
Grown from seeds, these take longer—usually around 15-20 years to begin producing nuts. 🍃
⏳ Full Production Takes Time ⏳
While your pecan tree may produce a small number of nuts early on, full-scale production doesn’t kick in until the tree matures. 🌳 A tree needs time to develop a strong root system, establish healthy branches, and adapt to its environment. 🍃
🌰 Full nut production usually happens around 12-20 years of age.
At this stage, your tree is well-established and capable of producing significant yields of delicious pecans. 🌰
🌞 Factors That Affect Early Production 🌞
Several factors can either speed up or delay when your pecan tree starts bearing nuts: 🧐
🌞 Climate:
Warm, subtropical climates are ideal for pecans. 🌞 Colder climates can slow down growth and delay production. ❄️
🌳 Pollination:
Pecan trees need cross-pollination to produce a good crop. 🌼 Planting more than one tree of different varieties ensures better nut production. 🌱
🌿 Soil:
Well-drained, nutrient-rich soil helps young trees grow quickly, leading to earlier nut production. 🌾
In Summary 📋
- Grafted pecan trees typically start producing in 6-10 years.
- Seedlings take 15-20 years to bear nuts. 🌰
- Full yields usually come when your tree is well-established, typically around 12-20 years. 🍂
By planting multiple trees, caring for them properly, and choosing the right variety for your climate, you can encourage earlier and better production. 🌳 Keep these factors in mind, and your pecan harvest is just around the corner! 🌰🌿
🌿💪 Maximizing Pecan Tree Yield 💪🌿
If you want your pecan tree to thrive and produce a bountiful harvest year after year, you’ll need to focus on its care. 🌱 Maximizing your tree’s yield requires a few key practices that ensure it stays healthy, strong, and productive. 🌳 Let’s explore the best strategies for getting the most out of your pecan tree! 🌰

🌱 1. Soil Preparation and Maintenance 🌱
The foundation of any healthy tree begins with good soil. 🌍 Proper soil conditions are essential for optimal growth and nut production. 🌰
🌿 Soil pH:
Pecan trees prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH of 6.0-6.5. Consider doing a soil test to ensure proper pH levels. 📊
🌳 Drainage:
Make sure the soil drains well. Pecan trees don’t like standing water, so ensure your soil is loose and aerated. 🌱
🌾 Organic matter:
Adding compost or organic mulch helps improve soil fertility and retains moisture. 💧 It also adds beneficial microbes to the soil. 🌿
💧 2. Watering and Irrigation 💧
Pecan trees require a steady supply of water, especially during dry spells. 🌞 Deep watering is essential to encourage strong roots and healthy growth. 🌱
💦 Water deeply once or twice a week, especially during the hot summer months. 🌞
🚫 Avoid overwatering:
While pecan trees need moisture, they also require good drainage. 🌿 Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases. 🦠
🌳 Irrigation systems like drip irrigation can help maintain consistent moisture levels without waterlogging the roots. 💧
✂️ 3. Pruning and Thinning ✂️
Pruning isn’t just for shaping your tree—it also promotes better airflow, reduces disease risk, and encourages more nut-bearing branches. 🌳
🍂 Remove dead or diseased wood regularly to keep the tree healthy. 🌿
🌞 Thin branches to allow sunlight to reach the inner parts of the tree, which helps with better nut production. 🌞
✂️ Cut back competing limbs:
If there are too many limbs vying for resources, they can stunt the tree’s growth and reduce overall nut yield. 🌱
🌼 4. Pollination and Tree Spacing 🌼
Pecan trees are dioecious, meaning they have male and female flowers on separate trees. 🌳 For maximum yield, you’ll need to plant at least two trees of different varieties to ensure cross-pollination. 🌱
🌸 Cross-pollination:
Choose pecan varieties that bloom at the same time to boost pollination rates. 🌼
🌳 Proper spacing:
Trees should be spaced at least 30-40 feet apart to prevent overcrowding and ensure each tree gets enough sunlight and nutrients. 🌞
🌾 5. Fertilization 🌾
Pecan trees are heavy feeders, so proper fertilization is essential for healthy growth and high nut yields. 🌰
🌱 Fertilize in early spring with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer that’s high in nitrogen to encourage vigorous growth. 🌿
🍂 Reapply every 2-3 years:
Test soil nutrients regularly and adjust fertilization based on the results. 🌾 You may need to add potassium, phosphorus, or micronutrients if the soil is deficient. 🍃
🌳 Mulch around the base of the tree to retain moisture and provide nutrients as it decomposes. 🌱
🦠 6. Pest and Disease Management 🦠
Healthy trees are productive trees, so keeping pests and diseases in check is crucial for maximizing yield. 🐞
🌱 Watch for common pests like pecan weevils, aphids, and scale insects, which can damage leaves and nuts. 🦗
🌾 Control pests organically or with pesticides if necessary—be sure to follow all recommended guidelines to avoid harming the tree. 🍃
🌿 Prevent diseases:
Fungal infections like powdery mildew or root rot can stunt growth, so make sure the tree is well-pruned, not overwatered, and regularly inspected. 🌳
📋 In Summary 📋
Maximizing pecan tree yield requires a balance of proper soil, water, pruning, and pest management. 🌿 By giving your tree the care it needs, such as fertilizing, ensuring proper pollination, and managing irrigation, you’ll set yourself up for a productive harvest season after season. 🌰 Get these basics right, and your pecan tree will reward you with abundant nuts and years of growth. 🌳🍂
🌳⚖️ Factors That Affect Pecan Tree Production ⚖️🌳
Pecan trees are fairly low-maintenance, but their productivity can be influenced by a variety of factors. 🌱 Whether you’re new to growing pecans or looking to troubleshoot an underperforming tree, understanding these key elements can help you boost your tree’s yield and ensure it stays healthy for years to come. 🌿 Let’s dive into the factors that affect pecan tree production! 🌰
🌞❄️ 1. Weather and Climate 🌞❄️
Pecan trees thrive in warm, subtropical climates. 🌞 They need a long, hot growing season to produce a healthy crop, and extreme cold or heat can negatively impact their productivity. 🌿
🌡️ Ideal temperature:
Pecan trees need temperatures between 70°F and 90°F (21°C to 32°C) during the growing season. 🌞
❄️ Frost:
Frost can damage flowers in the spring, leading to reduced yields. Ideally, pecan trees should be planted in areas where the last frost occurs before late spring. 🌱
🌵 Drought:
Extended periods of drought can severely impact the health of your tree and the size of the harvest. While pecan trees are drought-tolerant, they still need regular water to produce well. 💧
🌱 2. Soil Quality and Nutrients 🌱
Good soil is the foundation for a healthy pecan tree. 🌍 The quality of the soil directly impacts growth and production. 🌰
🌿 Soil pH:
Pecan trees prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5. If the soil is too acidic or too alkaline, the tree may struggle to absorb necessary nutrients. 🍃
🧪 Nutrient-rich soil:
Ensure the soil has adequate amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Nitrogen is especially important during the growing season to promote healthy foliage and nut production. 🌱
💧 Well-drained soil:
Pecan trees do not tolerate waterlogged soil. Be sure the area where you plant your tree has good drainage to prevent root rot. 🌾
🌳 3. Tree Age and Variety 🌳
The age and variety of your pecan tree are significant factors in how much it produces each season. 🌿
🌱 Mature trees:
Pecan trees typically produce their highest yields between the ages of 30-50 years. Younger trees will bear fewer nuts, and older trees may see their production decline. 🌰
🌳 Tree variety:
Some pecan varieties are more productive than others. For example, varieties like Desirable and Pawnee are known for their higher yields and resistance to pests. Consider choosing varieties that are well-suited to your local climate and soil type. 🌿
🌼 4. Pollination and Cross-Pollination 🌼
Pecan trees are dioecious, meaning they require two separate trees (one male and one female) for cross-pollination. 🌳 Without proper pollination, your pecan tree may not produce nuts, or the yield may be low. 🌱
🌸 Cross-pollination:
Planting at least two trees of different varieties will improve pollination and increase nut production. Trees should be spaced 30-40 feet apart to facilitate better pollination. 🌿
🌬️ Wind:
Pecan trees rely on the wind to carry pollen from male flowers to female flowers. Be sure to plant your trees in a location with good airflow to enhance the chances of successful pollination. 🌳
🐛🦠 5. Pests and Diseases 🐛🦠
Pests and diseases are a significant threat to the health of your pecan tree. If left unchecked, they can cause a decrease in nut production or even kill the tree. 🌿
🦗 Common pests:
Pecan weevils, aphids, and hickory shuckworms can all damage your tree’s leaves and nuts. Regularly inspect your trees and treat infestations early. 🍂
🍄 Fungal diseases:
Pecan trees are susceptible to diseases like powdery mildew, leaf spot, and phytophthora (root rot). Proper pruning, good air circulation, and avoiding overwatering can help reduce the risk of these issues. 🍃
🚫 Prevention:
Regularly apply organic or chemical treatments for pests and diseases. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid harming your tree. 🐞
💧 6. Watering Practices 💧
Water plays a critical role in the overall health and production of pecan trees. 🌱 Too much or too little water can stress the tree, reducing the quality of its nuts. 🌰
🌿 Consistent watering:
Deep watering, especially during dry spells, is important for keeping the tree’s roots hydrated and healthy. 🌞
🚫 Avoid overwatering:
While consistent watering is necessary, avoid keeping the soil soggy. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other water-related diseases that stunt production. 🌿
💦 Irrigation systems:
Consider installing a drip irrigation system to ensure your tree gets the right amount of water, especially during dry spells. 💧
📋 In Summary 📋
Maximizing pecan tree production means understanding the factors that affect its growth. 🌳 Weather, soil quality, tree variety, pollination, pests, and watering all play vital roles in ensuring a fruitful harvest. By keeping an eye on these elements and making the necessary adjustments, you can help your pecan tree produce nuts year after year! 🌰🌿
🌳🌰 Pecan Tree Varieties and Their Yield Potential 🌰🌳
Choosing the right variety of pecan tree is one of the most important decisions you’ll make as a grower. 🌱 Different pecan varieties have varying growth habits, nut quality, and production rates. Some are better suited for specific climates, while others are more resistant to pests or diseases. 🌿 Let’s explore some of the most popular pecan tree varieties and their yield potential to help you make the best choice for your garden or orchard. 🌳

🍂 1. Desirable Pecan Tree 🍂
The Desirable pecan tree is one of the most widely grown and well-loved varieties for both home gardeners and commercial growers due to its high yield and quality. 🌰
🌳 Yield potential:
Desirable trees can produce large quantities of nuts once mature (typically after 12-15 years). 🌱
🌰 Nut quality:
The nuts are large, with thin shells and high-quality meat, making them popular for culinary uses. 🍽️
🌿 Best for:
Warmer climates (USDA hardiness zones 7-9), especially in areas with mild winters and long growing seasons. 🌞
🌰 2. Pawnee Pecan Tree 🌰
The Pawnee pecan tree is a high-yield variety that’s known for producing early, large crops. 🌳
🌳 Yield potential:
Pawnee trees can start producing in just 6-8 years (faster than many other varieties), making them an excellent choice for those looking for quicker results. 🌿
🌰 Nut quality:
Pawnee produces medium to large nuts with a high meat-to-shell ratio. They are sweet and flavorful. 🍬
🌿 Best for:
Warm, sunny climates (USDA hardiness zones 7-9), and they thrive in regions with longer growing seasons. 🌞
🌳 3. Chickasaw Pecan Tree 🌳
The Chickasaw pecan tree is a native variety often chosen for its resistance to disease and pests. 🌿
🌳 Yield potential:
Chickasaw trees produce a moderate but reliable yield, especially in less fertile soil. 🌱
🌰 Nut quality:
The nuts are smaller compared to other varieties, but they are well-suited for use in pies and other recipes. 🍰
🌿 Best for:
More tolerant of a variety of soil types, including clay. It’s suitable for USDA hardiness zones 6-9. 🌾
🌰 4. Stuart Pecan Tree 🌰
The Stuart pecan tree is another popular variety, often grown for its high yield and versatility. 🌳
🌳 Yield potential:
Once fully mature (around 12-15 years), Stuart trees can produce a generous amount of nuts each season. 🌱
🌰 Nut quality:
Medium-sized nuts with a good shell-to-meat ratio, often used for commercial production. 🌾
🌿 Best for:
Warmer climates and moderate soils (USDA hardiness zones 6-9). It’s more resilient to pests and diseases than other varieties. 🌳
🍂 5. Cape Fear Pecan Tree 🍂
The Cape Fear variety is gaining popularity for its resistance to common pecan diseases and its exceptional nut quality. 🌰
🌳 Yield potential:
High yields of large, high-quality nuts once the tree matures. 🌱
🌰 Nut quality:
Cape Fear pecans have a thin shell and are known for their excellent flavor and texture. 🍂
🌿 Best for:
Ideal for USDA hardiness zones 7-9, especially in areas where disease and pest resistance are a priority. 🌾
🌳 6. Mahan Pecan Tree 🌳
If you’re looking for a variety that can withstand harsher climates, the Mahan pecan tree might be the right choice. 🌱
🌳 Yield potential:
Mahan trees are reliable producers, though they take a little longer to mature (typically 12-18 years). ⏳
🌰 Nut quality:
The nuts are medium-sized, with a thicker shell but a rich, sweet flavor. 🍬
🌿 Best for:
USDA hardiness zones 7-9. It thrives in areas that experience colder winters and can handle light frost. ❄️
🌰 7. Elliott Pecan Tree 🌰
The Elliott pecan tree is known for its resistance to pests and high yields, making it a solid choice for growers. 🌳
🌳 Yield potential:
This variety starts producing around 8-12 years, with high yields once mature. 🌱
🌰 Nut quality:
Elliott nuts are small to medium in size, with a rich, buttery taste and a thinner shell. 🍪
🌿 Best for:
Warmer climates (USDA hardiness zones 7-9), particularly areas with long growing seasons. 🌞
🤔 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Variety 🤔
When selecting the right pecan tree variety for your garden or orchard, consider these key factors:
🌞 Climate:
Ensure the variety you choose is well-suited to your local climate. Some varieties, like Desirable and Pawnee, require warmer, subtropical conditions, while others, like Mahan, are more frost-tolerant. ❄️
🌱 Soil quality:
Some varieties are more adaptable to different soil types. For example, Chickasaw can handle less fertile soil, while others, like Desirable, prefer nutrient-rich, well-drained soils. 🌿
🌸 Pollination needs:
Pecan trees require cross-pollination. Planting multiple varieties nearby will boost yields and ensure better pollination. 🌳
🐛 Disease resistance:
Some varieties, like Cape Fear, are naturally more resistant to common diseases and pests, which can help reduce maintenance. 🌱
📋 In Summary 📋
Choosing the right pecan tree variety is essential for maximizing your yield potential. 🌳 Popular varieties like Desirable, Pawnee, and Stuart are known for their high yields and quality nuts. By considering your local climate, soil type, and pollination needs, you can select the perfect variety to suit your growing conditions. 🌰 Start with the best variety for your area, and you’ll soon be enjoying a bountiful pecan harvest! 🌳🌰
🌳❌ When Do Pecan Trees Stop Producing? ❌🌳
Pecan trees are known for their long lifespan, but just like any other tree, their productive years don’t last forever. 🌱 Knowing when your pecan tree’s production will begin to decline—and how to manage it—is key to maintaining a healthy, productive orchard or garden. 🌳 Let’s explore when pecan trees stop producing and what you can do to maximize their yield before that happens. 🌰

🌱 1. The Natural Decline of Older Trees 🌱
As pecan trees age, their ability to produce large quantities of nuts naturally decreases. 🍂 Most pecan trees have their most productive years between 30-50 years, after which production begins to decline. Here’s what you can expect as your tree ages: 🌳
🌿 Early years (6-15 years):
Trees are just starting to produce, and you’ll see a small number of nuts. 🌱
🌰 Prime years (15-50 years):
The tree is at its peak, producing large quantities of high-quality nuts. 🌰
🍂 Declining years (50+ years):
Nut production decreases, and trees may become more susceptible to diseases and pests. 🐜
🐾 2. Signs Your Pecan Tree is Slowing Down 🐾
While age is the most obvious factor in a pecan tree’s decline, there are other signs that your tree may be nearing the end of its productive years. 🌿
🌰 Reduced nut production:
If your tree produces fewer nuts each year, it could be a sign that it’s reaching the end of its productive life. 🌳
🍂 Smaller nuts:
Over time, the size of the nuts may decrease as the tree ages. 🌱
🌳 Weakened branches:
Older trees tend to have weaker limbs that are more prone to breaking, which can reduce the amount of fruit that is able to mature. 🌿
🌳 3. What Causes Older Trees to Stop Producing? 🌳
Several factors contribute to a pecan tree’s decrease in production as it ages. Here are the main ones: 🍂
🌱 Root decline:
As trees age, their root systems can deteriorate, making it harder for the tree to absorb the nutrients and water it needs. 💧
🦠 Pest and disease vulnerability:
Older trees are more prone to pest infestations and diseases, which can affect their overall health and productivity. 🐛
💪 Energy depletion:
After many years of producing nuts, the tree may not have enough energy to continue its high-output production. Nut-bearing branches may not develop as fully, leading to fewer nuts. 🌰
🌿 4. Can You Extend the Productive Life of a Pecan Tree? 🌿
While you can’t prevent aging, you can take steps to help your pecan tree remain productive for as long as possible. 🌱
🌳 Regular maintenance:
Pruning dead or diseased wood, ensuring proper irrigation, and applying fertilizers can help keep the tree healthy and maximize its remaining years of production. 🌳
🐛 Disease and pest control:
Regularly inspect your tree for signs of pests or diseases. Early treatment can prevent long-term damage and maintain the tree’s vitality. 🌿
🌱 Soil health:
Keeping the soil nutrient-rich and well-drained will support the overall health of the tree, even as it ages. 🌾
🌳➡️🌱 5. What Happens After the Tree Stops Producing? 🌳➡️🌱
Once a pecan tree significantly slows down its nut production, it may still have many years of life left. However, if you rely on it for harvesting nuts, you’ll likely need to replace it with a younger, more productive tree. 🌰
🌱 Replanting:
Consider planting new trees alongside older ones to ensure continued production. 🌳 It also allows for a smoother transition when your older tree starts producing less. 🍂
🌱 Alternatives:
Some growers opt for grafting new shoots or improving their care techniques to encourage a second wind of production from an aging tree. 🌿
📋 In Summary 📋
Pecan trees typically stop producing at full capacity around 50 years of age, but they can live much longer. 🌱 As trees age, you’ll see a decrease in both nut quantity and quality, and the tree may become more susceptible to diseases. Regular care can help extend the tree’s productive years, but eventually, you’ll need to plant younger trees to maintain a steady nut supply. 🌳 By understanding the natural life cycle of pecan trees, you can plan for the future and keep your orchard producing for decades to come! 🌰🌳
🌿🌳 Tips for Extending the Productive Life of Pecan Trees 🌳🌿
Pecan trees can live for over 100 years, but to ensure they continue to produce high-quality nuts throughout their lifespan, it’s important to take steps that support their health and productivity. 🌱 By following a few essential care practices, you can help extend the productive life of your pecan tree and keep it thriving for decades to come. 🌳
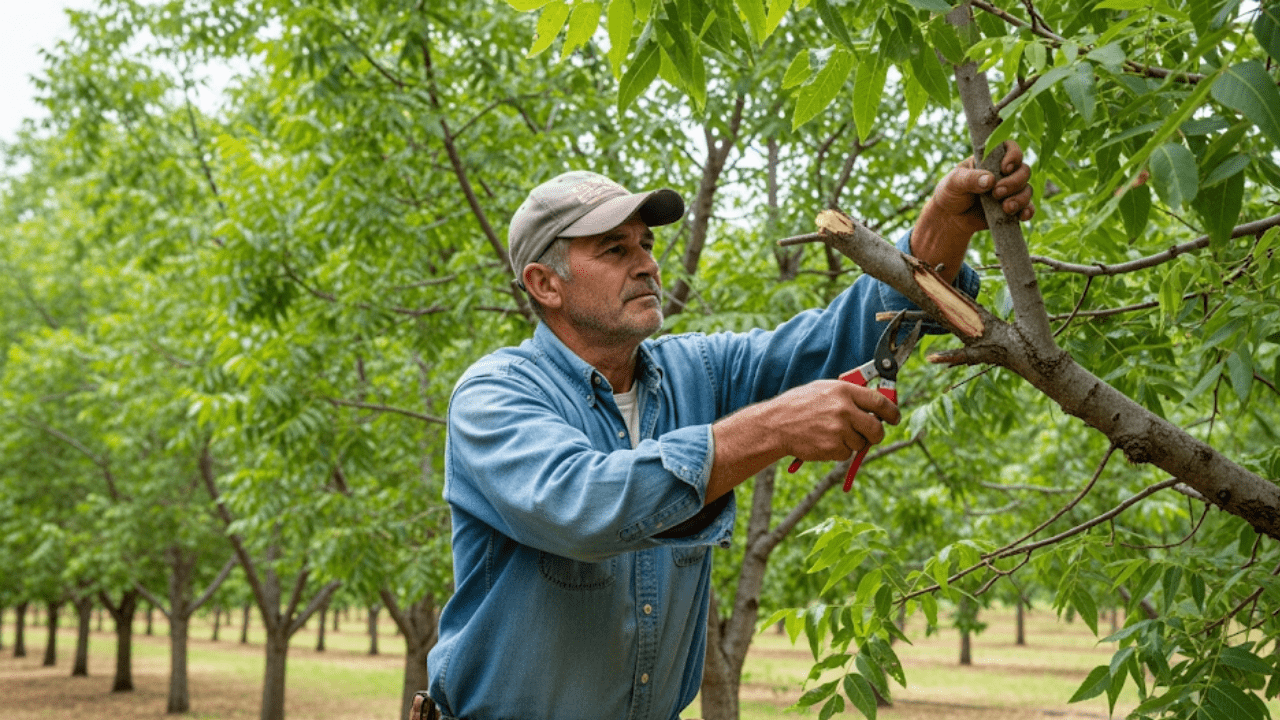

✂️ 1. Proper Pruning for Health and Airflow ✂️
Pruning is key to maintaining a healthy tree and maximizing nut production. 🌰 Regular pruning helps prevent disease, removes dead or damaged branches, and encourages better airflow within the tree canopy. 🌿
🌳 Remove dead or diseased branches regularly to avoid disease spread. 🦠
🌞 Thin crowded areas to allow sunlight to penetrate deeper into the tree, promoting better nut growth. 🌱
✂️ Cut back crossing branches that can rub together, causing injury or weakening the tree. 🌿
🌱 2. Maintain Soil Health and Fertilization 🌱
Healthy soil is the foundation for a productive pecan tree. 🍃 Ensuring the soil around your tree is nutrient-rich and well-drained will encourage strong roots and continued growth. 🌳
🌾 Test your soil regularly to ensure it’s within the ideal pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. If it’s too acidic or alkaline, adjust the pH accordingly. 🧪
🌿 Add organic compost around the base of the tree to improve soil fertility and support microbial activity. 🍂
🌱 Fertilize regularly: Apply a balanced fertilizer, particularly one high in nitrogen, during the growing season to promote healthy foliage and nut production. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can harm the tree. 🌱
💧 3. Monitor Watering Practices 💧
Proper watering is crucial, especially as your tree matures. 🌞 Consistent moisture helps maintain strong roots and encourages optimal growth. 🌱
🌳 Water deeply and less frequently rather than shallow watering to encourage deep root growth. Aim for about 1-2 inches of water per week, depending on weather conditions. 💧
🚫 Avoid overwatering: While pecan trees need regular moisture, standing water can damage roots and lead to diseases like root rot. Ensure good drainage around the tree. 🌱
🌾 Use mulch: Apply mulch around the base of the tree to help retain moisture and prevent weeds. Organic mulch will also enrich the soil as it decomposes. 🍂
🦠🛡️ 4. Control Pests and Diseases 🦠🛡️
As your pecan tree ages, it becomes more susceptible to pests and diseases, which can reduce its productivity. 🐜 Regular monitoring and preventive measures can help keep your tree healthy for longer. 🌳
🐛 Inspect for pests like pecan weevils, aphids, and hickory shuckworms, which can damage both the tree and its nuts. Apply organic pesticides or insecticidal soap if needed. 🌱
🍄 Prevent fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and leaf spot by maintaining proper tree spacing, avoiding overwatering, and pruning regularly to ensure good airflow. 🌿
🌿 Fungicide applications: During damp weather, applying fungicides can help prevent fungal infections, especially if your tree is susceptible to them. 🌾
🌼 5. Provide Adequate Pollination 🌼
Pollination is essential for a successful pecan harvest. 🌰 While pecan trees are wind-pollinated, ensuring good cross-pollination between different varieties can increase your yield and prolong productivity. 🌿
🌳 Plant multiple varieties: For better pollination, plant at least two different pecan tree varieties within proximity of each other. 🌰
🌱 Space trees properly: Trees should be spaced about 30-40 feet apart to encourage better airflow and cross-pollination. This also reduces the risk of disease spread between trees. 🌳
🌞🌧️ 6. Manage Tree Stress and Environmental Factors 🌞🌧️
Extreme weather conditions, like drought, frost, or high winds, can stress your tree and affect its productivity. 🌱 By reducing environmental stressors, you can help extend the life of your pecan tree. 🌳
❄️ Protect against frost: Young trees are especially vulnerable to late spring frosts. If frost is expected, cover the tree with frost cloths or blankets to protect delicate blossoms. 🌸
🌱 Avoid overcrowding: Ensure that your pecan tree isn’t competing for resources with other trees or plants. Give it plenty of space to grow and access sunlight. 🌞
🌞 Prevent heat stress: During extreme heat, be sure your tree is well-watered and shaded to avoid excessive stress. 💧
🌱 7. Replant or Graft New Growth 🌱
While you can’t stop aging, you can prolong your pecan tree’s productive years by encouraging new growth. 🌳
🌿 Graft younger limbs from a healthy tree to an older one to give it a new lease on life. This can stimulate production and rejuvenate the tree. 🌱
🌳 Replant nearby: When older trees start declining, consider planting younger trees alongside them to ensure continuous production. 🌱
📋 In Summary 📋
To extend the productive life of your pecan tree, focus on regular pruning, maintaining soil health, managing pests, and providing consistent care. 🌱 While no tree will produce indefinitely, these tips will help ensure your pecan tree remains healthy and productive for as long as possible. 🌳 With the right care, your tree can continue to produce delicious nuts for decades, making it a valuable asset in your garden or orchard! 🌰🌳
🌰⚠️ Common Problems That Limit Pecan Tree Production ⚠️🌰
Even the healthiest pecan trees can face challenges that limit their productivity. 🌳 Understanding these common problems—and how to solve them—is crucial for maximizing your tree’s potential. 🌱 Let’s explore some of the most frequent issues that can affect pecan tree production and practical solutions to overcome them. 🌿
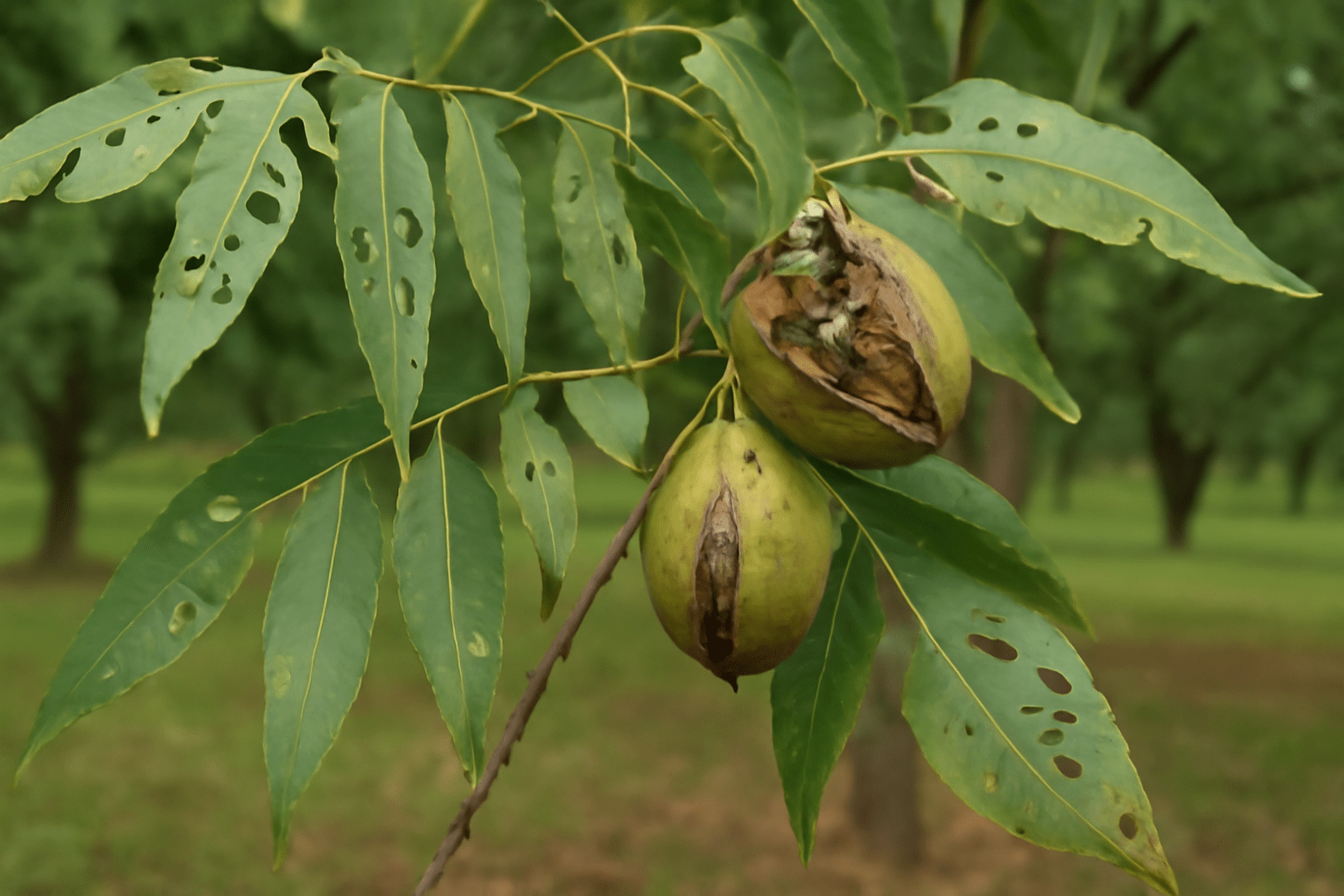
💧 1. Inconsistent Watering 💧
Water is one of the most important factors in pecan tree health, but inconsistent watering can lead to poor production. 🌞
🚨 Problem:
Overwatering or underwatering can cause stress to the tree, leading to poor nut development or tree decline. 🍂
✅ Solution:
Establish a consistent watering schedule. 🌱 Pecan trees prefer deep, infrequent watering rather than shallow, frequent watering. Aim to provide about 1-2 inches of water per week, especially during dry spells. 💦 A drip irrigation system can help maintain consistent moisture levels. 🌳
🌼 2. Poor Pollination 🌼
Pecan trees are dioecious, meaning they require both male and female trees for cross-pollination. 🌱 Without proper pollination, nut production can be minimal or non-existent. 🌰
🚨 Problem:
Lack of cross-pollination or planting only one variety can result in poor yields. 🥜
✅ Solution:
Plant at least two different pecan tree varieties nearby to ensure proper cross-pollination. 🌳 Make sure the trees are spaced at least 30-40 feet apart to allow for optimal pollen transfer. 🍃
🌱 3. Nutrient Deficiencies 🌱
Pecan trees require specific nutrients to grow well and produce a healthy crop. 🌾 A lack of essential nutrients can stunt growth and reduce nut production. 🌰
🚨 Problem:
Deficiencies in nitrogen, potassium, or phosphorus can weaken the tree and reduce its ability to produce nuts. 🌱
✅ Solution:
Regularly fertilize your tree with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer, especially during the growing season. 🌿 Perform soil tests to ensure the correct nutrients are being applied based on your soil’s needs. Adding organic compost can also improve soil fertility. 🌳
🐞🦠 4. Pests and Insects 🐞🦠
Pecan trees are vulnerable to a variety of pests, some of which can cause significant damage to the leaves, branches, and nuts. 🌳 Common pests include pecan weevils, aphids, and hickory shuckworms. 🍂
🚨 Problem:
Pests like the pecan weevil can destroy developing nuts, while aphids and scale insects can damage leaves and stunt tree growth. 🌿
✅ Solution:
Regularly inspect your tree for signs of pests. 🐜 Treat infestations with appropriate pesticides or natural remedies like neem oil. Consider using insect traps for early detection and prevention. 🦋
🦠💀 5. Diseases 🦠💀
Pecan trees are prone to several diseases that can impact their health and productivity. 🐛 Some of the most common diseases include powdery mildew, phytophthora root rot, and leaf spot. 🍂
🚨 Problem:
Fungal infections can weaken the tree, causing leaf loss, poor growth, and reduced nut production. 🦠
✅ Solution:
Practice good sanitation by removing fallen leaves and debris that could harbor disease. 🍂 Ensure proper spacing between trees to improve air circulation. If disease occurs, apply fungicides as needed (following label instructions). Avoid overwatering, as standing water can encourage fungal growth. 🌱
🌞🌧️ 6. Environmental Stress 🌞🌧️
Pecan trees are sensitive to extreme weather conditions like drought, frost, and high winds, which can stress the tree and lead to poor production. 🌳
🚨 Problem:
Drought can cause the tree to drop nuts prematurely, while frost can damage blossoms in early spring, reducing the yield. High winds can break branches or blow nuts off the tree before they’re mature. 🌬️
✅ Solution:
Protect your tree during extreme weather. 🌱 In areas prone to late frost, cover the tree with frost cloths during cold snaps. During dry periods, ensure regular deep watering. For wind protection, consider planting windbreaks or using tree supports to stabilize branches. 🌳
🌍 7. Soil Issues 🌍
Soil quality is vital for pecan tree production. Poor drainage, imbalanced pH levels, or compacted soil can prevent the tree from growing properly and producing high-quality nuts. 🌱
🚨 Problem:
Poor drainage leads to root rot, while soil that is too acidic or alkaline can limit nutrient uptake. 🌱
✅ Solution:
Ensure the soil has good drainage by adding organic matter and improving aeration. 🌾 Test your soil regularly to ensure it falls within the ideal pH range of 6.0-6.5. Amend the soil with lime or sulfur to adjust pH levels as needed. 🌿
🌳🌱 8. Overcrowding or Competition for Resources 🌳🌱
When pecan trees are planted too closely together or near other large plants, they may not get the resources they need to thrive. 🌳
🚨 Problem:
Overcrowding results in competition for water, sunlight, and nutrients, which can stunt the growth of your tree and reduce nut production. 🌱
✅ Solution:
Space your trees at least 30-40 feet apart to ensure each tree has adequate room to grow. 🌳 Avoid planting large shrubs or trees too close to your pecan tree, as they may take away essential resources. 🌿
📋 In Summary 📋
To keep your pecan tree producing at its best, it’s important to address common issues like inconsistent watering, poor pollination, nutrient deficiencies, pests, diseases, and environmental stress. 🌳 Regular care and monitoring are key to ensuring your tree’s health and maximizing its productivity. 🌰 By staying on top of these potential problems, you’ll be well on your way to a bountiful pecan harvest for years to come! 🌱🌰
🌳💭 Final Thoughts 💭🌳
Growing pecan trees can be a rewarding experience, but it requires patience, care, and a bit of know-how. 🌱 From understanding how long pecan trees produce, to selecting the right varieties, and implementing the best practices for care, you now have the tools to ensure your tree thrives for years to come. 🌰
Remember, maximizing your pecan tree’s yield involves more than just planting it and waiting for harvest season. ⏳ It’s about consistent care—proper soil, watering, pollination, and pest management. 🌳 By recognizing the signs of declining production and taking action, you can extend the productive years of your tree, keeping your harvest plentiful for decades. 🍂

Whether you’re starting with a young tree or caring for an older one, your efforts will pay off with a healthy, high-producing pecan tree. 🌿 Keep learning, keep experimenting, and most importantly, enjoy the process. 🌞
With the right knowledge and care, your pecan tree will continue to provide delicious nuts year after year. 🌰 Happy growing! 🌱🌳
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long do pecan trees live?
Pecan trees can live for over 100 years, with some reaching 200 years or more under ideal conditions. However, their most productive years usually span from 30 to 50 years, after which their nut production gradually declines.
When do pecan trees start producing nuts?
Grafted pecan trees typically begin producing nuts in 6-10 years, while trees grown from seed take around 15-20 years. Full production usually begins around 12-20 years as the tree matures.
How can I increase the yield of my pecan tree?
To boost yield, ensure your tree is properly cared for with healthy soil, deep watering, regular pruning, and fertilization. Plant at least two different pecan tree varieties to ensure cross-pollination and choose a well-draining site with good sunlight.
What affects pecan tree production?
Several factors influence pecan tree production, including weather conditions, soil quality, pest control, and proper pollination. Extreme temperatures, poor soil, and inadequate watering can significantly reduce nut yields.
Why is my pecan tree not producing nuts?
There could be several reasons why your pecan tree isn’t producing nuts. Common causes include poor pollination, lack of proper care (such as insufficient water or nutrients), pest infestations, or young age (trees under 10 years old may not produce nuts yet).
Do pecan trees need cross-pollination?
Yes, pecan trees are dioecious, meaning they need at least two different varieties of trees for proper cross-pollination. Without it, nut production will be poor or nonexistent, so plant multiple varieties for better yields.
How do I know when my pecan tree is too old to produce?
Pecan trees typically begin to show reduced productivity around 50 years old. Signs of aging include smaller nuts, lower yields, and weakened branches. If your tree is over 50 and showing these signs, it may be nearing the end of its productive years.
What’s the best time to plant a pecan tree for maximum production?
The best time to plant a pecan tree is during early spring or late fall when the tree is dormant. This allows the tree to establish its root system before the growing season begins, ensuring it has the best chance to thrive and produce in the future.
