
How to Grow and Care for a Northern Pecan Tree: Expert Tips for Thriving Trees and Bountiful Harvests
Table of Contents
Toggle🌳 Understanding Northern Pecan Trees 🌳
Before you dive into planting and caring for a northern pecan tree, it’s important to understand what makes these trees unique. 🌱 Knowing their characteristics will help you create the perfect environment for growth, ensuring a thriving tree and a bountiful harvest in the future. 🌰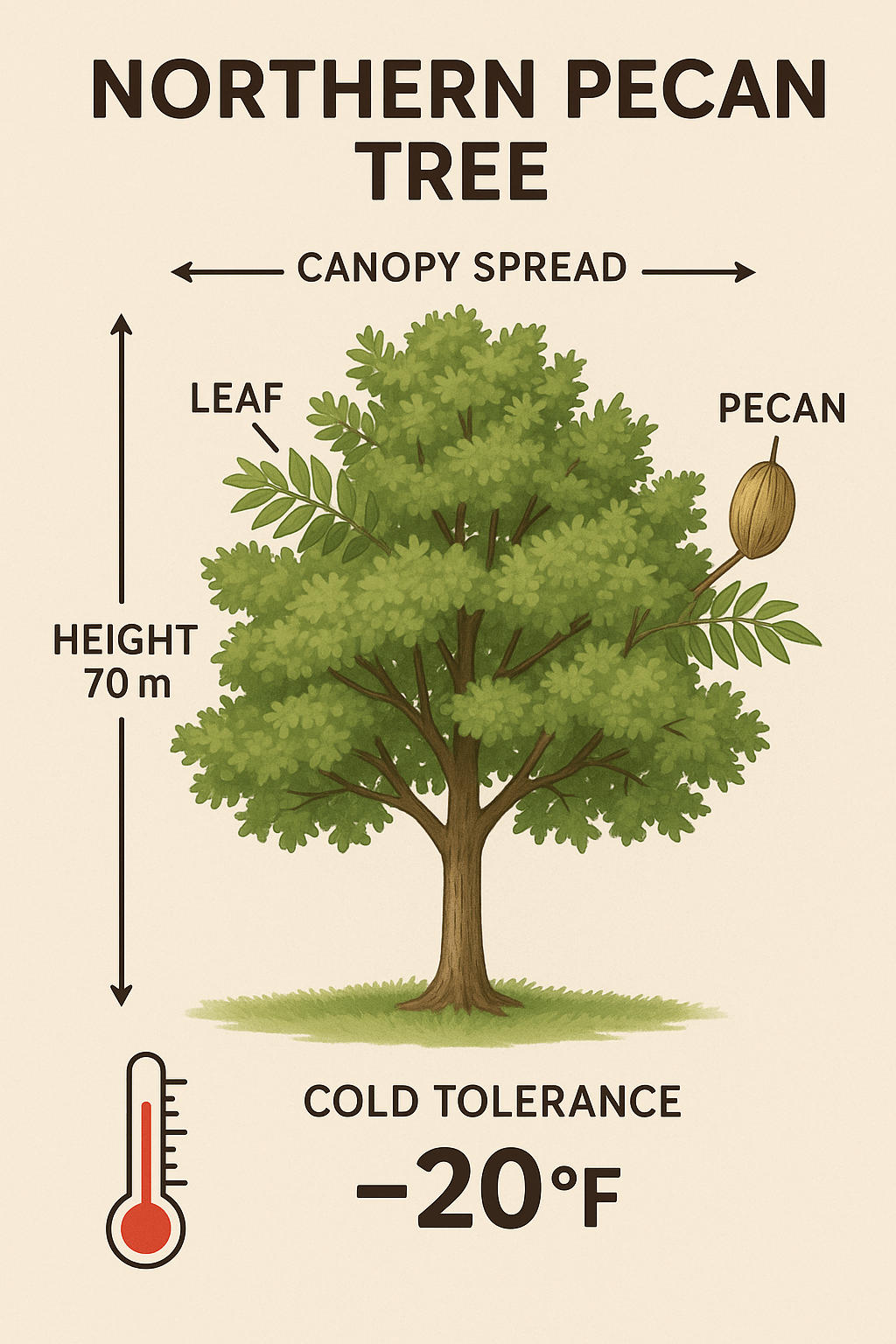
🌿 What Makes Northern Pecan Trees Special? 🌿
Northern pecan trees are a hardier variety of pecan, typically grown in cooler climates compared to their southern counterparts. 🌨️ These trees can handle the chilly winters found in USDA hardiness zones 4-9, making them ideal for regions that experience cold winters. ❄️ Unlike southern pecan trees, which thrive in warmer areas, northern pecans are more cold-tolerant and adapt well to frost. 🌨️ They typically reach a mature height of 70-100 feet, with wide spreading branches, making them a beautiful addition to any landscape. 🌳🌞 Key Growing Conditions for Northern Pecan Trees 🌞
Northern pecans need specific conditions to grow strong and produce high-quality nuts. 🌰 Here are the basics you need to know: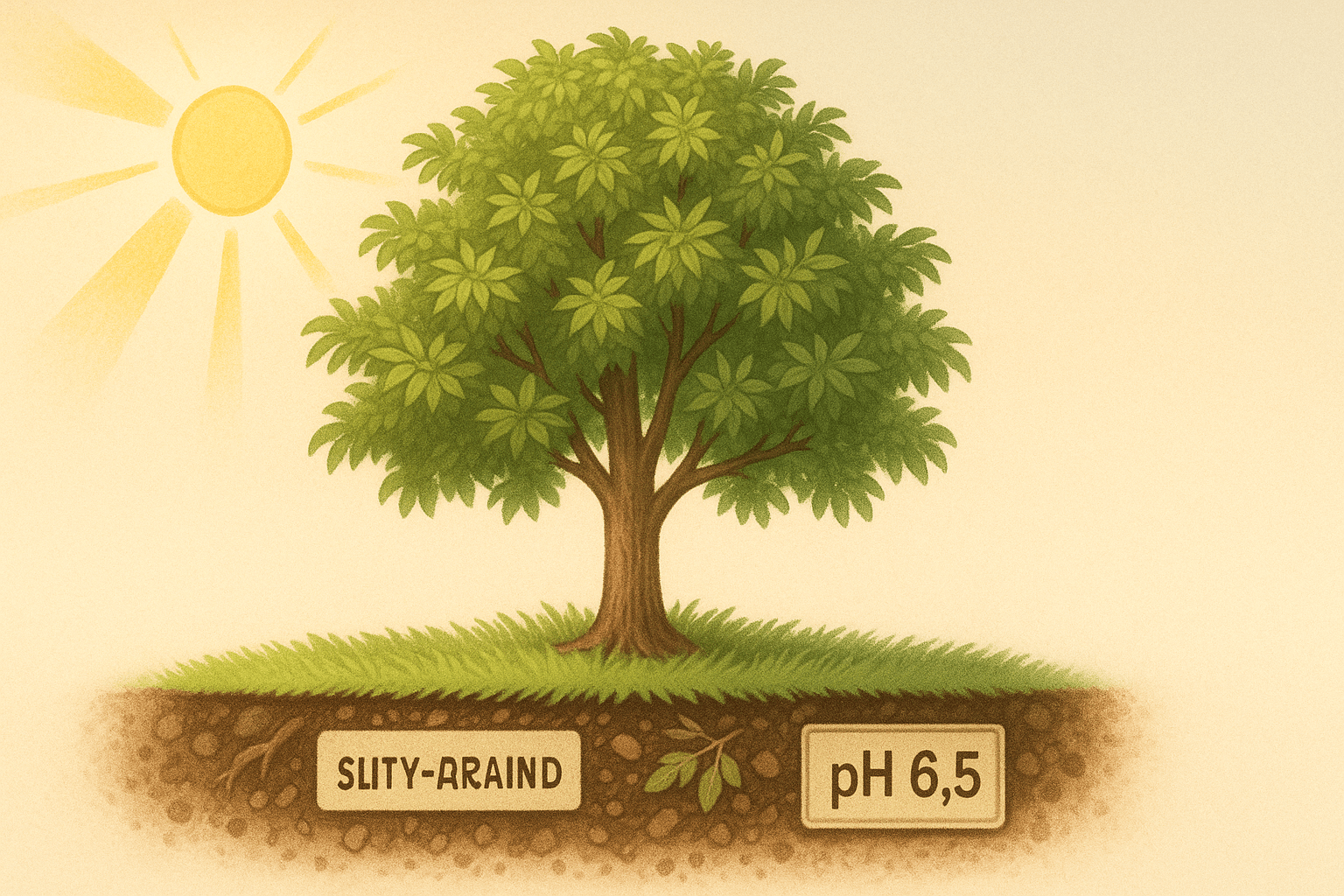
🌞 Sunlight:
Northern pecan trees require full sun to thrive. Make sure your tree gets at least 6-8 hours of sunlight each day. 🌞🏞️ Soil:
These trees prefer deep, well-drained soil with a slightly acidic pH (around 6.0-6.5). If your soil is heavy or poorly draining, consider amending it with organic matter to improve its structure. 🌱🌱 Space:
Pecan trees are large and need plenty of space to grow. Ensure they are planted at least 30-40 feet apart from other trees or structures. This allows them to develop their canopy and root system properly. 🌳🍂 How Northern Pecan Trees Thrive in Different Climates 🍂
While northern pecan trees are more frost-resistant than southern varieties, they still need warm summer temperatures to produce a good crop of nuts. 🌞 A long growing season, with temperatures between 75°F and 95°F (24°C – 35°C), is ideal for these trees to develop their delicious pecans. 🌰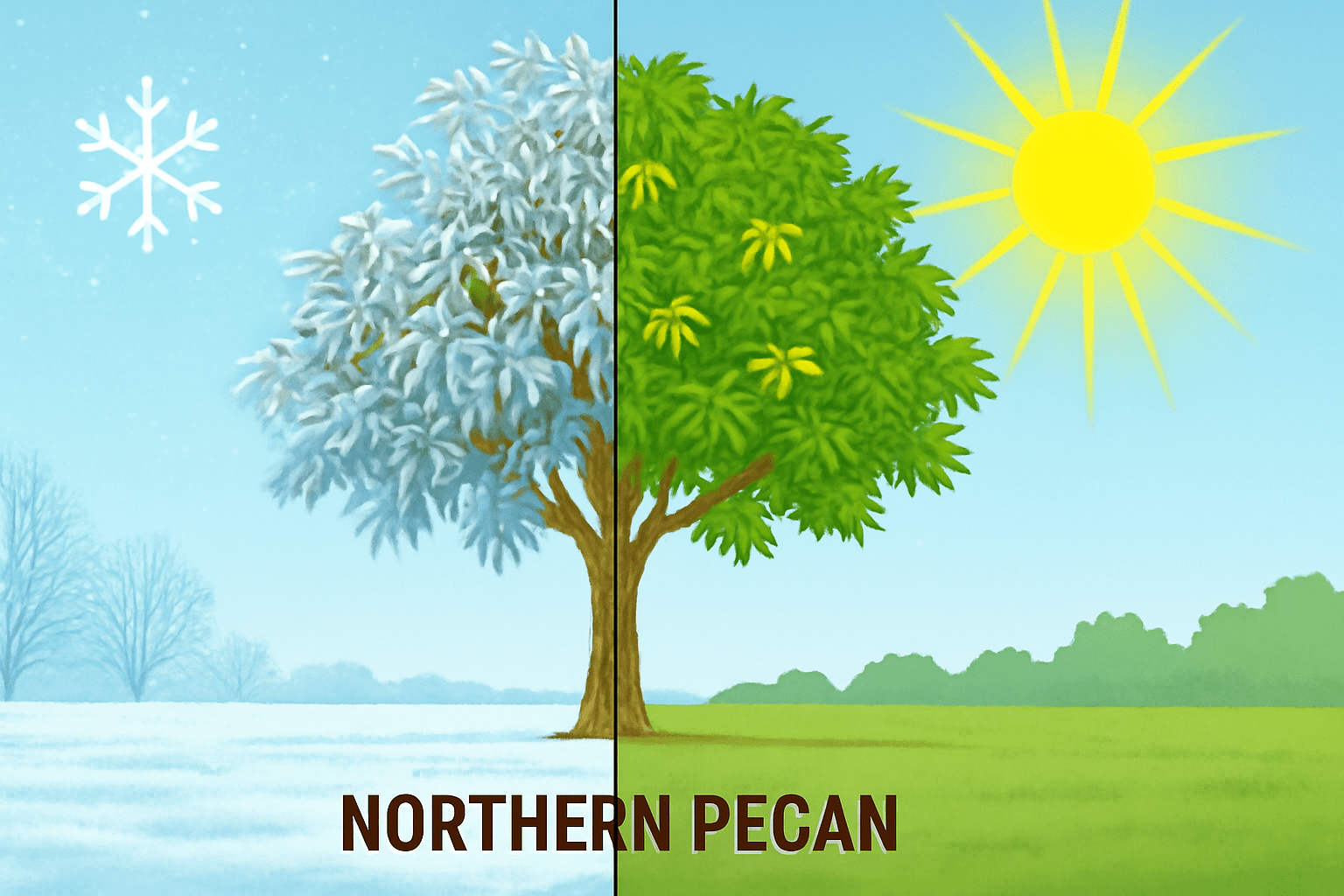
🌱 How to Plant a Northern Pecan Tree 🌱
Planting a northern pecan tree is an exciting step toward enjoying fresh, homegrown pecans. 🌰 However, to ensure your tree thrives and grows strong, it’s important to follow the right steps. Here’s a beginner-friendly, step-by-step guide on how to plant your tree for long-term success. 🌳🏡 Choosing the Right Location 🏡
The first step in planting your northern pecan tree is selecting the ideal location. Here’s what to look for:🌞 Full Sunlight:
Northern pecan trees need a lot of sunlight. Choose a spot that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sun each day. 🌞📏 Space:
These trees are large, so make sure there’s plenty of room to grow. Plant your tree at least 30-40 feet away from other trees, buildings, or fences to give it the space it needs to develop. 📐🌾 Well-Drained Soil:
Pecan trees don’t like “wet feet.” Look for a site with well-drained, deep soil. If your soil tends to hold water, consider improving drainage by adding organic matter like compost or planting on a slight mound. 🌍🕳️ Step-by-Step Guide to Planting 🕳️
Now that you’ve chosen the perfect spot, it’s time to plant your tree. Follow these steps for a successful planting: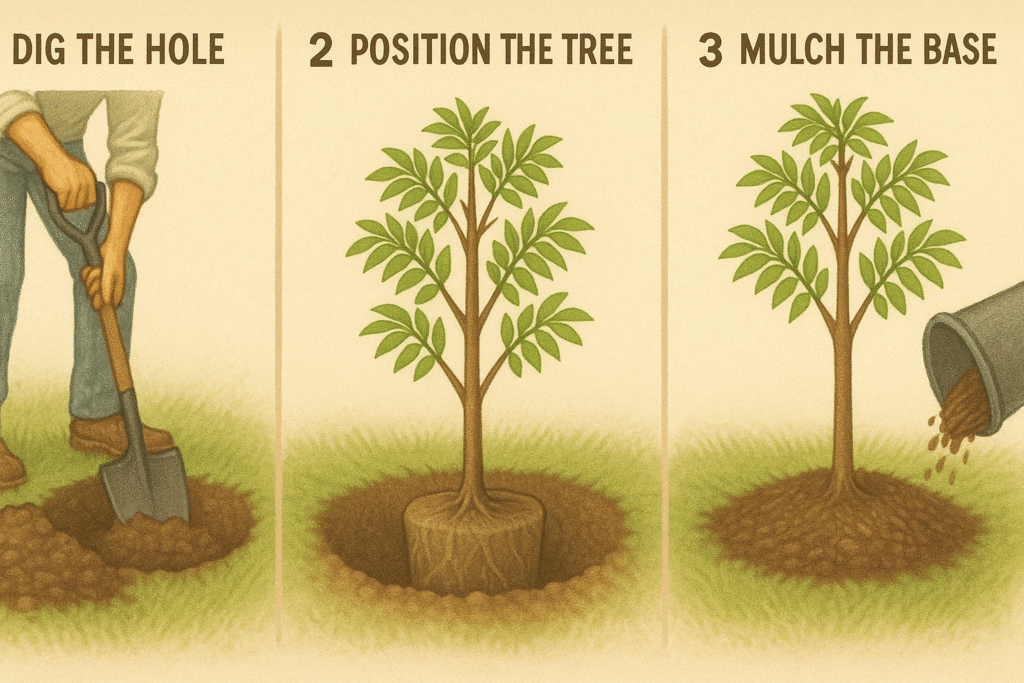
🧑🌾 Prepare the Soil:
Before planting, test the pH of your soil. Aim for a slightly acidic level (6.0-6.5). If needed, amend the soil with organic matter, compost, or mulch to improve its structure and drainage. 🧪🕳️ Dig the Hole:
Dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of your tree. This gives the roots room to spread and grow freely. The hole should be around 18-24 inches deep, depending on the size of your sapling. 🌱🌳 Position the Tree:
Gently remove the tree from its container, being careful not to damage the roots. Place the tree in the center of the hole, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with or slightly above the surrounding soil. 🌍🌿 Backfill the Hole:
Fill the hole with the soil you dug out, gently packing it around the root ball to remove any air pockets. Avoid covering the root flare (where the trunk meets the roots) with soil. 🌿💦 Water Thoroughly:
Once the tree is in place, water it deeply to help settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged in the first few weeks after planting. 🌧️🌿 Mulch Around the Base:
Add a layer of mulch (like wood chips or bark) around the base of the tree, about 2-3 inches thick. This helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Just make sure the mulch isn’t touching the trunk directly. 🍂🌾 Caring for Your Newly Planted Tree 🌾
After planting, keep an eye on your tree’s growth and make sure it gets the care it needs to establish itself. Here’s what to do:🌧️ Watering:
For the first year, water your tree regularly, especially during dry spells. Aim for deep watering, so the moisture reaches the roots. 💧🥕 Fertilizing:
While fertilization isn’t necessary right away, after 6-12 months, you can start fertilizing with a balanced fertilizer. Apply in the spring, before the tree begins its active growing season. 🌱🏗️ Staking (Optional):
If your tree is young or in a windy area, consider staking it for support. Use soft ties that won’t damage the trunk as it grows. 🌳 By following these simple steps, you’re setting your northern pecan tree up for success. 🌱 With the right location, care, and attention, your tree will grow strong and healthy, paving the way for a future filled with delicious pecans! 🌰🌿 Essential Care and Maintenance for Northern Pecan Trees 🌿
Now that your northern pecan tree is planted, the key to a healthy, thriving tree lies in the care and maintenance you provide. 🌳 With proper attention, your tree will grow strong, produce high-quality pecans, and become a long-term asset to your landscape. 🌱 Here’s a practical guide to keeping your northern pecan tree happy and productive. 🌰💧 Watering and Irrigation 💧
Proper watering is one of the most important aspects of tree care. Northern pecan trees need consistent moisture, especially during the first few years of growth. 🌱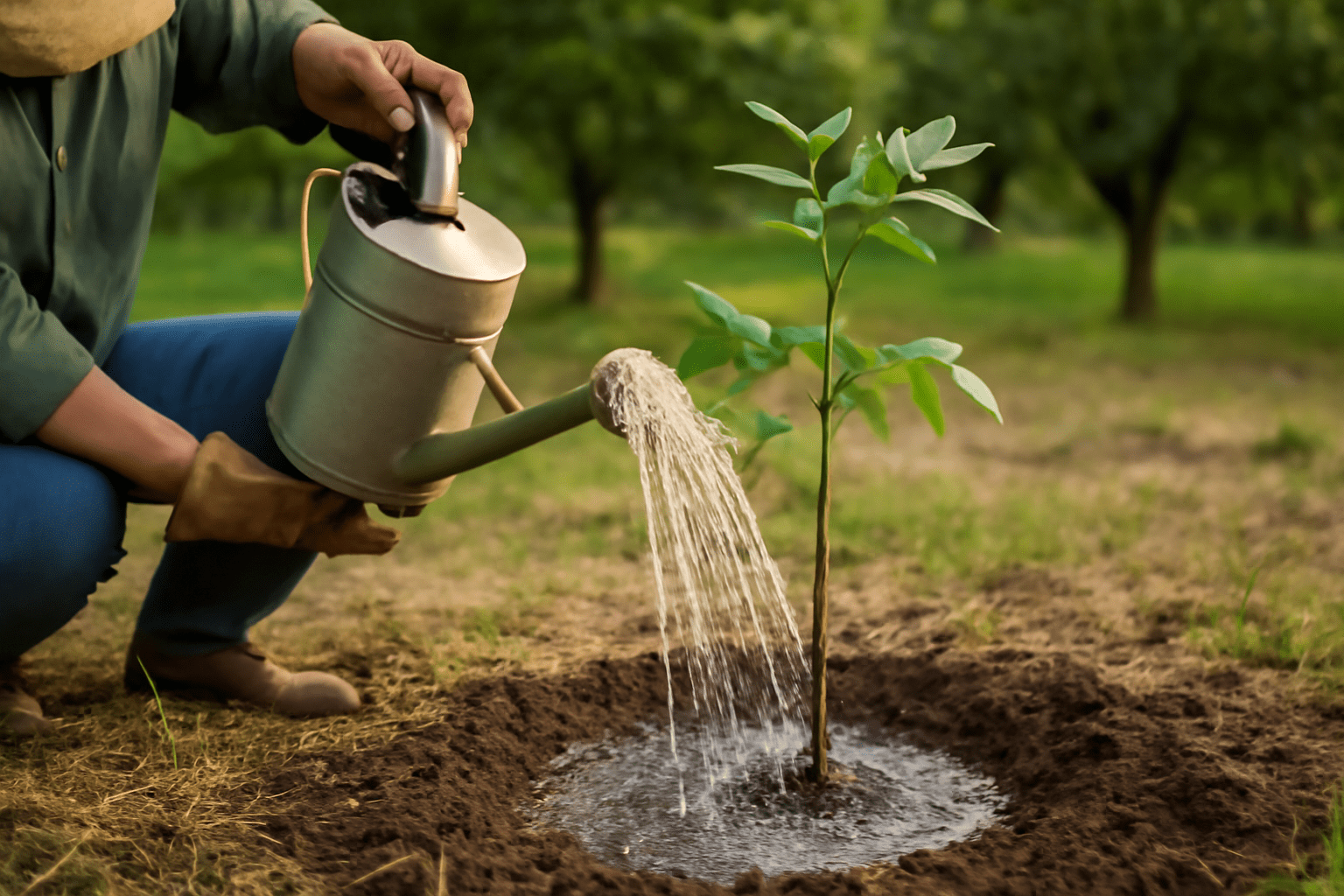
🌿 Deep Watering:
Pecans have deep root systems that need water at the root level. Water the tree deeply rather than frequently, ensuring the moisture reaches the roots. 🌳 This encourages healthy root growth. Aim for deep watering once a week, but adjust based on weather conditions. 🌧️🌵 Drought Stress:
During hot, dry spells, your tree may need extra watering. Check the soil moisture by digging a small hole near the tree. If the soil is dry a few inches down, it’s time to water. 💦🚫 Avoid Overwatering:
While pecans need water, they don’t like “wet feet.” Ensure the soil is well-draining to prevent root rot. If the soil doesn’t drain well, consider adding organic matter or adjusting the planting area for better drainage. 🌾🌾 Fertilizing Your Northern Pecan Tree 🌾
Fertilizing your northern pecan tree correctly helps promote healthy growth and nut production. 🌰 Here’s how to do it:🗓️ When to Fertilize:
Fertilize your tree in early spring, just before it begins its active growing season. This provides essential nutrients during its growth phase. Avoid fertilizing in the fall, as it can encourage soft growth that is vulnerable to winter damage. 🍂🥕 Type of Fertilizer:
Use a balanced fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) for general growth. Organic options, like compost or aged manure, can also be a good choice. 🌱 For a more specific nutrient boost, you can opt for a fertilizer high in nitrogen, especially for young trees that need extra growth support.⚖️ How Much to Apply:
Apply fertilizer according to the size of the tree. For young trees, about 1-2 pounds of fertilizer per year of growth is recommended. Be cautious not to over-fertilize, as this can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of nut production. 🌳✂️ Pruning and Shaping ✂️
Pruning helps your tree develop a strong structure, improves airflow, and maximizes sunlight exposure, all of which contribute to a healthier tree and better pecan production. 🌿🗓️ When to Prune:
The best time to prune your northern pecan tree is during late winter or early spring when the tree is dormant. Avoid pruning during the growing season, as it can lead to unnecessary stress or sap loss. 🌱🌳 What to Prune:
Focus on removing dead, damaged, or diseased wood first. Then, thin out any crowded branches to improve air circulation and light penetration. This also helps reduce the risk of fungal diseases. 🍂🌿 Shaping the Tree:
Aim for a strong, central leader (main trunk) with well-spaced side branches. A single leader structure helps the tree grow straight and tall, allowing for better nut production. Trim any competing leaders (side branches trying to become the main trunk) to encourage healthy growth. 🌳🚫 Common Pruning Mistakes to Avoid:
- Don’t remove more than 25% of the tree’s canopy at once.
- Avoid heavy pruning in the first few years; let the tree establish its form before doing extensive cutting. 🌱
🐝 Pollination Tips 🐝
Northern pecan trees are typically not self-pollinating, meaning you need at least two trees for successful pollination and nut production. 🌰 Here’s what to do:🌳 Plant Multiple Trees:
If you have the space, plant two or more northern pecan trees to ensure cross-pollination. 🌸 Choose varieties that bloom at the same time for the best results.🌬️ Wind-Pollinated:
Pecans are wind-pollinated, so ensure your trees are spaced correctly to allow for wind to carry pollen between them. This will boost nut production and ensure a healthy harvest. 🌾 With consistent care and maintenance, your northern pecan tree will reward you with robust growth, vibrant leaves, and an eventual nut harvest. 🌰 By watering correctly, fertilizing on schedule, pruning wisely, and ensuring proper pollination, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying a thriving tree for years to come! 🌳🐞 Common Pecan Tree Pests and Diseases 🐞
Northern pecan trees are beautiful and rewarding to grow, but like all trees, they can face challenges from pests and diseases. 🌱 Fortunately, with the right knowledge, you can tackle these problems before they harm your tree. In this section, we’ll cover common pests and diseases that affect pecan trees and provide practical solutions for managing them. 🌳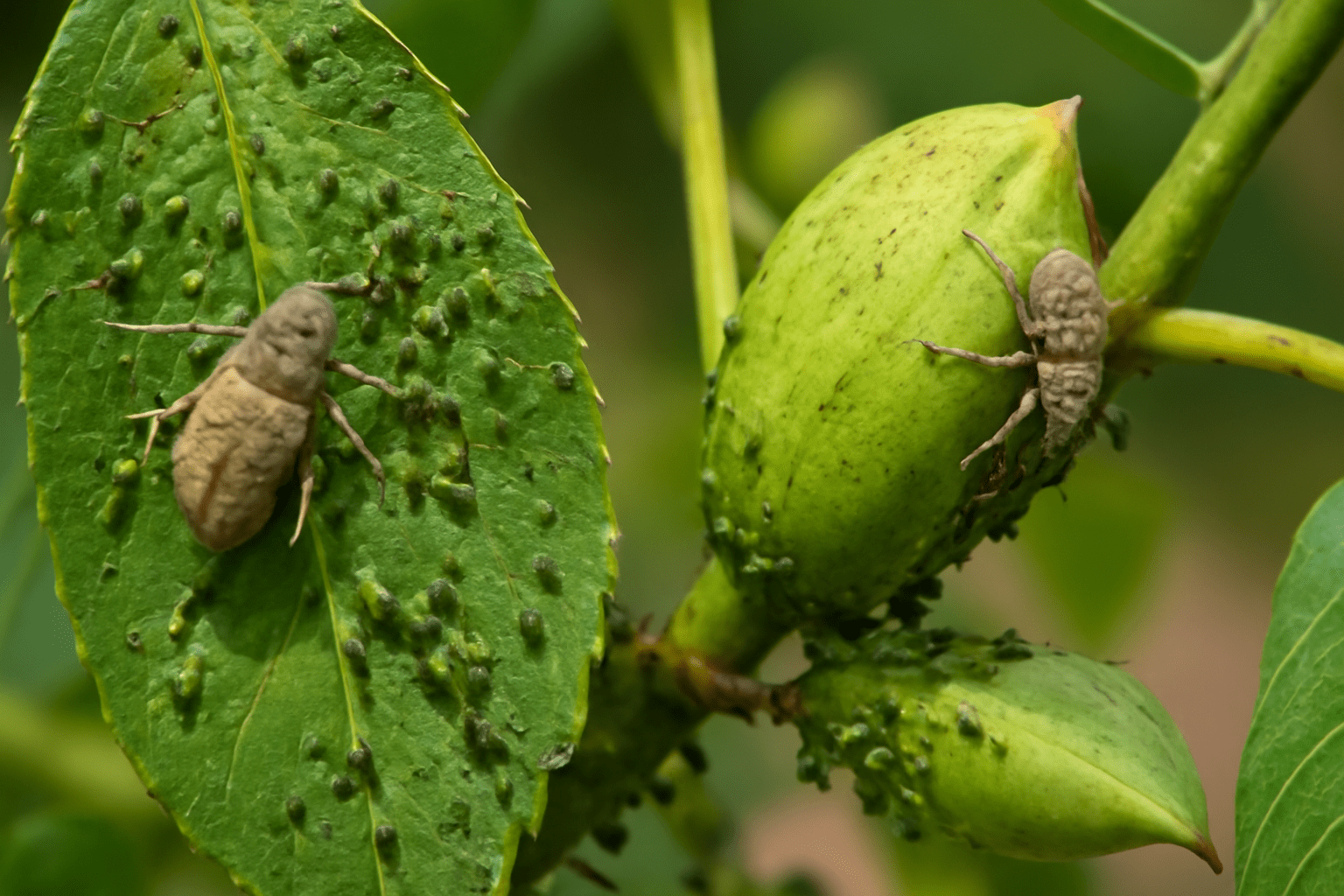
🐜 Common Pests That Affect Northern Pecan Trees 🐜
🐞 Pecan Weevil 🐞
The pecan weevil is one of the most destructive pests for pecan trees. The adult weevil lays eggs inside the nut, causing them to drop prematurely or become damaged and inedible. 🌰 Signs of Infestation:- Nuts with small holes or that drop early.
- Darkening or rotting of nuts. 🌿
- Use traps to catch adult weevils during the late summer and fall.
- Remove fallen nuts from the ground to eliminate larvae.
- Apply insecticides (like pyrethroids) before the nuts begin to form, following the manufacturer’s instructions. 🍂
🐜 Aphids 🐜
Aphids are small, sap-sucking insects that can weaken your pecan tree, causing yellowing of the leaves and stunted growth. They also excrete honeydew, which can lead to the growth of sooty mold. 🌿 Signs of Infestation:- Curling or yellowing leaves.
- Sticky residue or black mold on the leaves. 🌑
- Spray a mixture of water and mild soap to remove aphids from leaves.
- Encourage natural predators, such as ladybugs, which feed on aphids.
- Insecticidal soap or neem oil can also be effective for controlling aphids. 🌸
🕸️ Webworms 🕸️
Webworms are caterpillars that form large webs on the branches, often defoliating the tree and weakening it over time. These pests can be particularly damaging if left unchecked. 🐛 Signs of Infestation:- Visible webs around branches or leaves.
- Large sections of missing leaves. 🍂
- Remove webs by hand if the infestation is light. Simply cut out the affected branches and destroy the webs.
- For larger infestations, apply insecticides or biological controls like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which targets caterpillars without harming beneficial insects. 🌿
🌱 Common Diseases That Affect Northern Pecan Trees 🌱
🌬️ Powdery Mildew 🌬️
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects the leaves and branches, leading to a white, powdery coating. It thrives in humid, warm conditions and can reduce the photosynthetic ability of the tree. 🍃 Signs of Infestation:- White, powdery spots on leaves, twigs, and branches.
- Yellowing leaves and premature leaf drop. 🍂
- Prune your tree regularly to improve airflow and reduce humidity around the foliage.
- Apply fungicides in the early spring when the disease first appears, or use organic treatments like neem oil. 🌿
🌿 Pecan Scab 🌿
Pecan scab is one of the most common and damaging diseases for pecan trees. It causes dark, scabby lesions on leaves, nuts, and twigs, which can severely affect nut quality and yield. 🌰 Signs of Infestation:- Dark, circular lesions on leaves and nuts.
- Premature leaf drop and reduced nut production. 🍂
- Remove fallen infected leaves to reduce fungal spread.
- Apply fungicides during the growing season, especially during periods of high humidity. Be sure to follow the recommended spraying schedule for maximum effectiveness. 🌿
🌱 Root Rot 🌱
Root rot, caused by soil-borne fungi like Phytophthora, affects pecan trees by rotting their root system, leading to poor growth or tree death. Overwatering and poor drainage contribute to this problem. 🌳 Signs of Infestation:- Yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
- Soft or mushy roots when dug up. 🌱
- Ensure proper drainage by amending soil and planting on raised beds or mounds.
- Avoid overwatering—pecan trees prefer well-drained soil. 🌾
- In severe cases, you may need to remove and replace the affected tree or treat the soil with fungicides to combat the infection. 🍂
🍃 General Tips for Managing Pests and Diseases 🍃
👀 Regular Inspections:
Frequently check your tree for signs of pests or diseases, especially during the growing season. Early detection allows for easier management and treatment. 🧐🌸 Encourage Beneficial Insects:
Natural predators like ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory beetles can help control pests without the need for harsh chemicals. 🌿🌳 Proper Tree Care:
Healthy trees are more resistant to pests and diseases. Ensure your tree has the proper water, nutrients, and sunlight to stay strong. 🌞 By staying vigilant and addressing issues as they arise, you can keep your northern pecan tree healthy and free from major pests and diseases. 🌱 With the right care, your tree will thrive, producing a rich harvest of pecans for years to come! 🌰🌰 Harvesting Pecan Nuts 🌰
After nurturing your northern pecan tree with proper care, you’ll eventually be rewarded with a delicious harvest of pecans! 🌳 But when is the right time to harvest, and how do you go about it? In this section, we’ll walk you through the process of harvesting pecans so you can enjoy the fruits of your labor. 🌱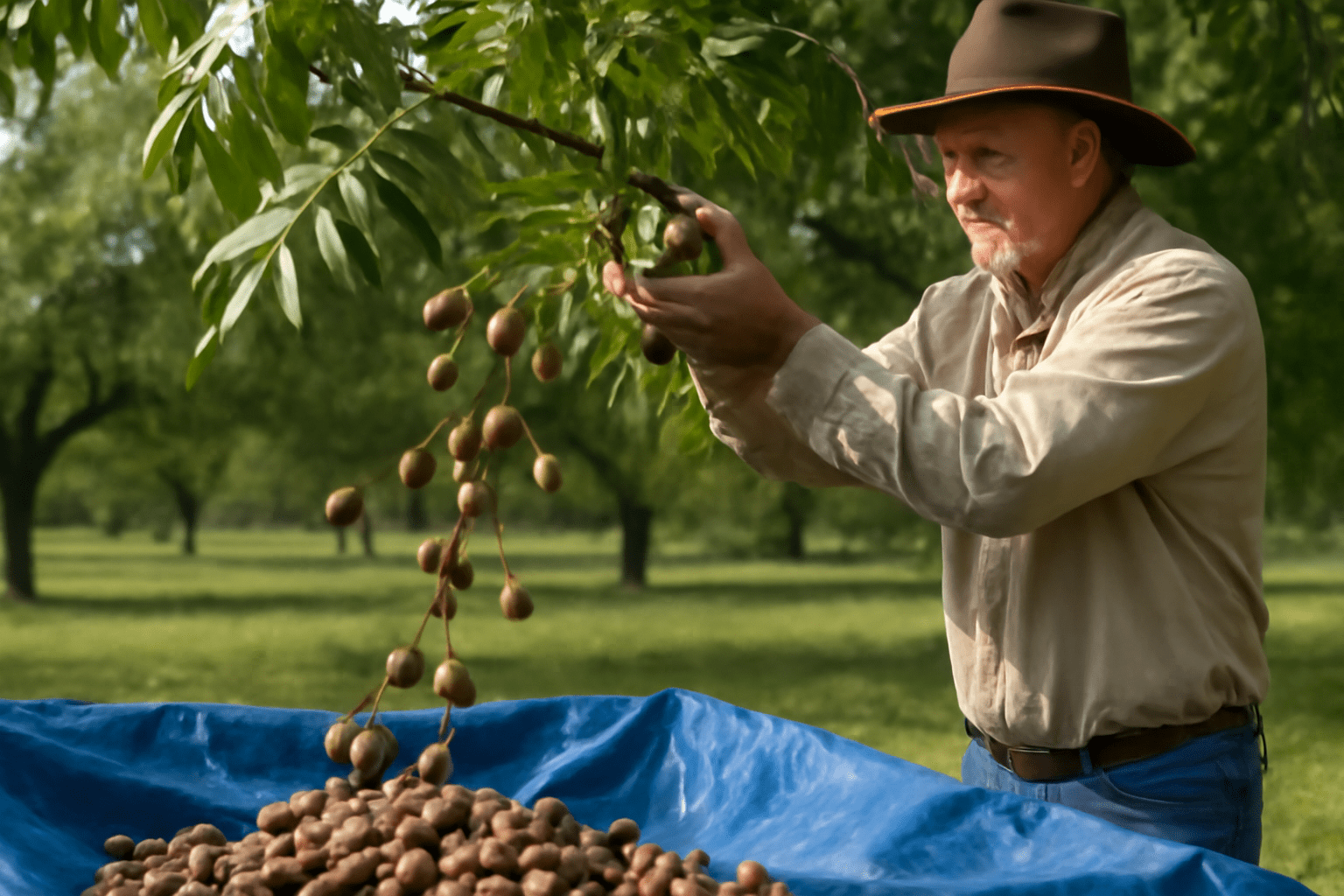
🕒 When to Harvest Pecans 🕒
Timing is crucial when it comes to harvesting pecans. If you pick them too early, they won’t be fully developed; pick them too late, and they may fall to the ground or become overripe. Here’s how to know when your pecans are ready to be harvested: 🌰🌿 Watch for Hull Splitting:
One of the most obvious signs that your pecans are ready for harvest is when the green hulls start splitting open. This typically happens in late fall (September to November), depending on your location and weather conditions. 🍃🌳 Check for Falling Nuts:
As the nuts ripen, they’ll naturally begin to drop from the tree. If you start seeing pecans fall to the ground, it’s a sign that harvesting time is near. However, it’s still a good idea to wait until the hulls have fully split before you gather them. 🌾📲 Shake Test:
Another way to check if the nuts are ready is to gently shake a branch. If the pecans rattle inside their husks, they’re ready to be picked. 🌱🧺 How to Harvest Pecans 🧺
Once your pecans are ripe and ready for harvest, follow these steps for a successful collection:🐜 Gather Fallen Nuts:
Start by collecting any pecans that have already fallen to the ground. These nuts may be partially or fully ripened. Make sure to pick them up as soon as possible to avoid pest problems or fungal infections. 🐞🛠️ Use a Harvesting Tool:
For nuts that are still on the tree, you’ll need a tool to help you reach them. A simple fruit picker or a long-handled rake can help you gently pull branches down and shake the nuts loose. Be careful not to damage the tree or the nuts during this process. 🌳🌾 Catch the Nuts:
If you’re shaking branches, place a tarp or large cloth underneath the tree to catch the falling nuts. This makes it easier to collect them and minimizes the chance of them getting damaged by hitting the ground. 🌿🌿 Remove the Husks:
Once you’ve gathered the pecans, it’s time to remove the green husks. You can do this by hand, or you may want to use a mechanical nut husker to speed up the process. The husks should come off easily when the pecans are fully ripe. 🍂🌬️ Drying and Curing Your Pecans 🌬️
After harvesting, it’s important to properly dry and cure your pecans to ensure they stay fresh and flavorful:🌞 Drying:
Spread the pecans in a single layer on a clean, dry surface, such as a tarp, mesh screen, or tray. Allow them to dry for about 1-2 weeks in a cool, well-ventilated area. Avoid direct sunlight, as this can cause the nuts to overheat or lose flavor. 🌿🍂 Curing:
Once the nuts are dry, store them in a cool, dry place for 4-6 weeks to cure. This helps the flavor develop and ensures the nuts remain crisp and delicious. 🍃🥜 Storing Pecans for Long-Term Freshness 🥜
Once your pecans are properly dried and cured, it’s time to store them. Proper storage will help you enjoy your pecans for months to come:🏺 In Shell:
Keep the nuts in their shells if possible. Pecan shells act as a natural barrier that helps preserve the nuts’ freshness. Store them in a cool, dry place in an airtight container. 🌾❄️ Shelled Pecans:
If you prefer shelled pecans, store them in an airtight container in the refrigerator or freezer to maintain their flavor and prevent them from becoming rancid. Pecans can stay fresh for up to 6 months in the fridge or up to a year in the freezer. 🧊🧳 Vacuum Sealing:
For extra-long storage, consider vacuum-sealing shelled pecans before freezing them. This removes air and keeps them fresh for up to 2 years! 🌰🌟 Tips for a Successful Pecan Harvest 🌟
- Harvest Before Heavy Rains: Wet conditions can cause the nuts to swell or become moldy. Aim to harvest on dry days to ensure the nuts stay healthy. 🌞
- Be Gentle: Pecans are fragile, so handle them gently to avoid cracking the shells or damaging the nuts inside. 🌱
🌳💡Troubleshooting Common Northern Pecan Tree Problems 💡🌳
While Northern Pecan trees are hardy and rewarding to grow, like any plant, they can face a few challenges. In this section, we’ll cover some of the most common problems you might encounter and offer practical solutions to keep your tree healthy and thriving. 🌰✨
🐛 Pecan Tree Pests: Keep Them at Bay 🐛
Pests can be a major nuisance to your Northern Pecan tree. The most common offenders include pecan weevils, aphids, and caterpillars. These pests can damage leaves, nuts, and the overall health of your tree. Here’s how to deal with them:Pecan Weevils:
If you notice holes in your pecans or the nuts are dropping prematurely, your tree might have a pecan weevil infestation. The best defense is to remove fallen nuts regularly and treat your tree with an insecticide during peak pest season. Organic options like neem oil can be effective too. 🌱Aphids:
Aphids can cause stunted growth and yellowing leaves. Control them by spraying the tree with a strong stream of water or using insecticidal soap. 🌿Caterpillars:
These pests can chew through leaves. Handpicking them off or using a biological insecticide like Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) can help reduce their numbers. 🦋🍂 Yellowing Leaves: Signs of Stress 🍂
If your Northern Pecan’s leaves turn yellow, it’s usually a sign that something’s off. Here are the most common causes and how to fix them:Nutrient Deficiency:
Yellowing leaves could be a sign that your tree lacks nitrogen or iron. Fertilizing with a balanced tree fertilizer can solve this issue. If the problem persists, consider getting a soil test to pinpoint the exact nutrient deficiency. 🌾Overwatering:
Too much water can suffocate the roots and lead to yellowing leaves. Make sure your tree has well-draining soil and water it only when the soil feels dry to the touch. 🚰Root Damage:
If the tree’s roots have been disturbed, perhaps due to a construction project or lawn care, it can lead to stress and yellowing leaves. Be gentle when working around the root zone, and avoid compacting the soil. 🏗️🌳 Tree Not Producing Nuts? Here’s Why 🌳
It can be frustrating if your Northern Pecan tree is growing beautifully but not producing nuts. Several factors could be behind this:Age:
Pecan trees can take 4–8 years to start producing nuts, so if your tree is young, be patient. 🌱Improper Pollination:
Pecans need cross-pollination to produce nuts. Make sure you have more than one pecan tree, preferably of different varieties, within 100 feet of each other to increase pollination chances. 🌰Excessive Pruning:
Over-pruning can limit nut production. Only prune your tree in late winter to remove dead or damaged wood, and avoid heavy pruning during the growing season. ✂️💧 Drought Stress: Protect Your Tree in Dry Times 💧
Northern Pecan trees are fairly drought-tolerant, but prolonged dry periods can stress them out. Here’s how to prevent drought-related problems:Watering:
During long dry spells, water your pecan tree deeply once a week, ensuring the water reaches the root zone. 🌊Mulching:
Apply a thick layer of mulch (about 3 inches) around the base of the tree to help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature. 🍂Shade:
If your tree is newly planted, provide some shade during the hottest part of the day until it gets established. 🏖️🦠 Fungal Infections: Keep the Fungus Away 🦠
Fungal infections, like powdery mildew and leaf spot, can weaken your Northern Pecan tree. Here’s how to control them:Preventative Sprays:
Apply fungicides in early spring before fungal problems emerge. Organic fungicides, such as copper sulfate, are a good choice for a more natural approach. 🍃Proper Spacing:
Ensure your tree has enough air circulation around it to reduce humidity and prevent fungal spores from spreading. 🌬️Pruning:
Remove any infected branches or leaves to stop the spread of disease and help the tree focus on healthy growth. ✂️🌞 Sunburned Leaves: Protect from the Heat 🌞
While Northern Pecans enjoy sunlight, they can suffer from sunburn in extreme heat. This typically happens in younger trees or during unexpected heatwaves. To prevent sunburn:Shade Protection:
Young trees can benefit from temporary shading during the hottest months to prevent the leaves from burning. Use shade cloth or garden fabric for this purpose. 🌿Water Consistently:
Keep the soil consistently moist, but not soggy, to help the tree cope with heat stress. 🌱🐦 Animal Damage: Keep Critters Away 🐦
Animals, such as squirrels and deer, can be a major nuisance for Northern Pecan trees, especially during the nut-growing season. To protect your tree:Tree Guards:
Install tree guards around the base of the tree to prevent animals from gnawing on the bark. 🦌Netting:
Use netting around the tree to keep animals away from the developing nuts. Just make sure it’s not too tight, so it doesn’t damage the tree. 🌰 By staying alert to these common issues and addressing them early, your Northern Pecan tree can continue to grow strong, healthy, and productive for years to come. Happy gardening! 🌿🌳😊🌰🌳 Northern Pecan Tree Varieties and Their Differences 🌳🌰
When it comes to growing a Northern Pecan tree, choosing the right variety for your climate, soil, and space is key to a healthy and productive tree. In this section, we’ll explore the most popular Northern Pecan varieties and help you decide which one is best for your garden or orchard. 🌿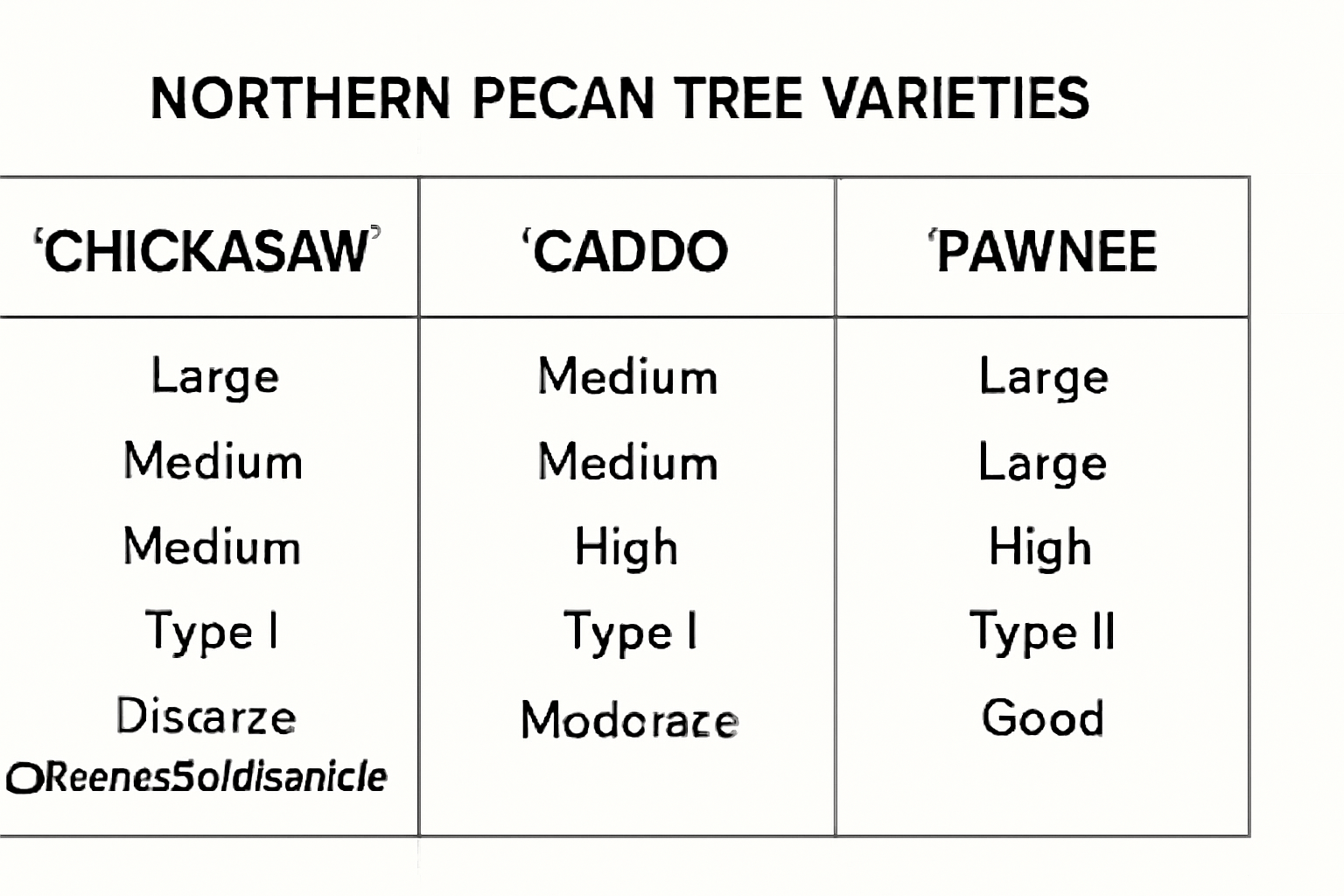
🌟 ‘Chickasaw’ – A Hardy All-Rounder 🌟
The ‘Chickasaw’ variety is a great choice if you live in a colder climate, as it’s one of the most cold-tolerant pecans. This variety is smaller in size but still produces good yields of medium to large nuts. It’s ideal for backyard orchards where space might be limited.Key Features:
- Cold-hardy, perfect for northern climates ❄️
- Small to medium-sized tree 🌳
- Fast-growing and adaptable 🌱
- Nuts are sweet and flavorful 🍬
🌟 ‘Caddo’ – High Yields and Disease Resistance 🌟
For a productive tree with excellent disease resistance, the ‘Caddo’ variety stands out. It grows moderately fast and produces large, high-quality nuts. With proper care, it can thrive even in hot, dry conditions, making it a top pick for growers in warmer climates.Key Features:
- Excellent disease resistance, especially against scab 🌿
- Large, tasty nuts with a thick shell 🥜
- Moderate growth rate 🌳
- Great for warm climates ☀️
🌟 ‘Pawnee’ – A Fast-Growing Superstar 🌟
If you’re looking for a pecan tree that grows quickly, the ‘Pawnee’ variety is your best bet. It is one of the fastest-growing pecans, making it a great choice for those who want to see results sooner. Not only does it grow fast, but it also produces medium to large nuts with excellent flavor.Key Features:
- Fast-growing 🌱
- Medium to large-sized nuts with a sweet taste 🍯
- High resistance to diseases like scab 🛡️
- Ideal for orchards and larger spaces 🌳
🌟 ‘Western Schley’ – Perfect for the West 🌟
For those in the western U.S. or dry regions, the ‘Western Schley’ variety thrives in hot, arid conditions. It’s known for its strong resistance to drought and its ability to produce large, tasty nuts. This variety is a favorite among commercial growers.Key Features:
- Drought-resistant 🌞
- Large, flavorful nuts with a thin shell 🥜
- Grows well in dry, sandy soil 🌵
- Moderate growth rate 🌳
🌟 ‘Stuart’ – A Classic for Nut Lovers 🌟
The ‘Stuart’ variety is one of the most well-known and widely planted pecans. It’s recognized for its large, tasty nuts and adaptability to different soil types. While it requires a bit more maintenance, its generous nut production makes it well worth the effort.Key Features:
- Large, flavorful nuts with a thick shell 🥜
- Adaptable to various soil types 🌱
- Excellent for areas with moderate climates 🌤️
- High yield but requires more care 💪
🌟 ‘Kanza’ – A Top Pick for Commercial Growers 🌟
If you want a top-performing pecan tree with a high yield, the ‘Kanza’ variety is a favorite for commercial growers. It produces large, sweet nuts with a thick shell and has excellent resistance to pests and diseases. This variety requires more space but rewards you with consistent production.Key Features:
- High yield of large, sweet nuts 🍬
- Excellent resistance to pests and diseases 🛡️
- Requires ample space to grow 🌳
- Thrives in warmer climates ☀️
How to Choose the Right Variety for You 🤔
Selecting the best Northern Pecan variety depends on several factors:- Climate: Consider your local weather conditions. Cold-tolerant varieties like ‘Chickasaw’ are perfect for colder regions, while drought-resistant varieties like ‘Western Schley’ are better suited for hot, dry climates. 🌞❄️
- Space: Larger varieties like ‘Pawnee’ and ‘Kanza’ need more space to grow. If you have limited room, smaller trees like ‘Chickasaw’ are a better fit. 🌳
- Yield: If you’re after high yields, go for varieties like ‘Caddo’ or ‘Kanza,’ which are known for their excellent production. 💰
- Maintenance: Some varieties are easier to care for than others. If you want a low-maintenance option, ‘Chickasaw’ and ‘Caddo’ are both solid choices. 🌱
🌳💡Advanced Tips from Expert Growers 💡🌳
For those who want to take their Northern Pecan tree care to the next level, we’ve gathered expert tips that go beyond the basics. Whether you’re aiming for an abundant harvest or simply want to fine-tune your tree’s growth, these advanced techniques will help you grow healthier trees and achieve bountiful yields. 🌰🔬 Soil Health: Go Beyond Basic Fertilization 🔬
Soil is the foundation of healthy trees. While basic fertilization is important, expert growers recommend paying closer attention to soil health. Here’s how:pH Testing:
Pecans prefer slightly acidic soil (pH 6-7). Use a soil test kit to check your pH levels, and if necessary, adjust it by adding sulfur to lower the pH or lime to raise it. 🌱
Organic Amendments:
Go beyond synthetic fertilizers by adding organic compost or aged manure to improve soil structure and nutrient content. This boosts microbial activity and promotes long-term soil health. 🍂Micronutrient Supplements:
While nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are crucial, micronutrients like zinc and manganese are equally important for pecan trees. Consider foliar sprays or soil injections for micronutrient supplementation if your soil is deficient. 🌾💧 Water Management: Master the Art of Deep Watering 💧
Proper watering is vital, but expert growers emphasize the importance of deep watering over frequent shallow watering. Here’s how to do it right:Deep Watering:
Water your tree slowly and deeply to encourage deep root growth. Use a soaker hose or drip irrigation system to water around the root zone (about 2-3 feet from the trunk). This ensures the water reaches the deeper roots where it’s needed. 🌊Avoid Overwatering:
Pecan trees don’t like “wet feet,” so ensure proper drainage. Allow the top 2 inches of soil to dry out between waterings. Overwatering can lead to root rot, which is a common issue for pecans. 🚰Rainwater Harvesting:
If possible, set up a rainwater harvesting system to provide your pecan trees with natural, chemical-free water. This is not only better for the trees but also a sustainable option for your garden. 🌧️🌞 Strategic Pruning: Let the Sun In 🌞
Pruning is key to a productive pecan tree, but expert growers take a strategic approach to maximize yields and tree health. Here’s how:Focus on Structure:
Early in the tree’s life, focus on shaping the tree with strong, central leaders and well-spaced branches. This will ensure your tree grows tall and strong, allowing light to penetrate the canopy. 🌳Remove Dead or Diseased Wood:
Regularly inspect your tree for dead or diseased branches and remove them promptly. This helps prevent the spread of disease and keeps the tree healthy. ✂️Selective Thinning:
During late winter, thin out crowded branches. This allows air to circulate and light to penetrate the tree, which promotes better nut production. Be careful not to over-prune, as this can reduce yields. 🌿🌾 Companion Planting: Boost Your Tree’s Health 🌾
Companion planting isn’t just for vegetables—it can benefit your pecan trees too. Expert growers recommend planting certain herbs or flowers near your trees to improve growth and deter pests:
Nitrogen-Fixing Plants:
Plant legumes like clover or peas around the base of your pecan tree. These plants fix nitrogen in the soil, which helps provide the nutrients your tree needs. 🌱Pest-Repelling Plants:
Marigolds, garlic, and chives can help deter pests like aphids and caterpillars. These plants act as natural repellents, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. 🌸Mulching with Comfrey:
Comfrey is an excellent companion for pecan trees as it helps add valuable nutrients like potassium and phosphorus to the soil when used as mulch. 🍃🐜 Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Keep Pests Under Control 🐜
Rather than relying on chemical pesticides, expert growers use Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques to control pests naturally and sustainably:Attract Beneficial Insects:
Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory beetles are natural enemies of aphids, weevils, and other pests. By planting flowers that attract these beneficial insects, you can create a balanced ecosystem that keeps pests in check. 🐞Pheromone Traps:
Use pheromone traps to monitor and capture pest populations, especially for issues like pecan weevils. These traps can help you identify the problem early before it becomes widespread. 🐛Biological Controls:
Consider using biological pesticides such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) for caterpillar infestations or nematodes to target soil-borne pests. These methods are effective and environmentally friendly. 🌿🌰 Harvest Timing: Perfect the Art of Timing 🌰
The timing of your harvest is crucial for maximizing the quality and quantity of your pecan crop. Here’s what expert growers recommend:Watch for Shell Cracking:
Pecans are ready to harvest when the shells begin to crack open naturally on the tree. Don’t wait for the nuts to fall to the ground, as this could lead to spoilage. 🌰Check for Nut Quality:
Before harvesting in large quantities, check a few nuts for the quality of the kernels. A high-quality nut will have a firm, plump kernel, while a poor-quality nut will have a shriveled or discolored kernel. 🍽️Harvest in Dry Conditions:
Try to harvest your pecans when the weather is dry. Moist conditions can lead to mold or fungal issues, which can ruin the nuts. 🌞🧑🌾 Soil Amendments and Care for Long-Term Success 🧑🌾
To keep your Northern Pecan trees thriving for decades, expert growers suggest making soil amendments part of your yearly routine:Regular Soil Testing:
Perform soil tests every couple of years to monitor pH and nutrient levels. Adjust your fertilization plan based on the results to keep your soil in optimal condition. 🧪Deep Root Feeding:
For established trees, deep root feeding can provide essential nutrients directly to the root zone, where they are most needed. Use a long injector tool to apply liquid fertilizer or compost tea deep into the soil. 🌱Preventing Soil Compaction:
Avoid heavy equipment or foot traffic around the root zone to prevent soil compaction. Compacted soil restricts root growth and reduces the tree’s ability to take up nutrients. 🚜 By implementing these expert tips, you’ll be well on your way to growing Northern Pecan trees that thrive year after year, offering you a beautiful canopy and a bountiful harvest. Happy growing! 🌳😊🌳💭 Final Thoughts 💭🌳
Growing a Northern Pecan tree is an incredibly rewarding experience, whether you’re a backyard gardener or a seasoned orchard owner. With the right care, attention to detail, and a bit of patience, your tree can thrive, produce bountiful nuts, and add beauty to your landscape. By following the expert tips, from selecting the right variety to managing pests and improving soil health, you can ensure your pecan tree remains healthy and productive for years to come. Remember, each step—whether it’s deep watering, strategic pruning, or companion planting—helps to build a stronger foundation for your tree’s growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best location for planting a Northern Pecan tree?
The best location for a Northern Pecan tree is in full sunlight with well-drained soil. It needs plenty of room to grow, so choose a spot with at least 40-50 feet of space away from buildings, other trees, and power lines. Avoid areas that are prone to flooding or heavy winds. 🌞
How long does it take for a Northern Pecan tree to produce nuts?
Northern Pecan trees typically start producing nuts 4 to 8 years after planting, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Younger trees may take longer to mature, while faster-growing varieties like ‘Pawnee’ may yield nuts sooner. 🌰
How often should I water my Northern Pecan tree?
Water your Northern Pecan tree deeply about once a week, especially during dry periods. Make sure the soil is well-drained to prevent overwatering. During the first few years, more frequent watering may be necessary, but avoid watering too much once the tree is established. 💧
What are the signs of nutrient deficiencies in a Northern Pecan tree?
Common signs of nutrient deficiencies in pecan trees include yellowing leaves (often a sign of nitrogen or iron deficiency) and stunted growth. If your tree is not producing nuts or has poor leaf development, consider fertilizing with a balanced tree fertilizer or getting a soil test for better accuracy. 🌱
How can I protect my Northern Pecan tree from pests?
To protect your tree from pests like pecan weevils or aphids, consider using organic insecticides such as neem oil, or beneficial insects like ladybugs to control aphid populations. Regularly inspect the tree for pests and remove any affected branches or leaves. 🐞
When is the best time to prune a Northern Pecan tree?
The best time to prune your Northern Pecan tree is in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Focus on removing dead or damaged wood and thinning out crowded branches to improve air circulation. Avoid heavy pruning during the growing season, as it can reduce nut production. ✂️
Why are the leaves on my Northern Pecan tree turning yellow?
Yellowing leaves on a Northern Pecan tree can be caused by overwatering, nutrient deficiencies, or pests. Check your watering habits and consider applying a balanced fertilizer. If the problem persists, inspect for aphids or fungal issues that may be affecting the tree. 🌿
How do I know when my Northern Pecan tree is ready to harvest?
Your Northern Pecan tree is ready to harvest when the nuts begin to naturally fall to the ground or when the outer husks start cracking open. Don’t wait for the nuts to drop completely, as they may spoil if left too long. Check the nuts for plump, firm kernels to ensure they are ripe. 🌰
