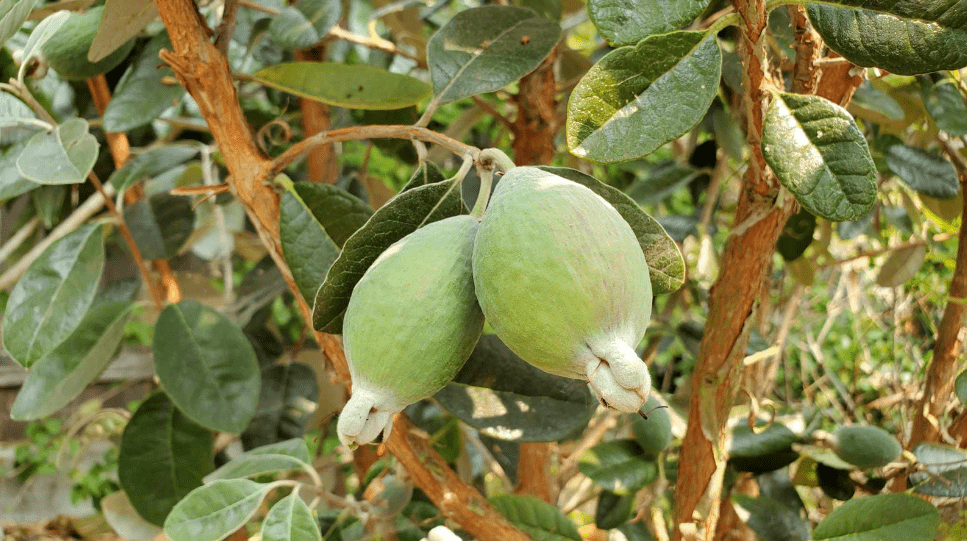

Pineapple Guava Bush Care: Essential Tips for Beginners
Pineapple guava bush are a beautiful and delicious addition to any garden, but they do require some specific care to thrive. In this post, we’ll cover the essential tips for beginners on how to care for pineapple guava bushes, including watering, pruning, and soil requirements. By following these tips, you’ll be able to ensure that your pineapple guava bushes thrive and produce delicious fruit for years to come. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will help you keep your pineapple guava bushes healthy and happy.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Pineapple Guava Bush
A. Botanical Overview
The pineapple guava bush, also known as Feijoa sellowiana, is a versatile shrub that is native to South America. It is known for its attractive, silvery-green foliage and unique, edible fruit that tastes like a combination of pineapple, guava, and mint. It is a hardy and low-maintenance plant, making it a popular choice for home gardeners.
B. Varieties and Cultivars
There are several different varieties and cultivars of pineapple guava bushes, each with their own unique qualities and flavors. Some popular varieties include Coolidge, Mammoth, and Trask. When choosing a variety, consider factors such as fruit size, flavor, and cold hardiness to ensure the best fit for your specific growing conditions. It’s also important to note that pineapple guava bushes are self-fertile, meaning they can produce fruit without the need for a separate pollinator plant. Caring for Your Pineapple Guava Bush.

Getting Started with Pineapple Guava Bush
A. Selecting the Right Plant
When it comes to caring for pineapple guava bushes, the first step is to select the right plant for your garden. There are several different varieties and cultivars of pineapple guava bushes, each with their unique qualities and flavors. Some popular varieties include Coolidge, Mammoth, and Trask. When choosing a variety, consider factors such as fruit size, flavor, and cold hardiness to ensure the best fit for your specific growing conditions.
It’s also important to note that pineapple guava bushes are self-fertile, meaning they can produce fruit without the need for a separate pollinator plant. This makes them a great choice for home gardeners looking for a low-maintenance fruit plant. By choosing the right variety for your garden, you can ensure that your pineapple guava bushes thrive and produce delicious fruit for you to enjoy.

B. Ideal Planting Location
When caring for pineapple guava bushes, it’s important to consider the ideal planting location. Pineapple guava bushes thrive in well-drained soil and prefer full sun but can also tolerate partial shade. It’s important to plant them in a location with good air circulation to prevent disease. Additionally, pineapple guava bushes can tolerate a wide range of soil types, but they do best in fertile, slightly acidic soil. When planting, be sure to space the bushes at least 10 feet apart to allow for adequate growth and airflow. By choosing the right planting location, you can ensure that your pineapple guava bushes have the best chance of thriving and producing delicious fruit.
C. Planting Guidelines
1. Preparing the soil (amending with compost)
Before planting your pineapple guava bushes, it’s important to prepare the soil. One way to do this is by amending the soil with compost. Compost adds valuable nutrients to the soil, improves its structure, and helps to retain moisture. To amend the soil with compost, simply spread a layer of compost over the planting area and mix it into the soil to a depth of about 12 inches. This will provide a rich and fertile environment for your pineapple guava bushes to thrive. Additionally, it’s a good idea to perform a soil test to determine the pH level of the soil and make any necessary adjustments to ensure that it is slightly acidic, which is ideal for pineapple guava bushes. With the right soil preparation, your pineapple guava bushes will have a strong foundation for healthy growth and fruit production.
Ongoing Care and Maintenance
A. Watering Needs
Pineapple guava bushes require regular watering, especially during dry periods. It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Deep, infrequent watering is best, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering to encourage deep root growth. Using a soaker hose or drip irrigation system can help ensure even and efficient watering. Be sure to water the plants at the base, avoiding wetting the foliage to prevent diseases. Consider mulching around the base of the plants to help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature. With proper watering, your pineapple guava bushes will stay healthy and productive.
B. Fertilization
Pineapple guava bushes benefit from regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and fruit production. Using a balanced fertilizer with a higher potassium content can help encourage flowering and fruiting. Apply fertilizer in the spring as new growth begins, and again in the summer to support continued growth and fruit development. Be sure to follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging and avoid over-fertilizing, as this can harm the plant. With proper fertilization, your pineapple guava bushes will thrive and produce delicious fruit.

C. Pruning and Shaping
Pruning and shaping your pineapple guava bushes is an important part of maintaining their health and promoting fruit production. Pruning can help encourage new growth, remove dead or damaged branches, and shape the bushes for a more aesthetic appearance. It’s best to prune pineapple guava bushes in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Use sharp, clean tools to make clean cuts and avoid causing unnecessary damage to the plant. Focus on removing any crossing or crowded branches, as well as any diseased or damaged growth. By regularly pruning and shaping your pineapple guava bushes, you can help promote healthy growth and ensure a bountiful fruit harvest.
D. Mulching and Weed Control
Mulching and weed control are important practices for maintaining the health and appearance of your garden or landscape. Mulching helps to retain moisture in the soil, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. It also adds nutrients to the soil as it breaks down over time. When mulching around pineapple guava bushes, use organic materials such as wood chips, bark, or compost to provide a natural and nutrient-rich environment for the plants.
Weed control is also essential for the growth and development of pineapple guava bushes. Weeds compete with the plants for water, nutrients, and sunlight, which can hinder their growth and fruit production. Regularly removing weeds from around the bushes and applying a layer of mulch can help prevent weed growth and create a healthier environment for the pineapple guava bushes to thrive.
By incorporating mulching and weed control into your gardening routine, you can help promote the overall health and appearance of your pineapple guava bushes.
Encouraging Fruit Production
A. Pollination Requirements
Pineapple guava bushes require pollination from bees or other pollinators to produce fruit. Planting a variety of flowers and plants that attract pollinators can help ensure successful pollination of the pineapple guava bushes. Additionally, having multiple pineapple guava bushes in close proximity can also increase the likelihood of fruit production through cross-pollination. In some cases, hand-pollination may be necessary to ensure a bountiful harvest of fruit. By understanding the pollination requirements of pineapple guava bushes, you can take steps to encourage fruit production in your garden.
1. Understanding self-pollination vs. cross-pollination
Self-pollination occurs when a plant’s flowers are fertilized by their own pollen, while cross-pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from one plant to another. Pineapple guava bushes are typically self-pollinating, but cross-pollination can increase fruit production. Understanding the difference between these two methods can help you take the necessary steps to encourage fruit production in your pineapple guava bushes.
2. Hand-pollination
In some cases, hand-pollination may be necessary to ensure a bountiful harvest of fruit. This involves manually transferring pollen from one flower to another. By understanding when and how to hand-pollinate your pineapple guava bushes, you can take proactive steps to encourage fruit production in your garden.
B. Flowering and Fruiting Cycle
Understanding the flowering and fruiting cycle of pineapple guava bushes is important in order to maximize fruit production. Pineapple guava bushes typically bloom in the spring and fruits develop in the late summer to fall. By understanding this cycle, you can plan and take necessary steps to ensure optimal fruit production, such as proper pruning and fertilization techniques.
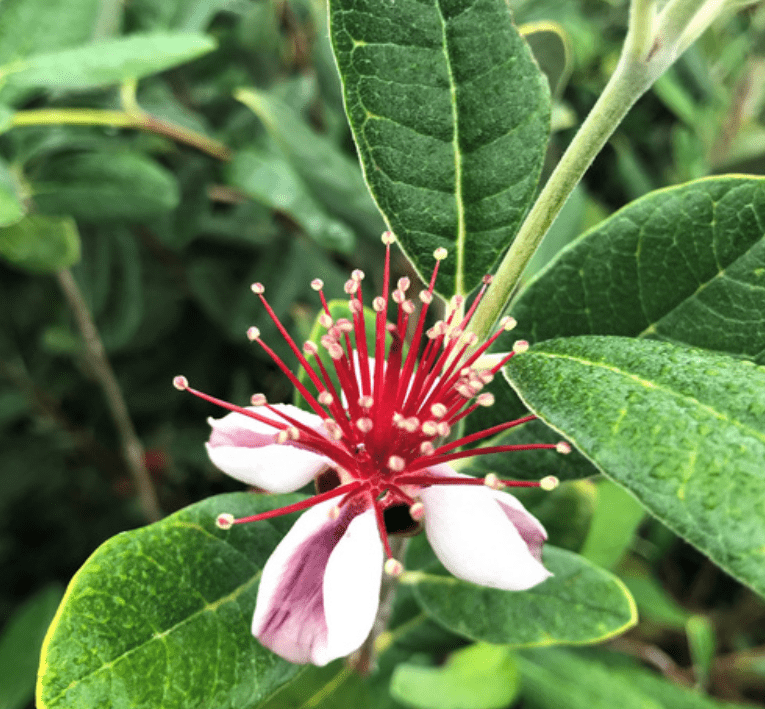
C. Maximizing Fruit Yield
To maximize fruit yield in pineapple guava bushes, hand-pollination can be a proactive step to take. This involves manually transferring pollen from one flower to another, which can help ensure a successful fruit set. By understanding when and how to hand-pollinate your pineapple guava bushes, you can take proactive steps to encourage fruit production in your garden. Additionally, understanding the flowering and fruiting cycle of pineapple guava bushes is important in order to plan and take necessary steps to ensure optimal fruit production, such as proper pruning and fertilization techniques. By combining these strategies, you can work towards maximizing fruit yield in your pineapple guava bushes.
Managing Pests and Diseases
A. Common Pests
Common pests that can affect pineapple guava bushes include aphids, scale insects, and thrips. These pests can cause damage to the foliage and fruit of the bush, leading to reduced fruit yield. To manage these pests, regular monitoring of the bushes is important to detect any early signs of infestation. Additionally, using natural predators, such as ladybugs or lacewings, can help control pest populations. In cases of severe infestation, insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils can be used as a last resort. It is important to follow integrated pest management practices to effectively manage pests and minimize the use of chemical controls. Regular inspection and proactive management can help ensure healthy pineapple guava bushes and maximize fruit yield.
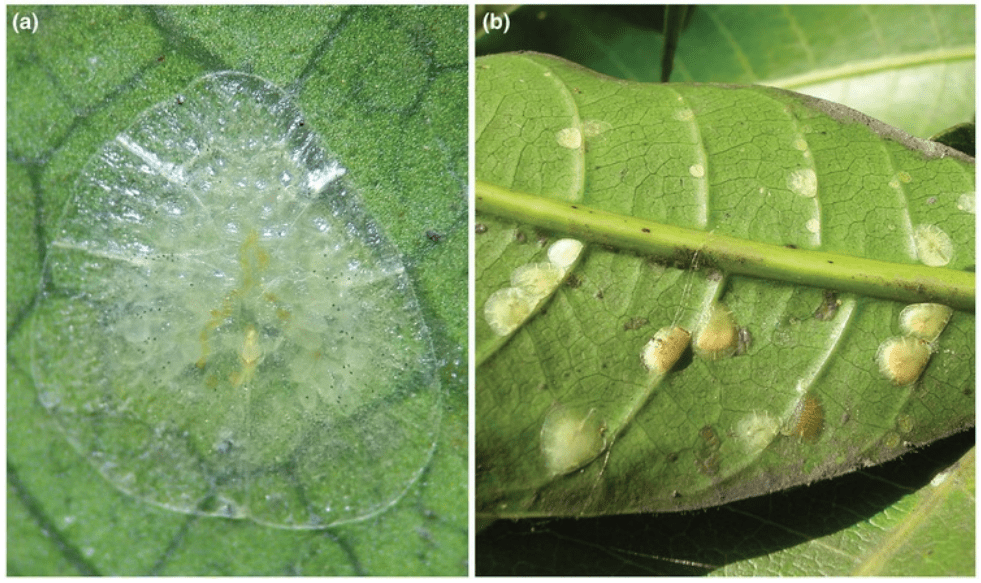
B. Disease Prevention and Treatment
Pineapple guava bushes can be susceptible to diseases such as leaf spot, wilt, and rust. To prevent these diseases, it’s important to keep the bushes well-ventilated and to water at the base of the plant to avoid wetting the foliage. Additionally, pruning the bushes to promote air circulation can help prevent the spread of diseases. If you notice any signs of disease, such as yellowing or spotted leaves, it’s important to treat the bushes promptly. This may involve removing infected foliage, applying fungicides, or adjusting watering and fertilization practices. Proper care and proactive disease prevention can help keep your pineapple guava bushes healthy and thriving.
Harvesting and Using Pineapple Guava
A. Harvesting Guidelines
When harvesting pineapple guava, it’s important to wait until the fruit is fully ripe, which is typically when it falls to the ground. The fruit should have a sweet, tropical aroma and yield slightly to gentle pressure when ripe. To harvest, simply pick the fruit off the ground or gently twist it off the tree. It’s best to use the fruit immediately after harvesting, as it can spoil quickly. Pineapple guava can be eaten fresh, used in desserts, or made into jams and jellies. The fruit can also be stored in the refrigerator for a few days, or frozen for longer-term use. Enjoy the delicious and tropical flavor of your homegrown pineapple guava!
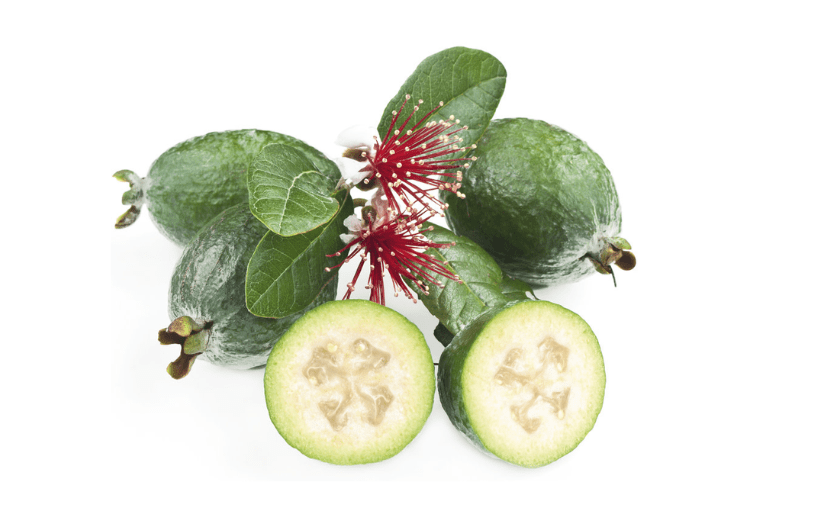

B. Culinary Uses
Pineapple guava can be used in a variety of culinary ways. It can be eaten fresh, used in desserts such as fruit tarts or salads, or made into jams and jellies. The fruit has a unique tropical flavor that can add a delicious twist to any recipe. Additionally, pineapple guava can be stored in the refrigerator for a few days or frozen for longer-term use. So, feel free to get creative and enjoy the delicious flavor of your homegrown pineapple guava in your favorite dishes!
C. Preserving and Storing
Pineapple guava can be preserved and stored in a few different ways. If you have an abundance of fruit, you can make jams, jellies, or preserves to enjoy the flavor year-round. Another option is to freeze the fruit for longer-term storage. Simply wash and dry the fruit, then place it in a sealable plastic bag or airtight container before placing it in the freezer. This will allow you to enjoy the delicious flavor of pineapple guava even when it’s out of season. With these preservation and storage methods, you can continue to enjoy your homegrown pineapple guava for months to come!
In conclusion, caring for pineapple guava bushes is relatively easy as long as you follow a few essential tips. Make sure to water them regularly, especially during dry periods, and prune them to maintain their shape and encourage fruit production. Additionally, ensure that they are planted in well-draining soil to prevent root rot. By following these basic care tips, you can enjoy healthy and fruitful pineapple guava bushes in your garden.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Pineapple guava bushes should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods. However, be careful not to overwater as they are susceptible to root rot.
The best time to plant a pineapple guava bush is in the spring or fall, when the weather is mild.
Pineapple guava bushes thrive in full sun, so they should be planted in a location that receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day.
Yes, pineapple guava bushes benefit from regular fertilization, especially in the spring and summer months. Use a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for fruit trees.
Prune your pineapple guava bush in late winter or early spring to remove any dead or damaged branches and to shape the bush.
Pineapple guava bushes typically start producing fruit 3-5 years after planting, so be patient and continue to care for the bush.
Pineapple guava bushes are relatively pest and disease resistant, but they can be susceptible to scale insects and fungal diseases in humid conditions. Keep an eye out for any signs of infestation or disease and take appropriate measures to address them.
Yes, pineapple guava bushes can be grown in containers, but make sure the container is large enough to accommodate the root system and provide proper drainage. Use a well-draining potting mix and water regularly.
